This document discusses different philosophies of teaching:
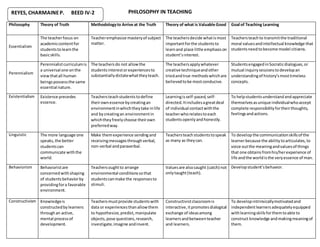
- Essentialism focuses on academic content mastery and transmitting traditional values, with teachers deciding what's important.
- Perennialism uses a universal curriculum based on human nature, with creative techniques to develop understanding of timeless concepts.
- Existentialism teaches students to define their own essence through self-paced, self-directed learning with individual teacher guidance.
- Linguistic philosophy develops communication skills through multiple languages to articulate experiences.
- Behaviorism shapes student behavior through environmental arrangements and learning from others.
- Constructivism has students actively construct knowledge through experiences, questioning, and dialogical exchange between teachers and peers.