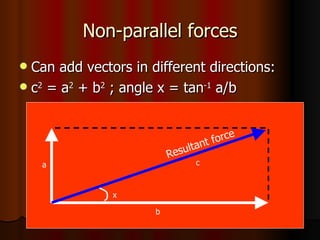
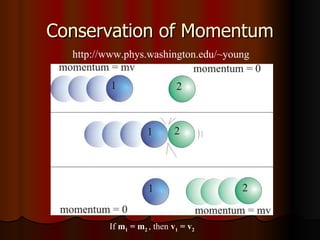
Newton's laws of motion and concepts related to forces and motion are discussed. Key points include: Newton's 3 laws of motion, that force is a vector quantity with magnitude and direction, and concepts like impulse, momentum, conservation of energy and momentum. Newton's 2nd law, which relates force, mass and acceleration, is identified as particularly relevant for understanding acceleration.