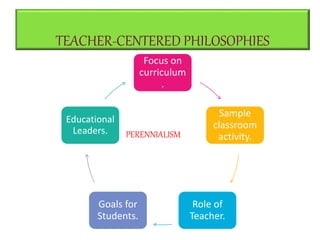
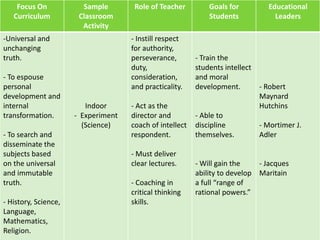
Perennialism is a philosophy of education that aims to develop students' intellectual and moral qualities by focusing on teaching concepts and ways of thinking through enduring disciplines like history, science, literature and art. It emphasizes teaching ideas and knowledge that are considered universal and unchanging rather than information that may become outdated. In the perennialist classroom, the teacher plays a central role by delivering clear lectures and coaching students in critical thinking skills in order to train their intellect and develop their moral character so they can gain the ability to think deeply and analytically. Prominent advocates of perennialism like Robert Hutchins and Mortimer Adler believed it could help address failing educational systems by producing more thoughtful citizens.














![The advocates
MORTIMER J. ADLER
[1902-2001]
JACQUES MARITAIN
[1882-1973]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perennialism-121110051604-phpapp02-160502021616/85/Perennialism-121110051604-phpapp02-17-320.jpg)






