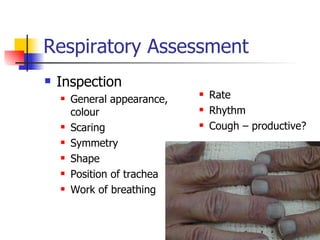
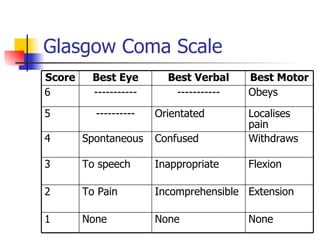
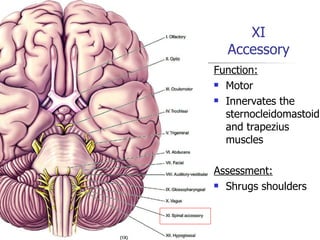
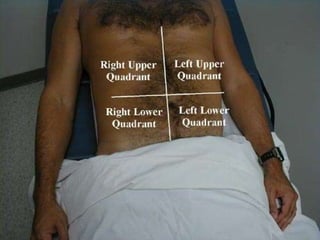
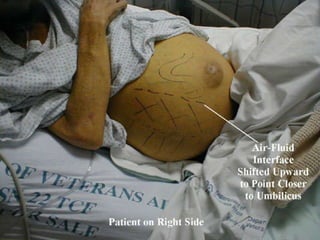
This document outlines the process and assessments for several body systems including respiratory, cardiac, neurological, abdominal, and neurovascular. It describes the steps in the assessment process as inspection, palpation, percussion, and auscultation. For each body system, it lists the specific points to examine, techniques to use, and normal and abnormal findings to note during the physical assessment of a patient in an acute care setting.