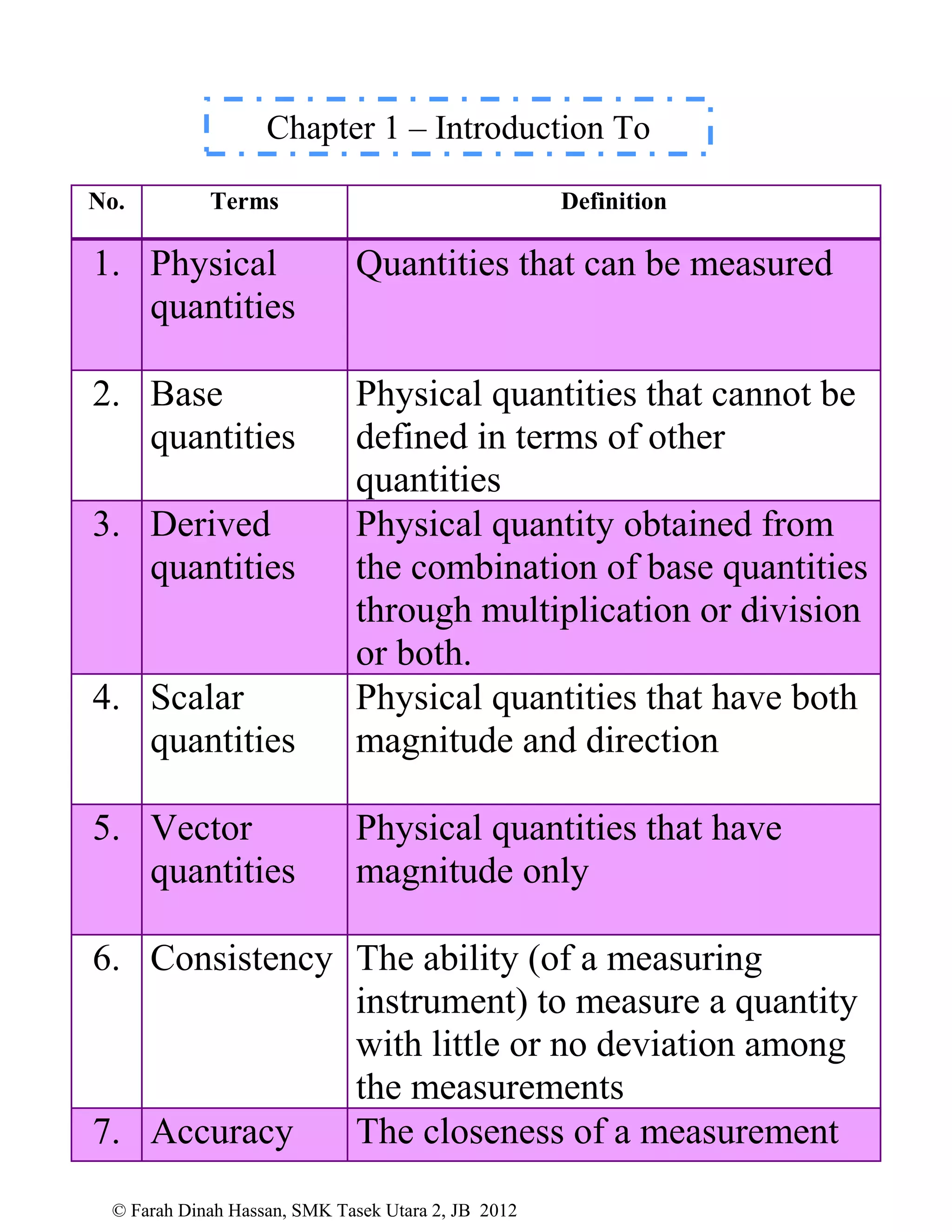
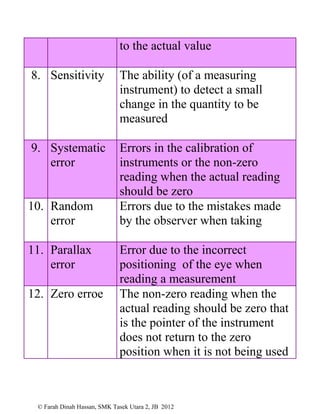
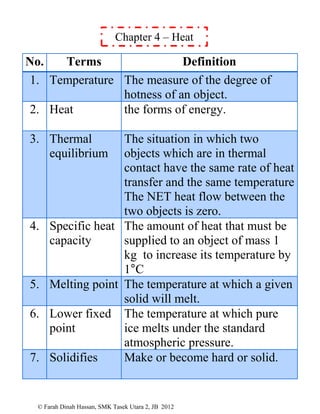
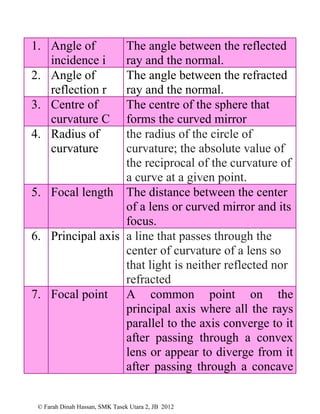
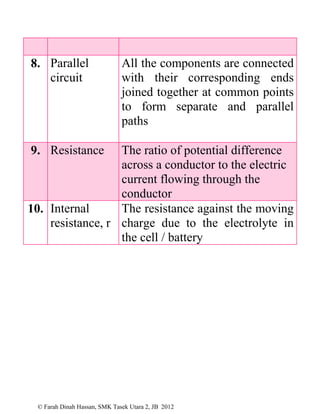
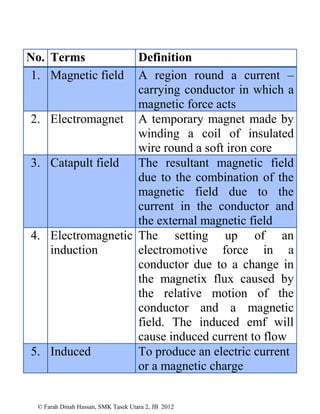
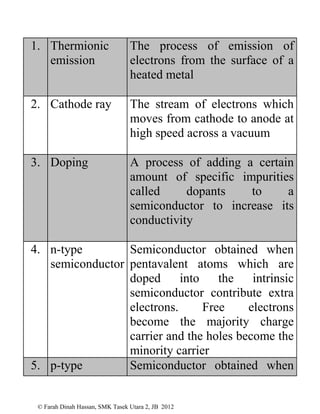
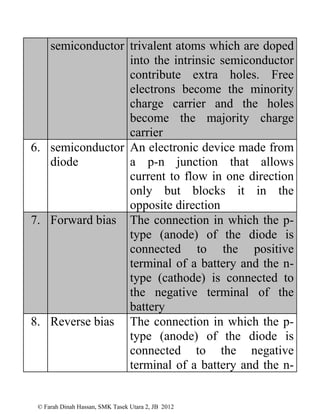
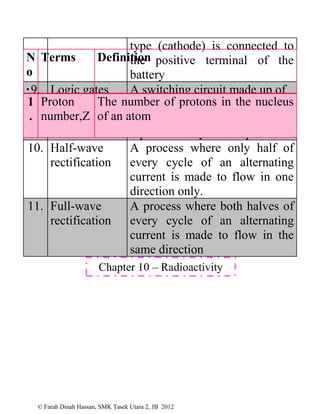
This document defines various physics terms across multiple chapters. It provides definitions for over 100 terms related to physical quantities, force and motion, heat, light, waves, electricity, electromagnetism, and electronics. The terms are organized into tables with their number, term, and definition.