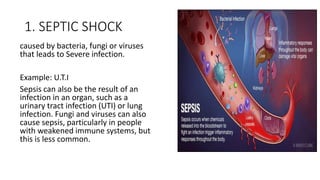
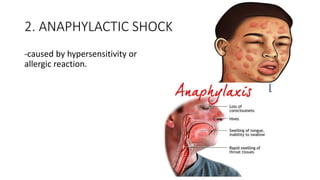
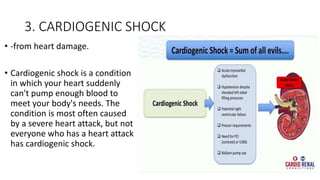
Shock is a life-threatening condition caused by inadequate blood flow to tissues in the body. Symptoms include weakness, fast heart rate, fast breathing, sweating, anxiety, and increased thirst. Shock can be caused by issues with the circulatory system, blood loss, infection, allergic reaction, heart damage, brain or spinal cord injury, respiratory failure, extreme emotions, or excess acid in the body. It is a medical emergency requiring immediate emergency assistance.