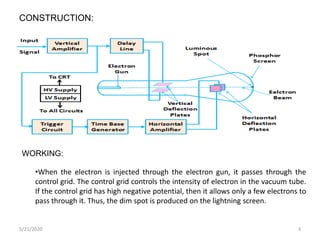
The document presents information on cathode ray oscilloscopes (CRO), detailing their purpose as instruments for measuring and analyzing waveforms with components like an electron gun and fluorescent screen. It explains the working mechanism of a CRO, including how electron beams are controlled and deflected to create visual displays. Additionally, it outlines advantages and disadvantages of using CROs, as well as their various applications in measuring voltage and current.