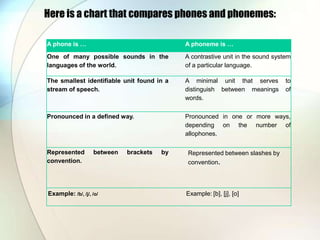
The document provides an overview of phonetics, highlighting its focus on the physical properties of speech sounds and their production, perception, and acoustics. It distinguishes between phonetics and phonology, noting that phonetics explores sound production while phonology examines the organization and meaning of sounds in languages. Additionally, it defines key concepts such as phonemes and allophones, illustrating their significance in linguistic studies.







![What is an allophone?DefinitionAn allophone is a phonetic variant of a phoneme in a particular language.Examples (English)[p] and [pH] are allophones of the phoneme /p/.[t] and [tH] are allophones of the phoneme /t/.Examples (Spanish)[b] and [B] are allophones of the phoneme /b/.[d] and [D] are allophones of the phoneme /d/.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicconceptsinphonetics-110629164911-phpapp02/85/Basic-concepts-in-phonetics-8-320.jpg)
![Examples (English): Minimal pairHere are examples of the phonemes /r/ and /l/ occurring in a minimal pair:• rip• lipThe phones [r] and [l] contrast in identical environments and are considered to be separate phonemes. The phonemes /r/ and /l/ serve to distinguish the word rip from the word lip.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicconceptsinphonetics-110629164911-phpapp02/85/Basic-concepts-in-phonetics-10-320.jpg)
![What is a grapheme? Linguistics one of a set of orthographic symbols (letters or combinations of letters) in a given language that serve to distinguish one word from another and usually correspond to or represent phonemes, e.g. the f in fun, the ph in phantom, and the gh in laugh[from Greek graphēma a letter]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicconceptsinphonetics-110629164911-phpapp02/85/Basic-concepts-in-phonetics-11-320.jpg)

