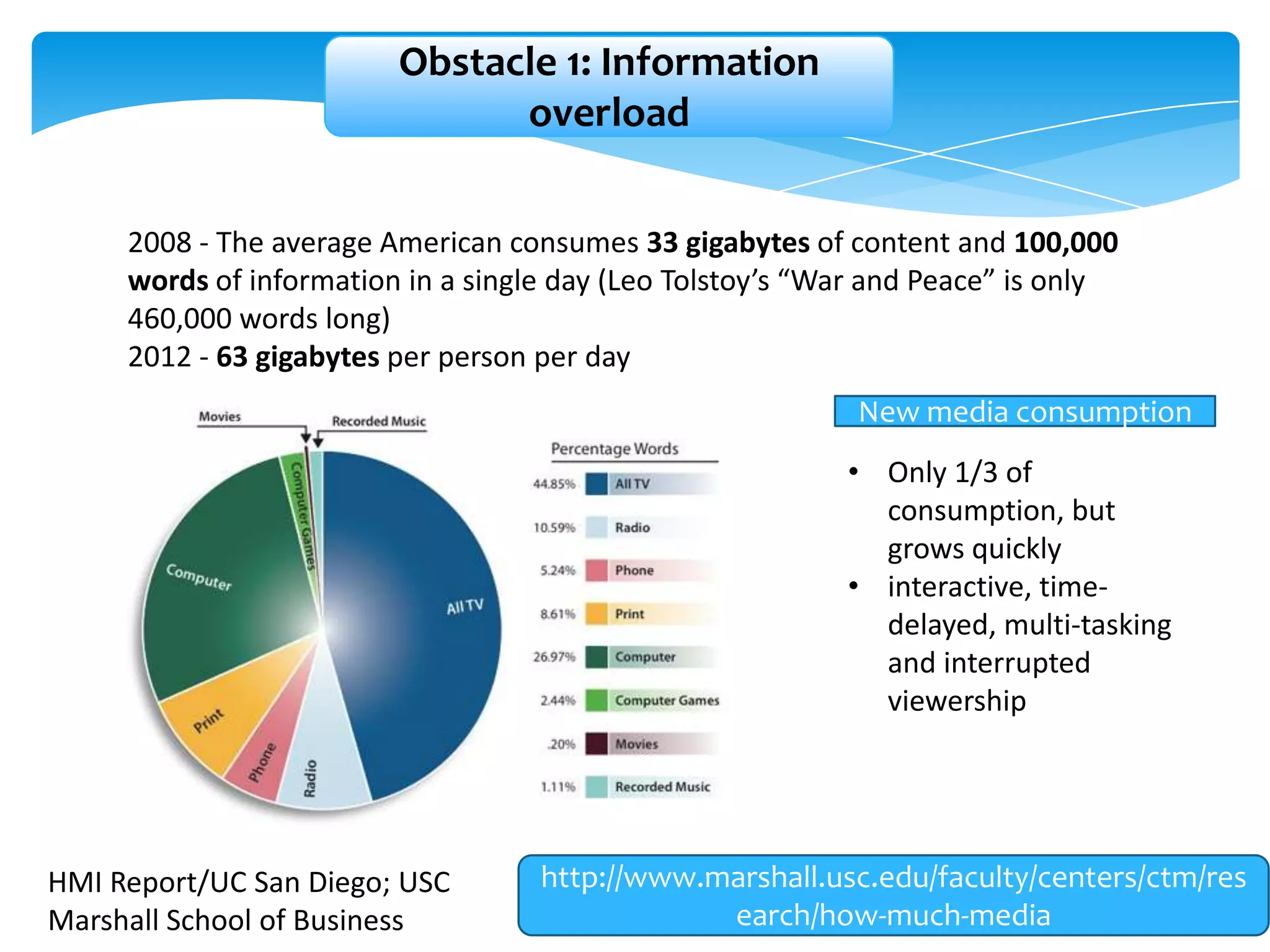
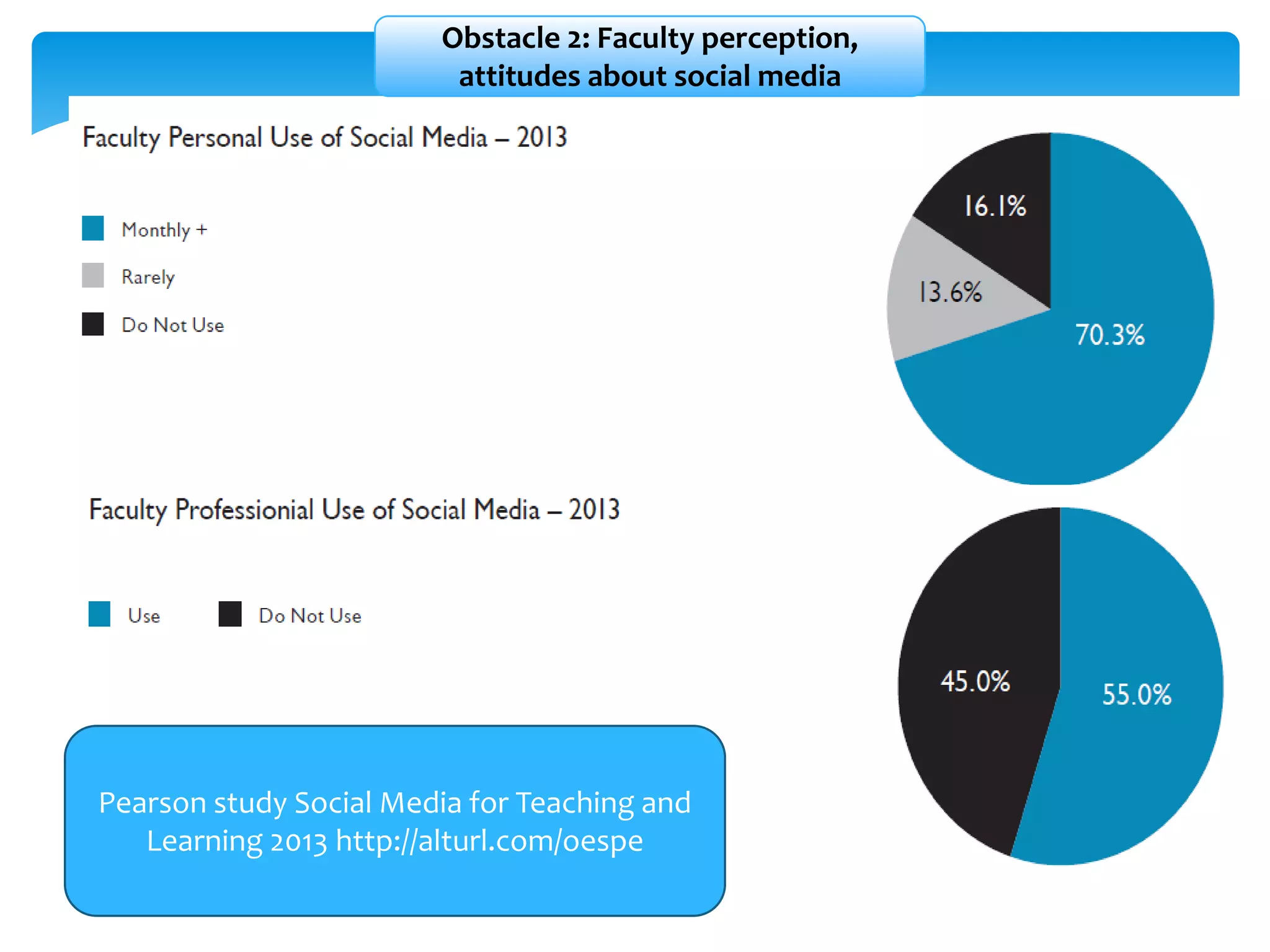
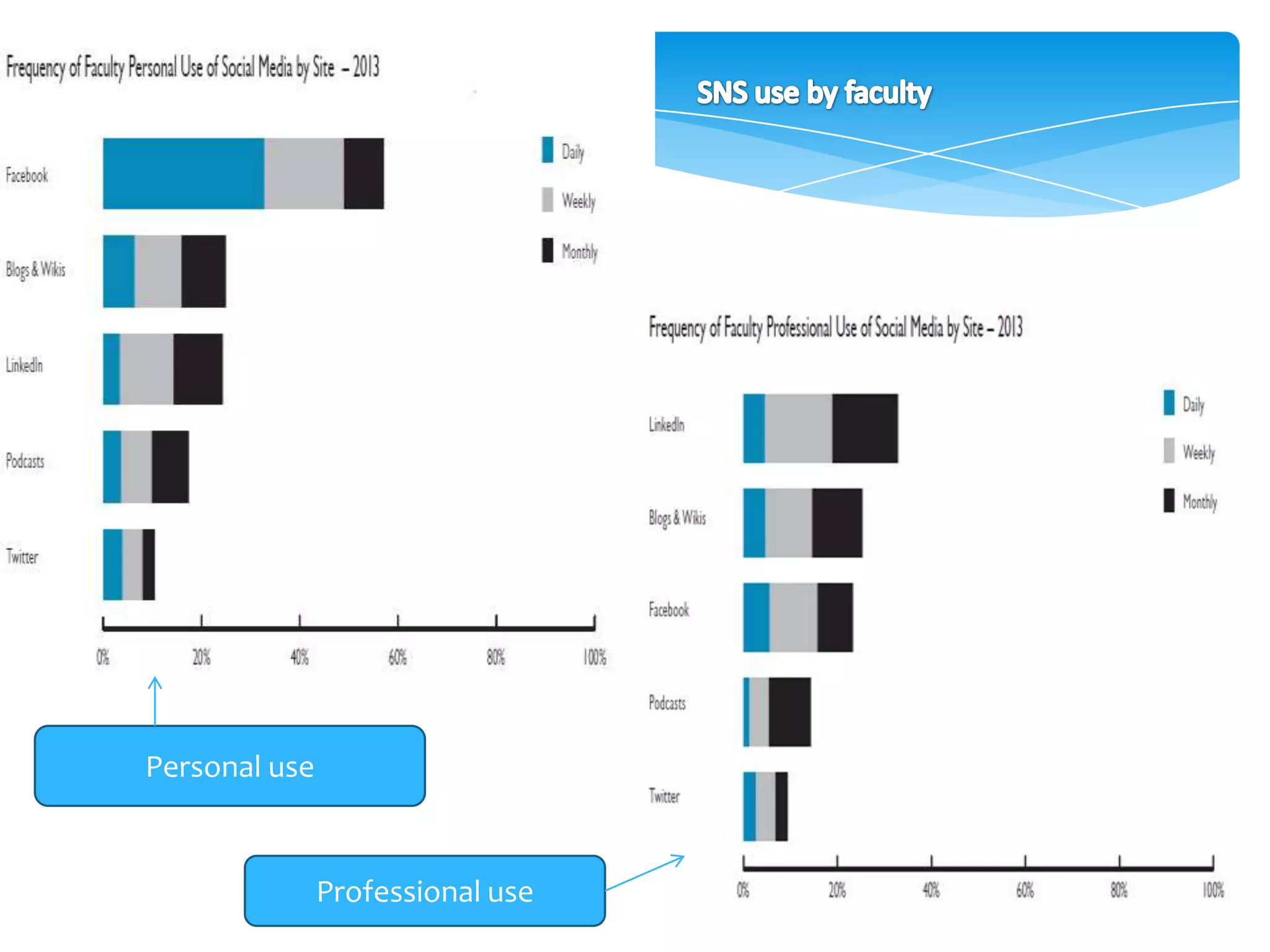
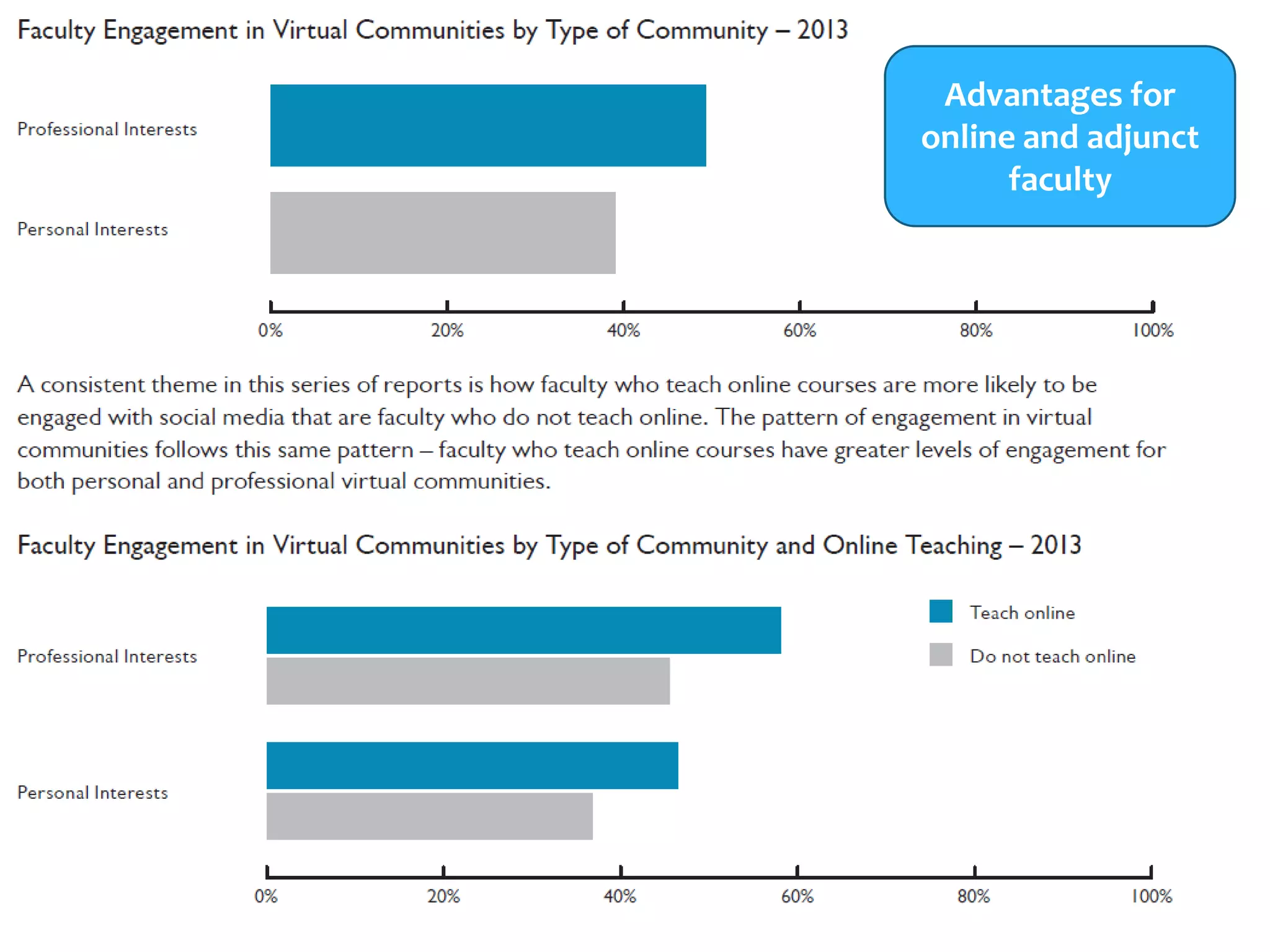
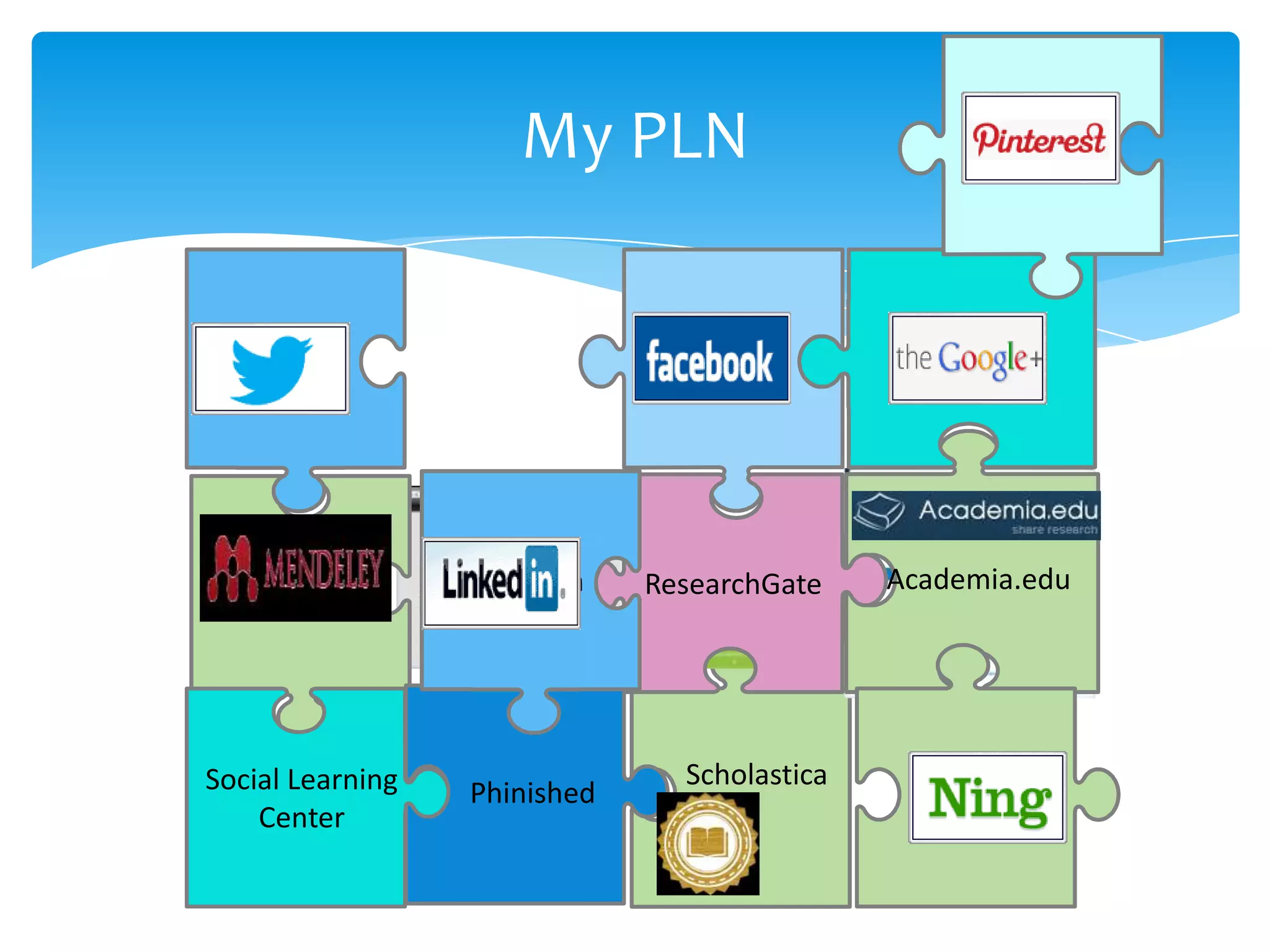
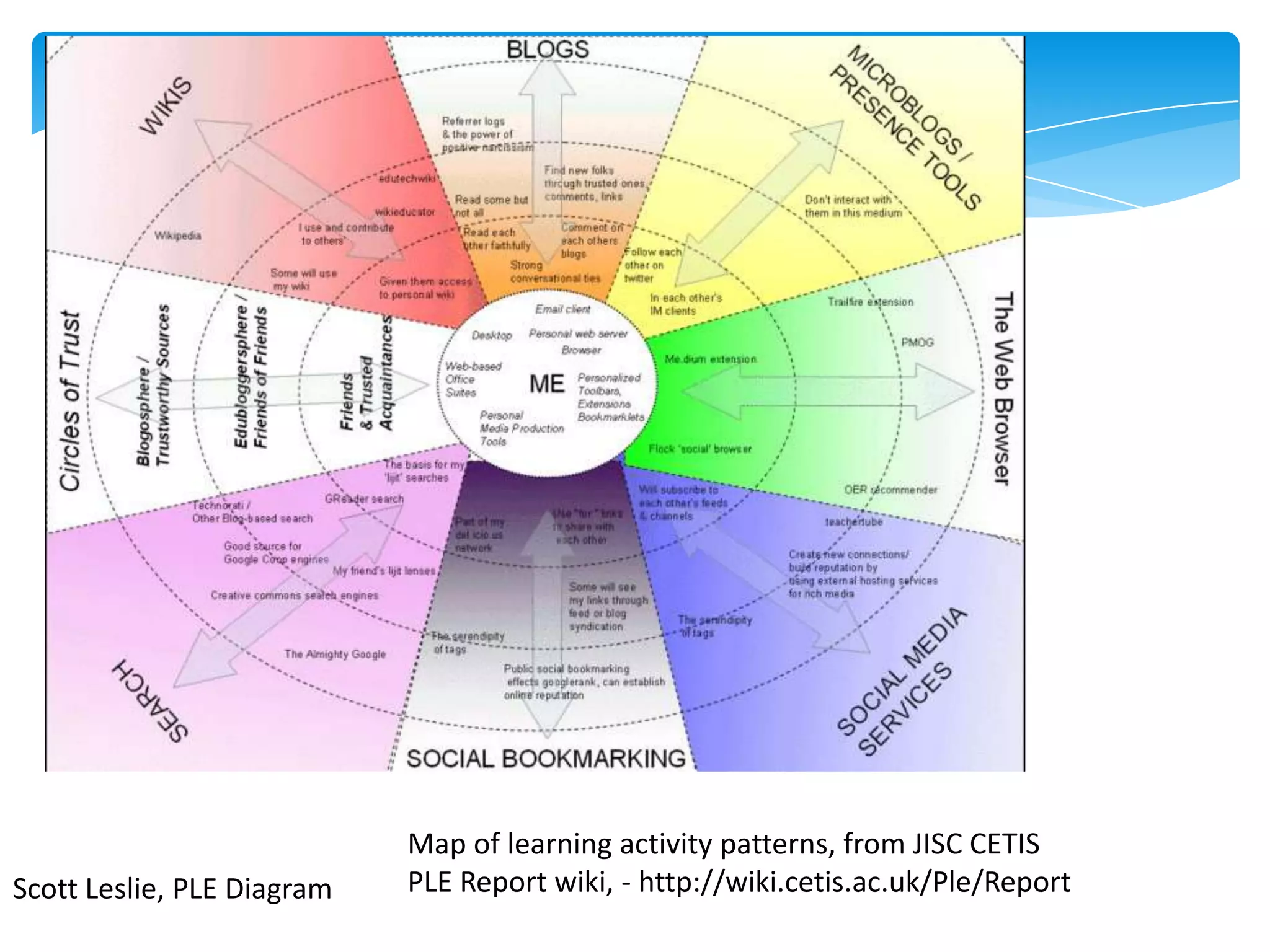
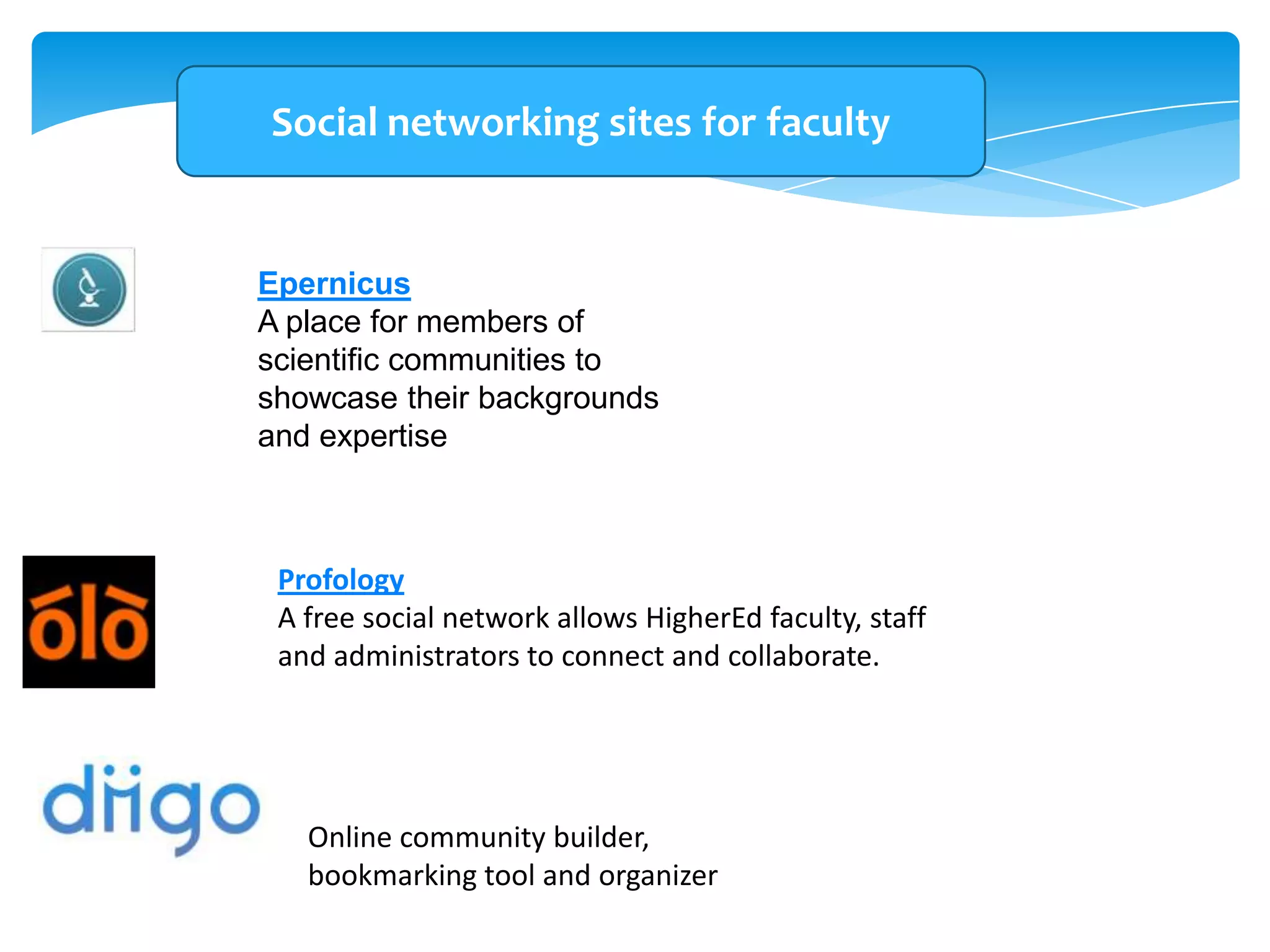
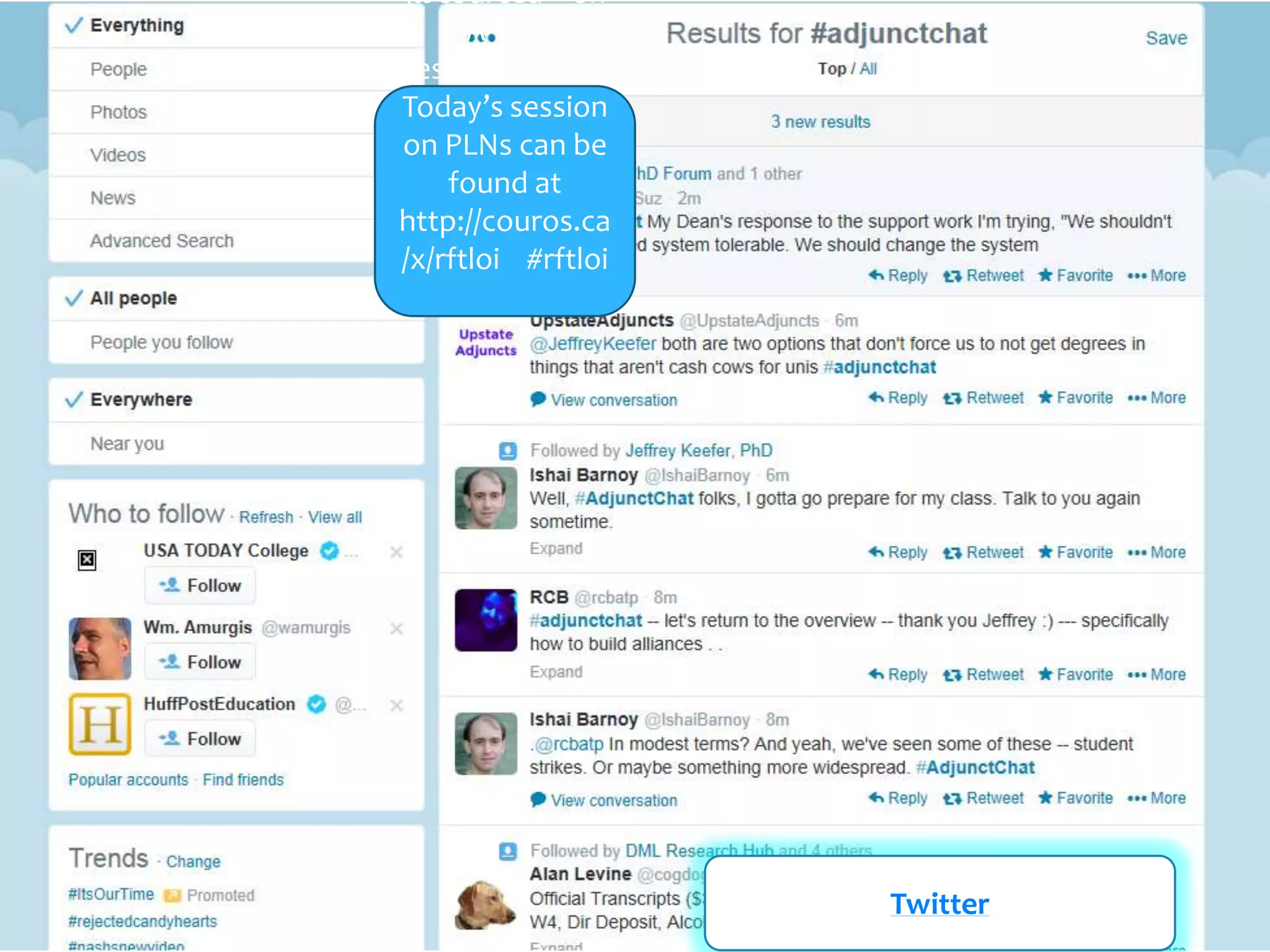
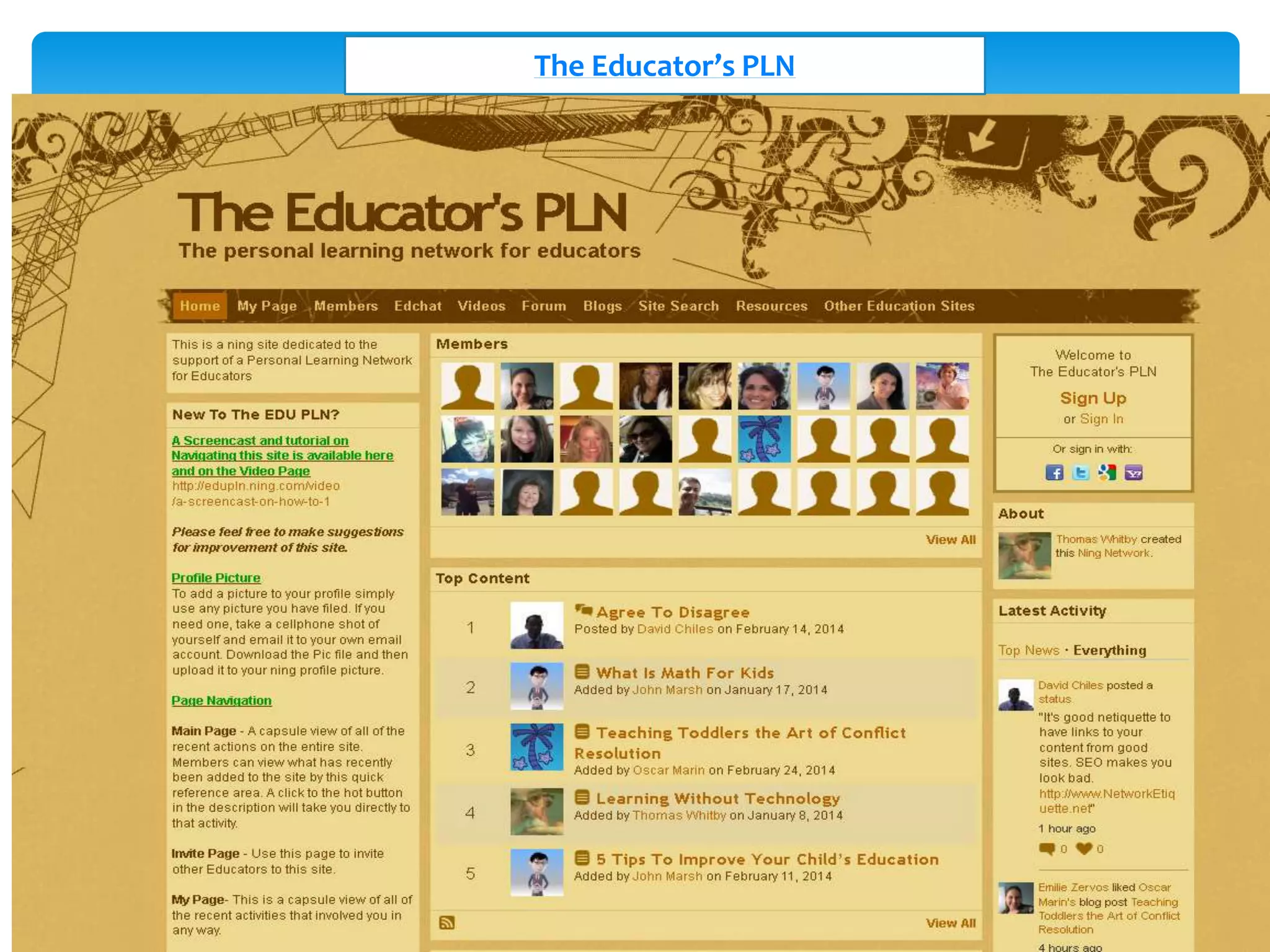
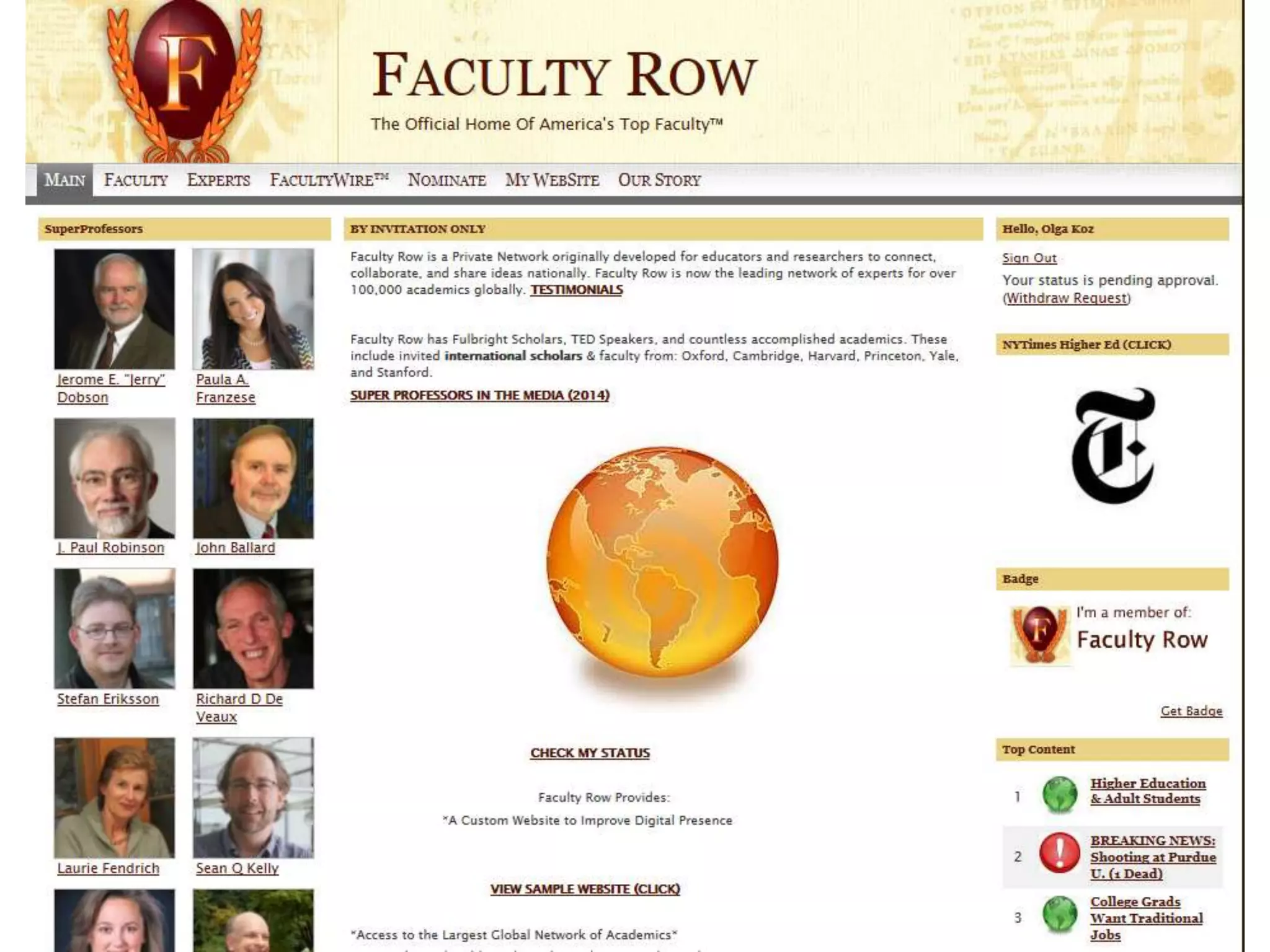
The document discusses personal learning networks (PLNs) and their significance in enhancing professional development, emphasizing the challenges faculty face with social media use in education. It highlights key theories of social and situated learning, while addressing obstacles like information overload and faculty perceptions of social media. The content includes various tools and platforms that support social learning, alongside a faculty survey aimed at understanding the impact of PLNs on professional growth.