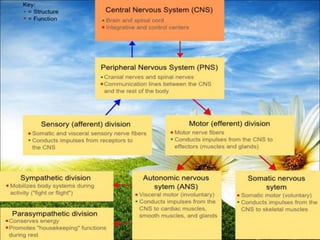
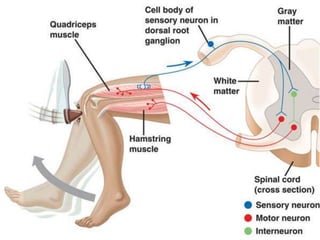
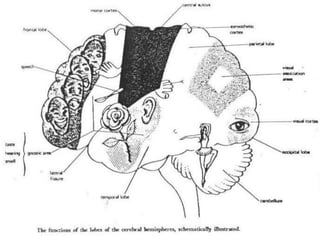
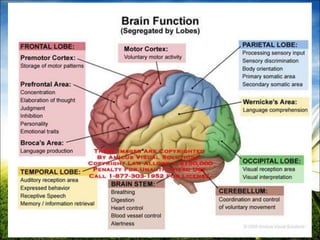
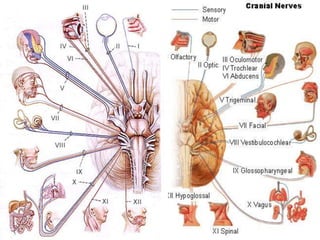
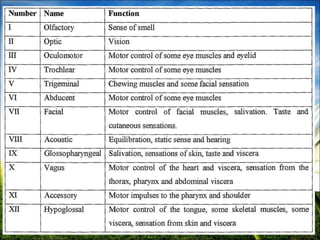
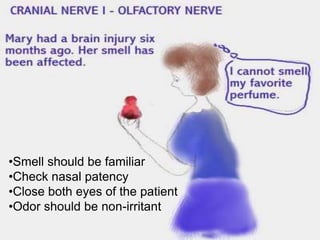
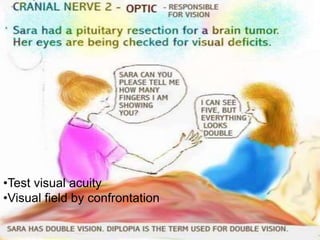
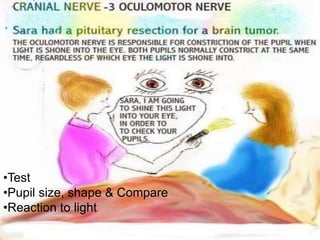
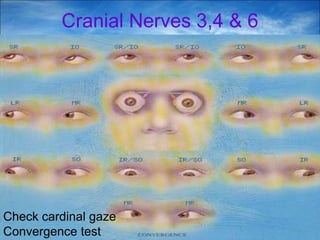
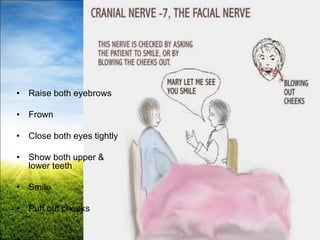
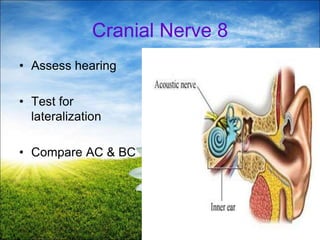
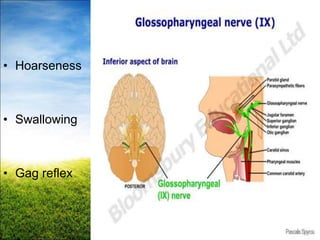
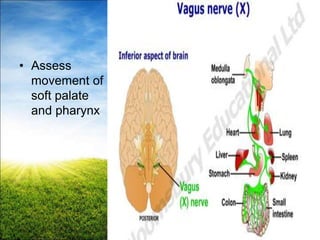
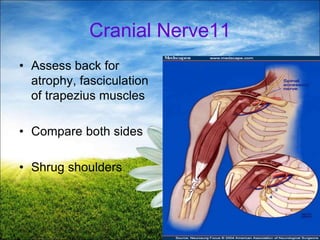
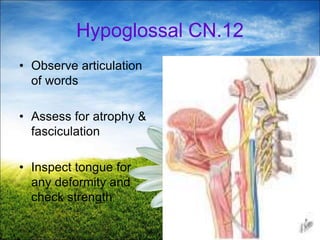
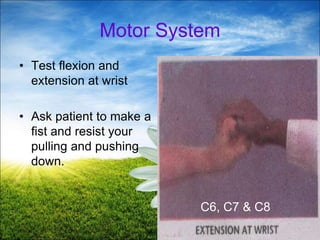
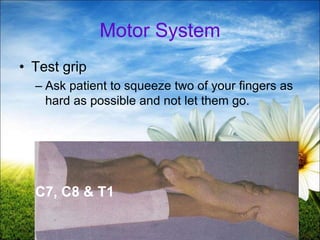
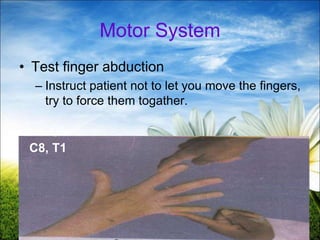
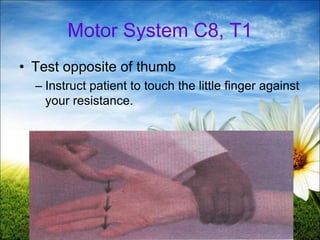
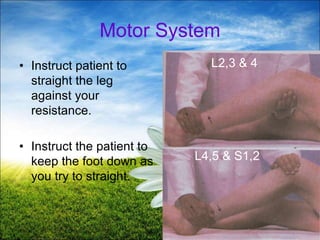
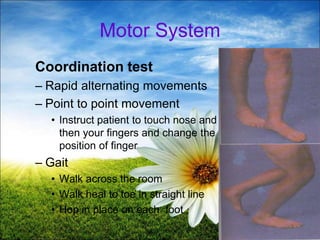
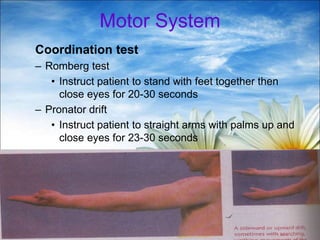
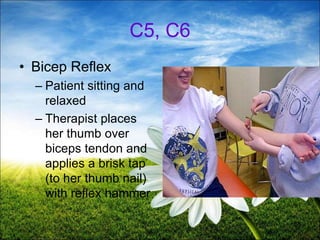
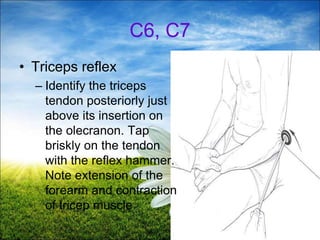
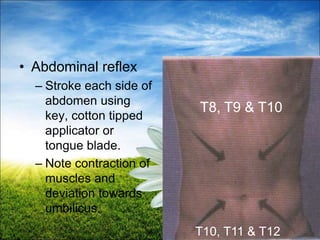
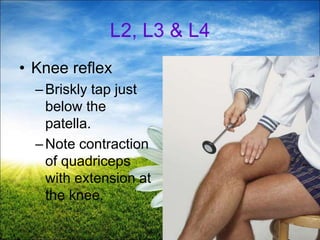
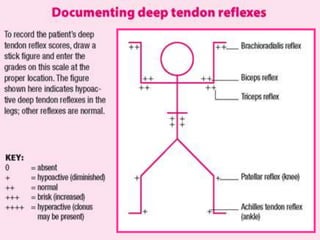
The document provides a comprehensive guide to conducting a neurological assessment, detailing the objectives, methods for evaluating cognitive functions, cranial nerves, motor system, reflexes, and sensory assessments. It includes specific procedures for assessment and documentation of findings in patients. Additionally, the document discusses normal neurological changes associated with aging, impacting vision, hearing, smell, taste, and touch.