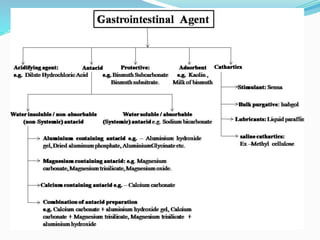
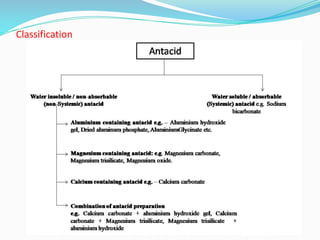
This document provides an overview of gastrointestinal agents used to treat various gastrointestinal disorders. It discusses acidifiers that increase acid in the stomach and are used to treat achlorhydria. It also covers antacids that neutralize excess stomach acid and are used for hyperacidity/hyperchlorhydria. Finally, it discusses cathartics/laxatives that relieve constipation through increasing bowel movements. Specific agents covered include ammonium chloride, dilute hydrochloric acid, sodium bicarbonate, aluminum hydroxide gel, and magnesium hydroxide mixture.