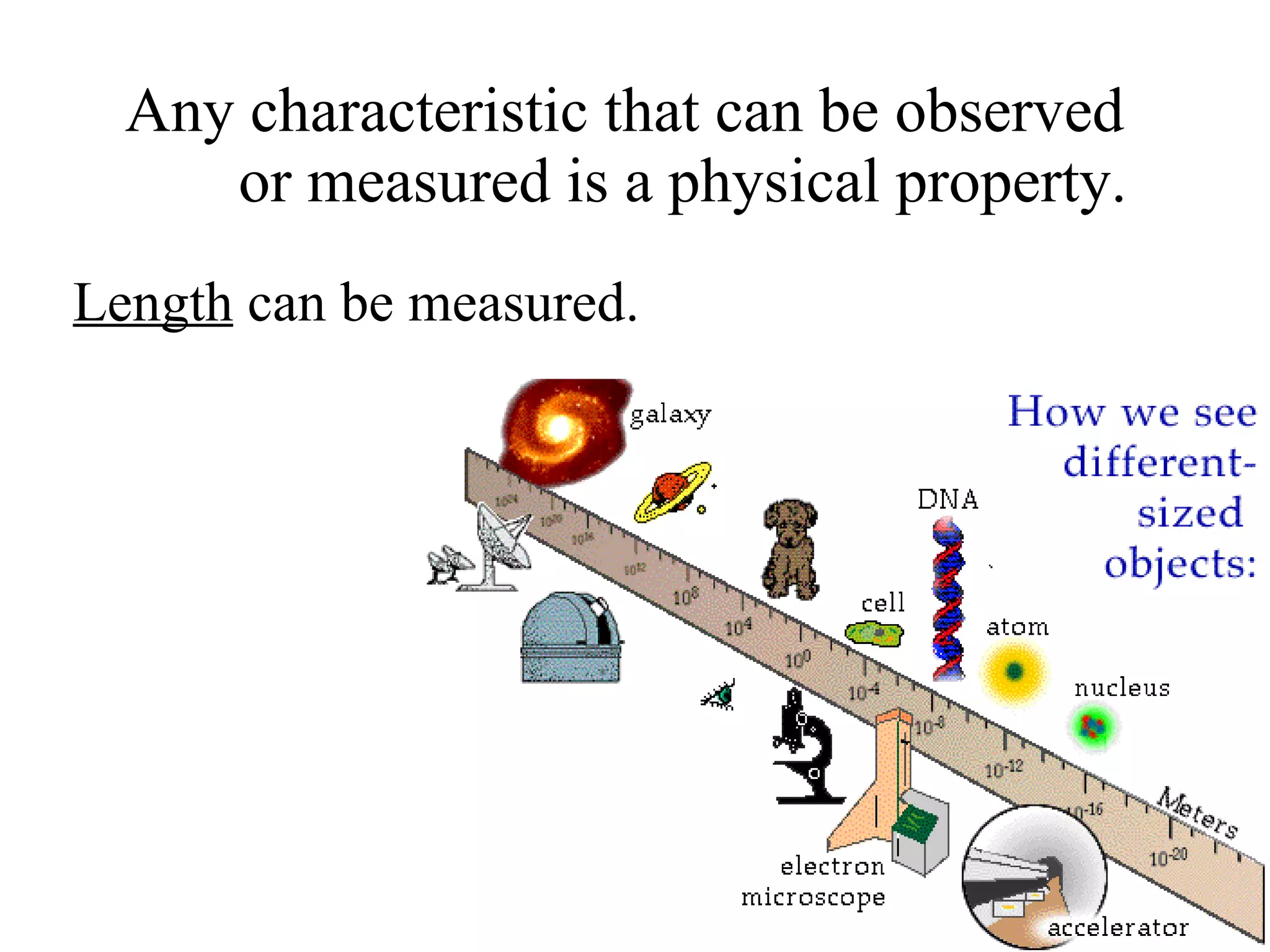
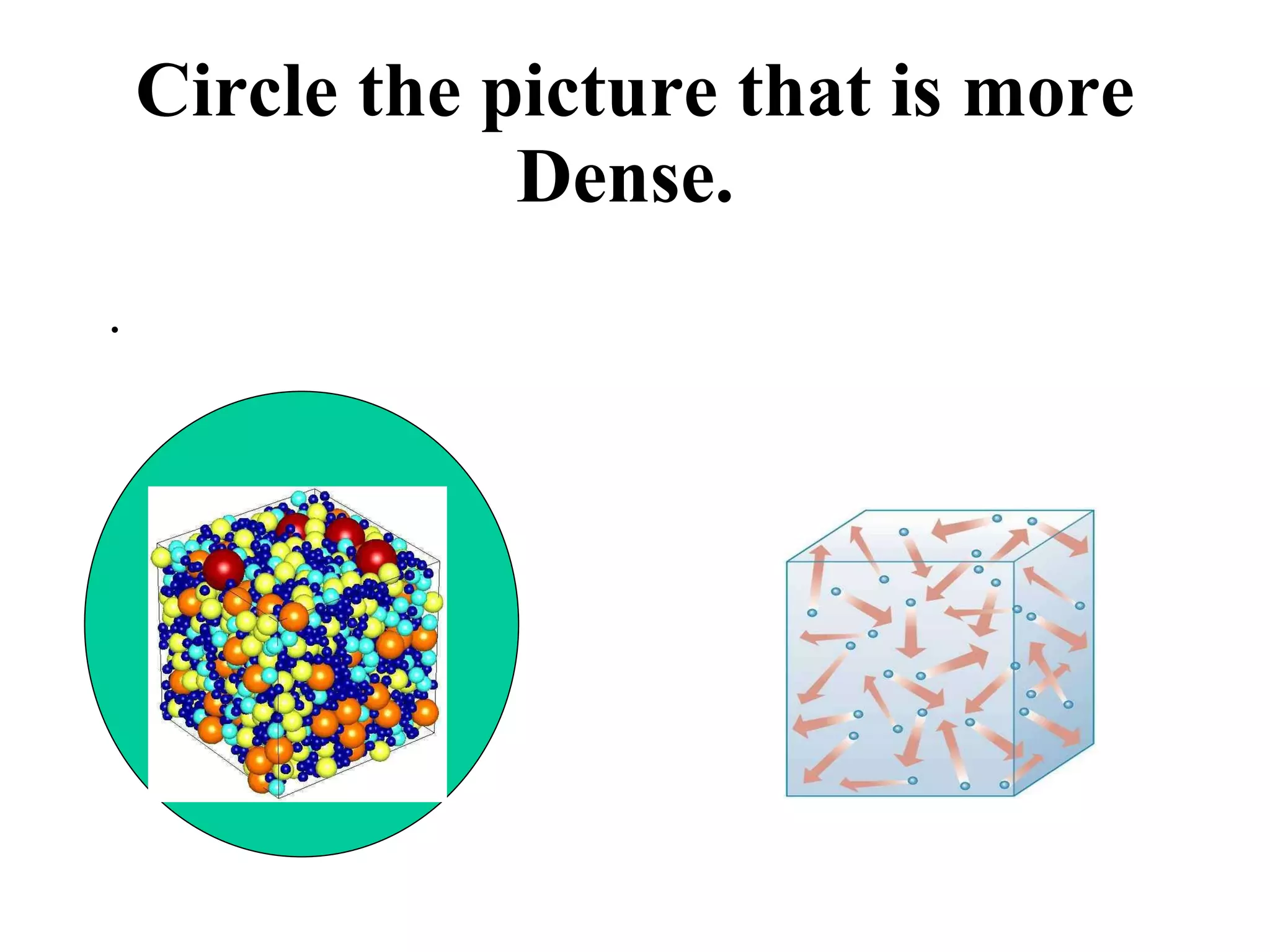
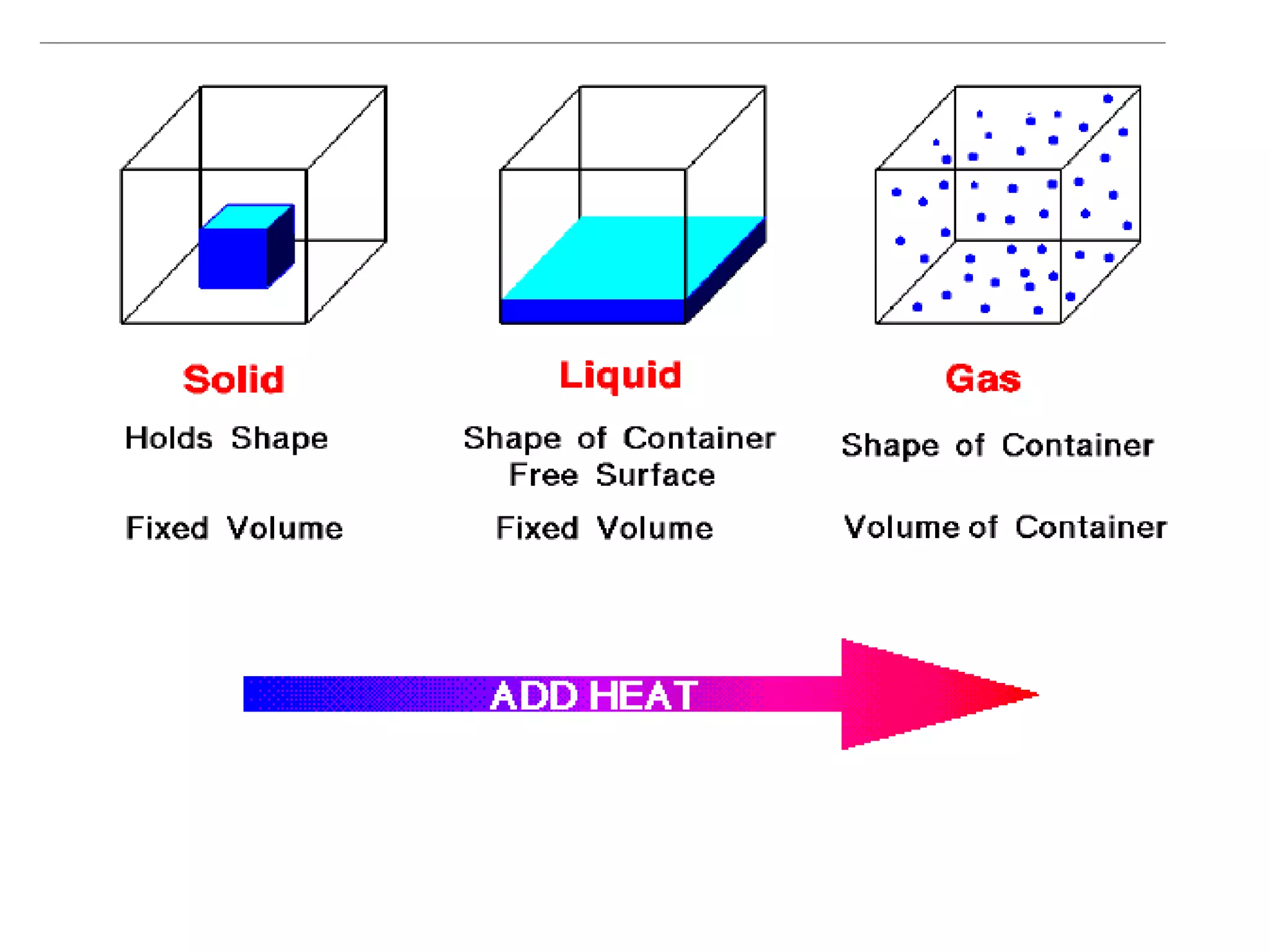
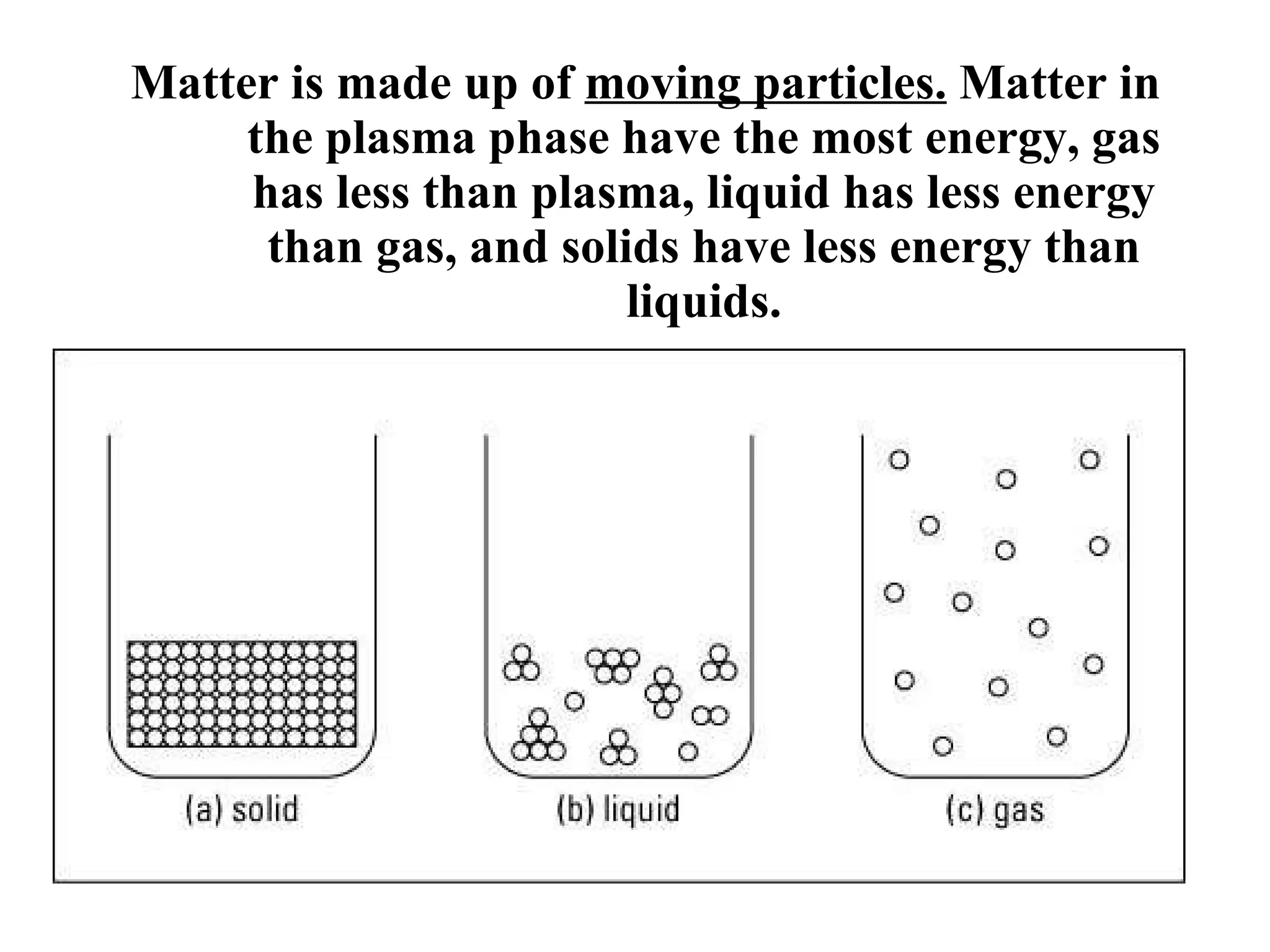
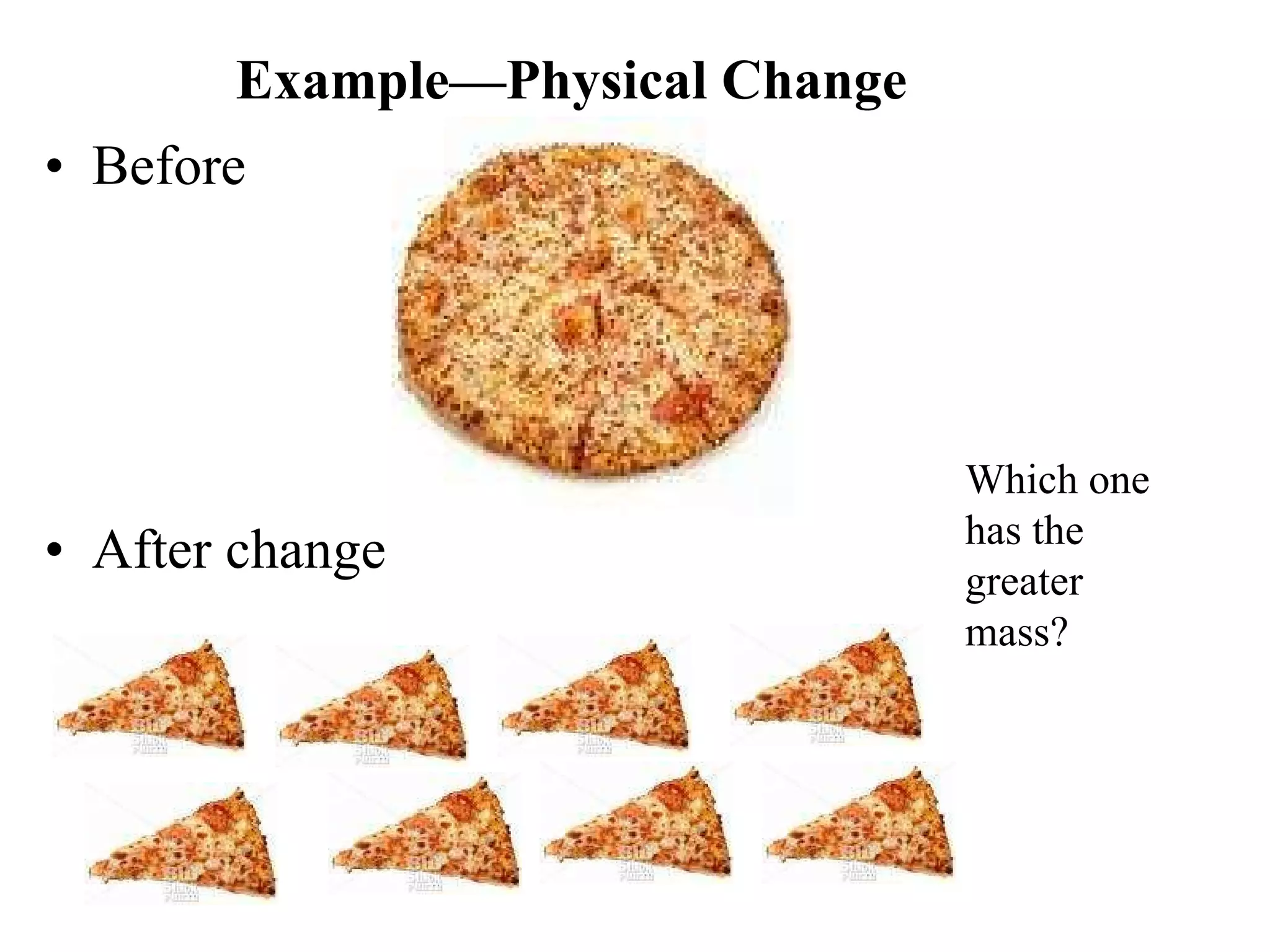
The document discusses physical and chemical properties of matter. It defines physical properties as characteristics that can be observed or measured without changing the identity of the substance, such as length, mass, volume, and density. It also discusses physical changes which alter physical properties but not chemical identity. Chemical properties allow substances to undergo chemical reactions resulting in new substances. Chemical changes alter chemical identity and are not reversible through physical means alone. The law of conservation of mass states that mass is never lost or gained during physical or chemical changes.