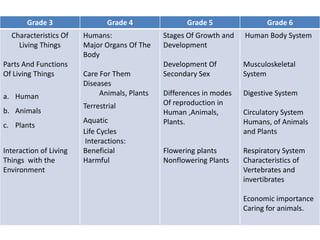
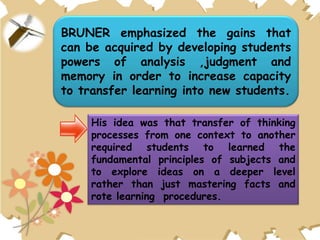
The document discusses the spiral curriculum, an approach to teaching where basic facts are first introduced without details, and then more details are added with each repetition to help reinforce learning. It is both a sequencing and teaching strategy that exposes learners to concepts and skills through continually revisiting topics with increasing complexity. An example spiral curriculum for science is provided, showing how topics like characteristics of living things are revisited each year with more details. The approach aims to improve retention of concepts while allowing progressive elaboration of topics to broaden understanding.