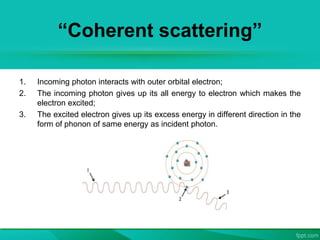
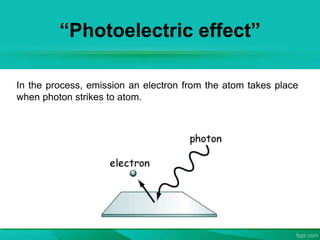
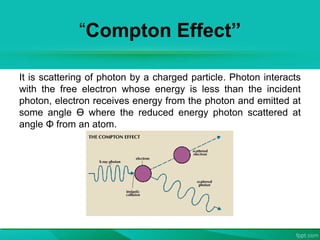
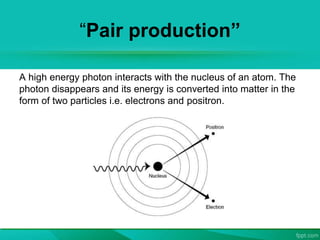
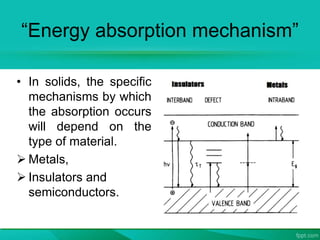
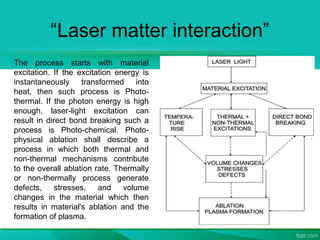
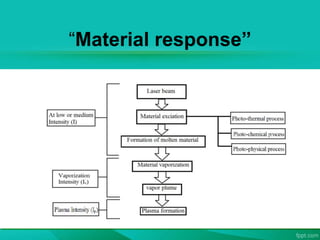
The document discusses the interaction between laser light and matter, detailing various processes such as coherent scattering, the photoelectric effect, Compton effect, and pair production. It explains different energy absorption mechanisms in solids, liquids, and gases, highlighting how these are influenced by material properties and laser parameters. Additionally, it categorizes laser processes into photo-thermal, photo-chemical, and photo-physical, emphasizing that the material's response varies based on laser conditions and intensities.