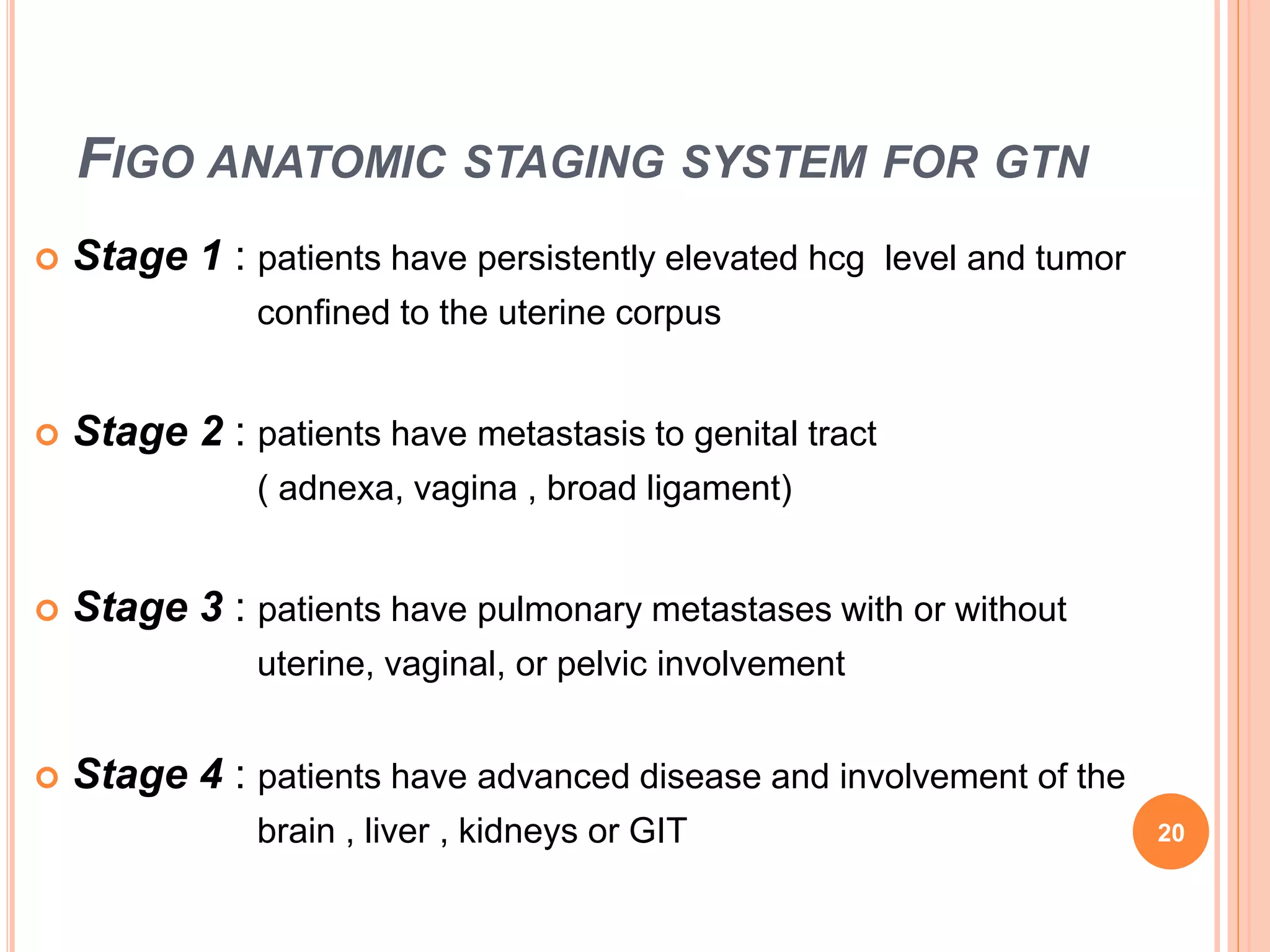
Gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD) includes invasive mole, choriocarcinoma, placental site trophoblastic tumor, and epithelioid trophoblastic tumor. These develop after molar or non-molar pregnancies. Treatment depends on disease stage and risk score. Low-risk GTD is treated with single-agent chemotherapy like methotrexate or actinomycin D. High-risk GTD receives multi-agent chemotherapy like EMA/CO. Residual masses may require additional treatment. Relapsed or resistant GTD can be treated with salvage chemotherapy, surgery, or high-dose chemotherapy with stem cell transplant. Side effects depend on chemotherapy drugs used.