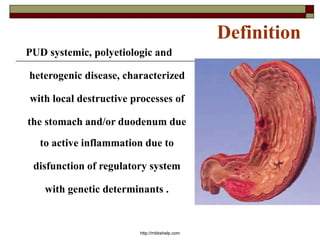
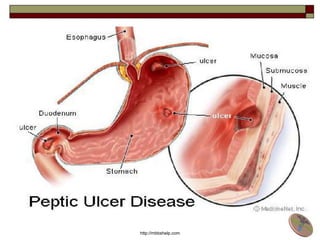
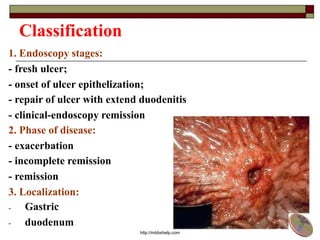
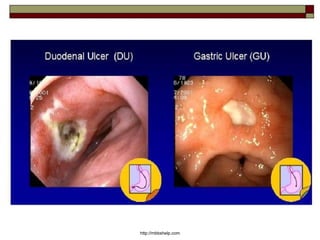
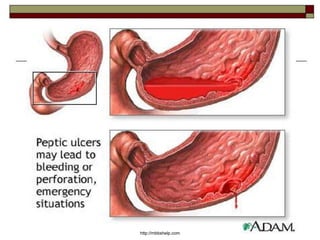
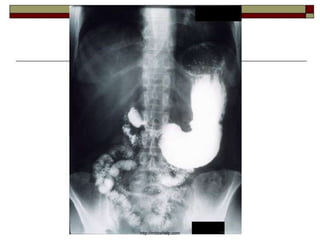
Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD) is characterized by local destructive processes of the stomach and/or duodenum due to active inflammation caused by dysfunctions in the regulatory system and genetic determinants. Common causes include H. pylori infection, NSAID use, stress, and alcohol use. PUD can be classified based on its endoscopic stage, phase of disease, localization in the stomach or duodenum, and potential complications such as bleeding, perforation, and obstruction. Symptoms include abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Treatment involves eradicating H. pylori infections, stopping NSAID use, and prescribing proton pump inhibitors.