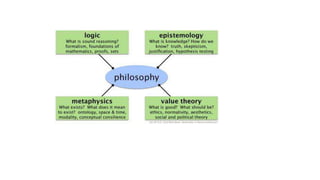
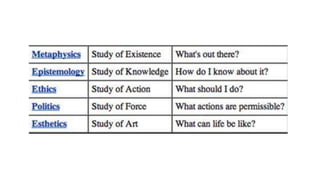
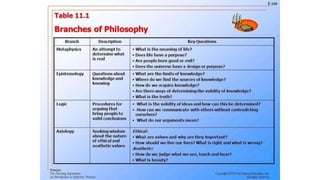
The document discusses various perspectives on the meaning and nature of philosophy. Etymologically, philosophy means "love of wisdom." Philosophers have defined philosophy differently, such as Fichte viewing it as the science of knowledge and Kant as the science and criticism of cognition. Philosophy is considered a way of life as people live according to their philosophical views. It is an analytical and synthetic pursuit seeking truth and understanding through experience and inquiry into fundamental questions about reality, knowledge, values and life. Philosophy encompasses broad domains like metaphysics, epistemology, axiology and logic.