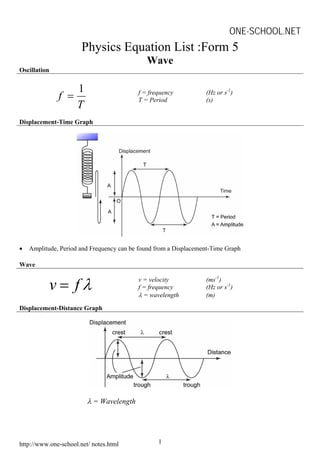
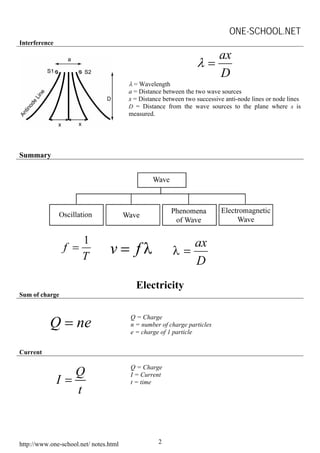
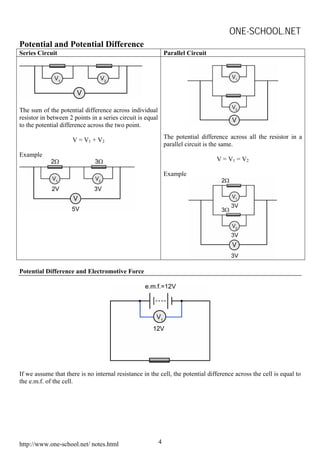
This document contains physics formulas and concepts related to waves, electricity, electromagnetism, electronics, and radioactivity. It includes equations for oscillation, wavelength, interference, charge, current, potential difference, resistance, electromotive force, transformers, alpha decay, beta decay, gamma emission, and nuclear energy. The document provides definitions and explanations for key terms as well as examples of applying the formulas.