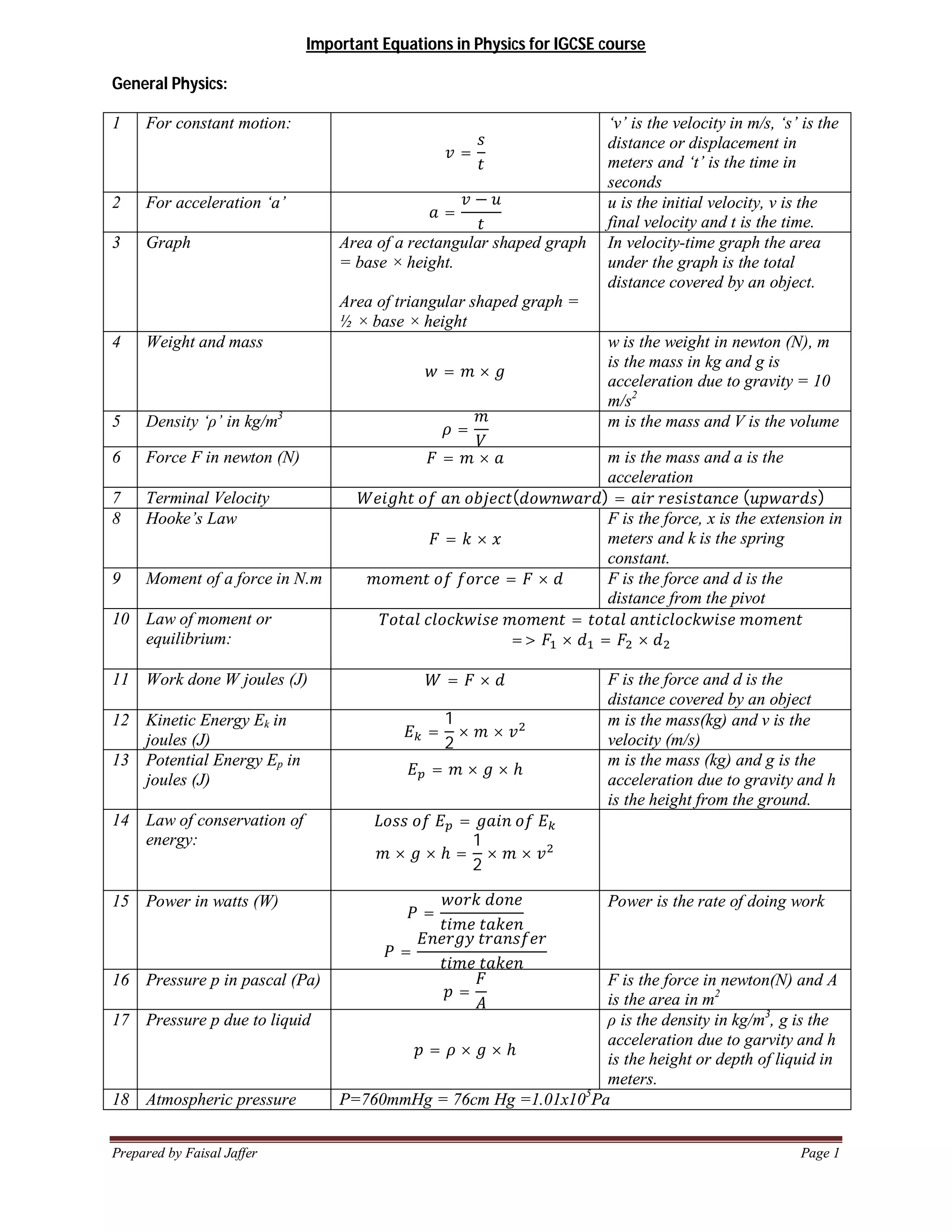
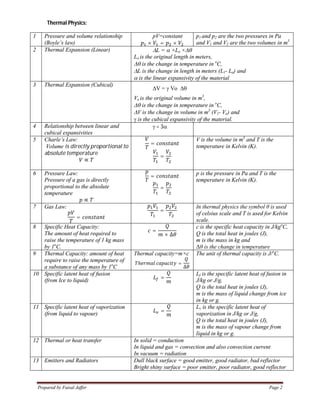
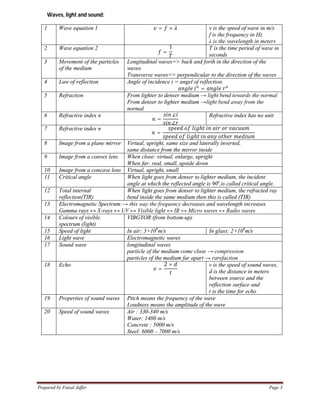
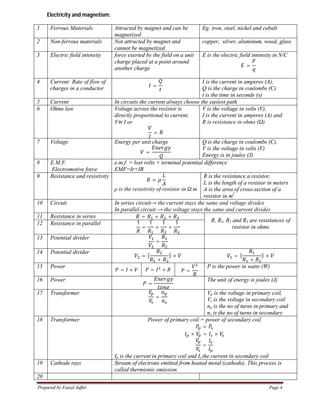
1. Important equations in physics for IGCSE courses include equations for constant motion, acceleration, work, energy, power, density, pressure, waves, light, electricity and more.
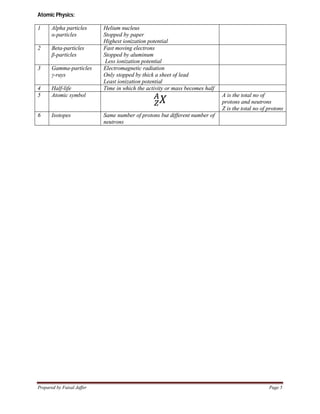
2. Key concepts covered include kinematics equations, Newton's laws of motion, energy equations, gas laws, wave properties, optics, electromagnetism, atomic structure and radiation.
3. Over 20 core physics topics are summarized with their most important equations for quick reference in studies for IGCSE physics exams.