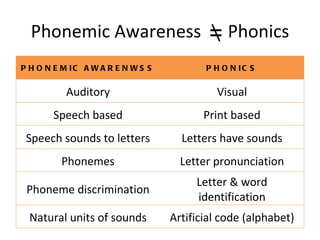
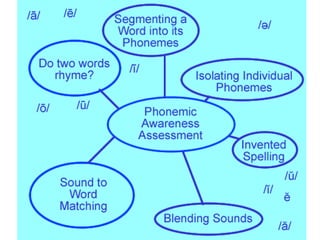
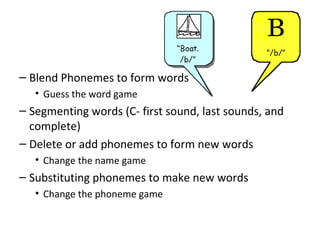
This document discusses phonemic awareness and how it differs from phonological awareness. Phonemic awareness refers to the ability to identify, manipulate, and blend phonemes, the smallest units of sound, in spoken words. It is an oral skill that predicts reading ability. The document provides examples of how to assess and teach phonemic awareness through direct instruction, small group activities, and phoneme manipulation games.