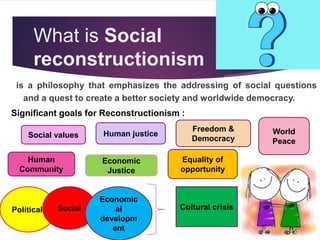
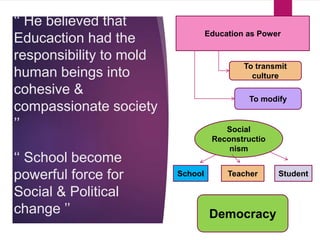
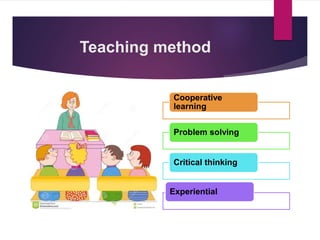
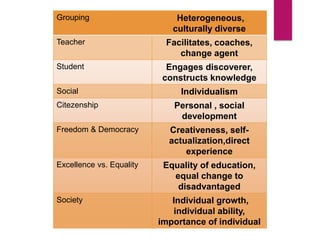
Social reconstructionism is a philosophy that emphasizes addressing social problems and creating a better, more just society. It focuses on using education to promote social reform and change the world for the better. Reconstructionist educators believe schools should encourage meaningful dialogue among students to critique and transform society, rather than simply telling children what to think. The major premises of reconstructionism are that society constantly needs reconstruction or change, and such social change involves reconstructing education to reconstruct society. Prominent reconstructionist thinkers like Theodore Brameld, George Counts, and Paulo Freire saw education as a means of preparing people to create a new social order and resist oppression.