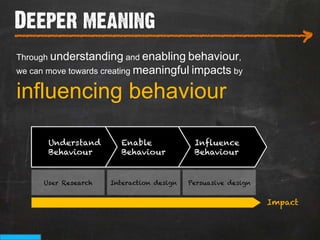
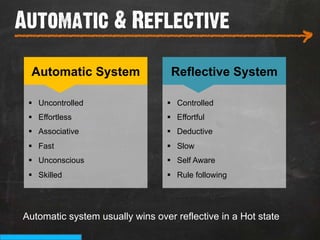
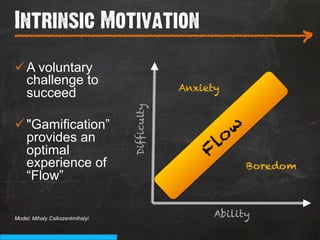
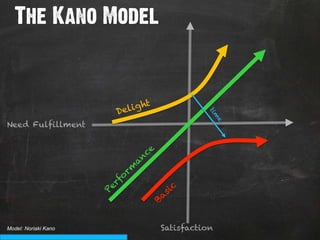
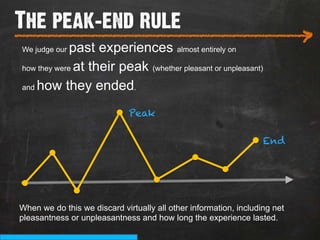
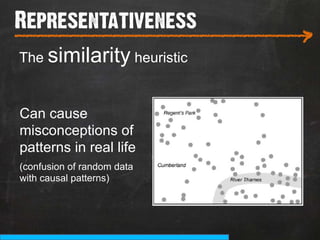
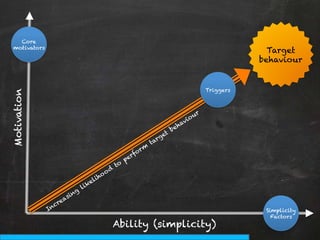
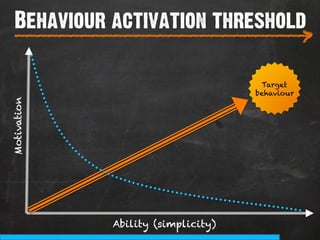
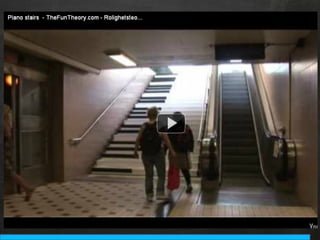
The document discusses the concept of persuasive design, which is about influencing choices without coercion. It explains that designers can subtly influence behavior through small details and by understanding human psychology. Specifically, it describes how people tend to discount future rewards and benefits, are swayed more by immediate needs and emotions, and have biases that can be addressed through design, such as by making positive behaviors the default choice or easy option. The overall goal of persuasive design is to automate behavior change for the better by addressing human tendencies and biases.