The document summarizes key concepts about the periodic table of elements, including:
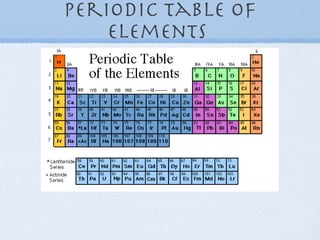
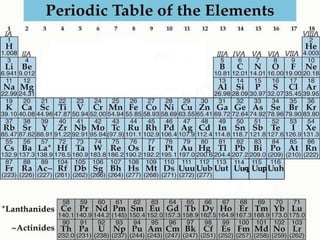
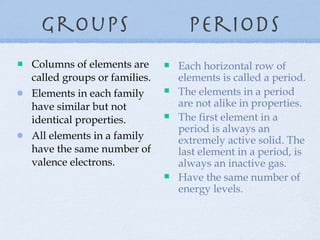
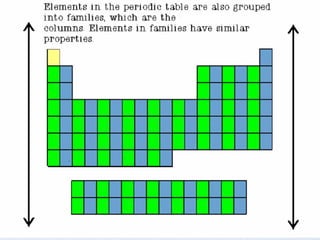
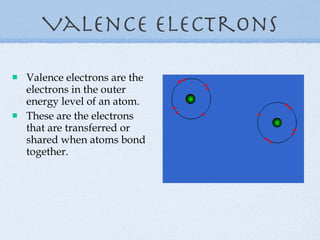
1) Elements are organized into groups based on their valence electrons, with elements in the same group having similar properties.
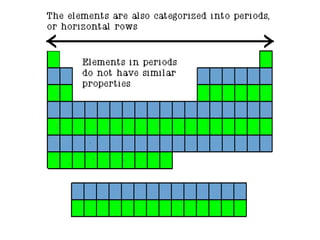
2) Periods refer to horizontal rows, with the first element being very reactive and the last being an inactive gas.
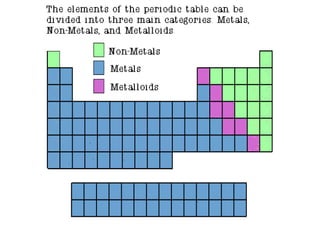
3) Non-metals are generally poor conductors while metals are good conductors.
4) Metalloids have properties between metals and non-metals.
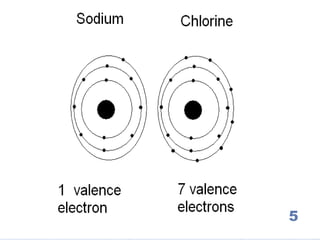
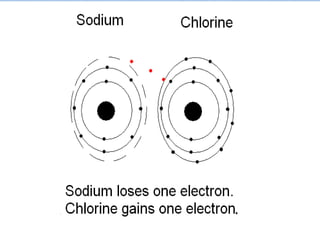
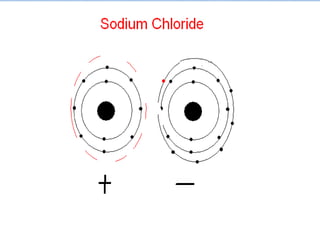
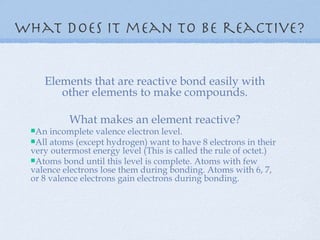
5) Reactive elements easily bond to complete their outer electron levels.