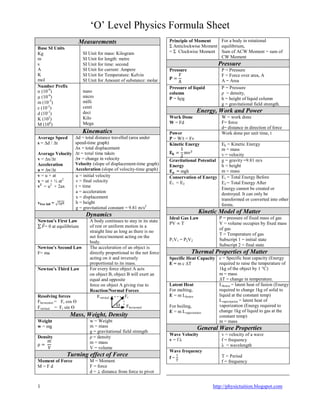
This document contains a summary of key physics formulas and concepts for 'O' Level Physics. It includes:
1) Definitions of base SI units for common physical quantities like mass, length, time, current, temperature, and amount of substance.
2) Formulas for measurements, kinematics, dynamics, work, energy, power, gas laws, heat, electromagnetism, optics, and electricity.
3) Descriptions of important physics principles like Newton's laws of motion, conservation of energy, Ohm's law, Kirchhoff's laws, and more.