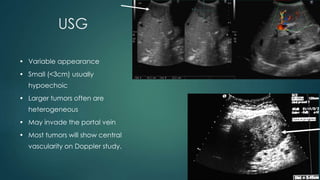
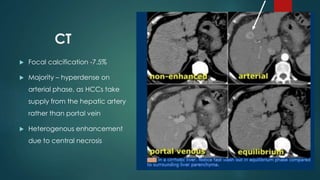
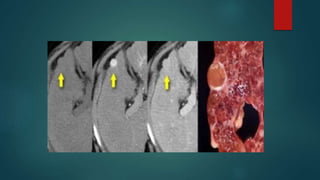
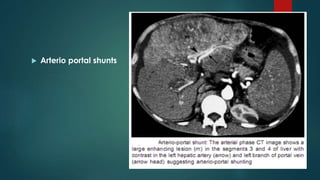
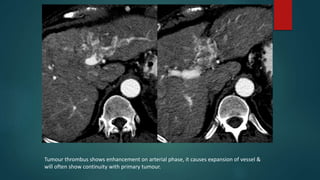
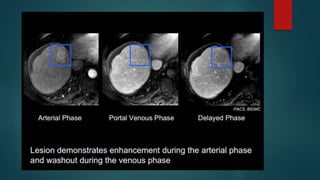
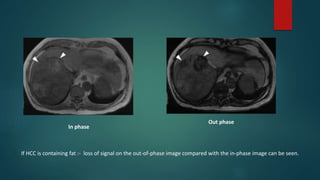
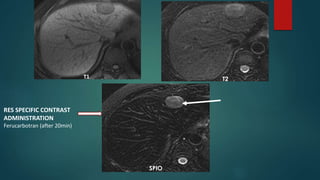
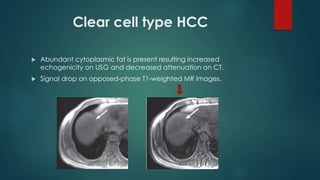
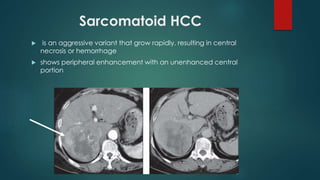
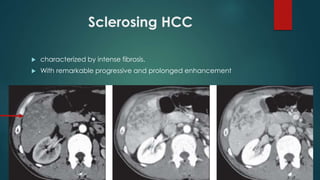
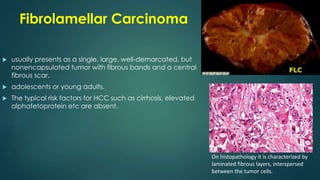
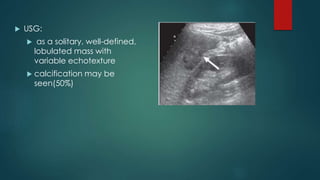
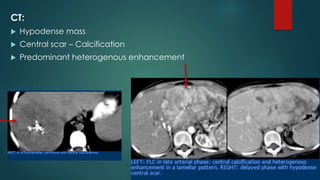
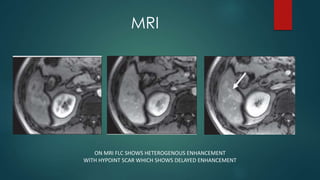
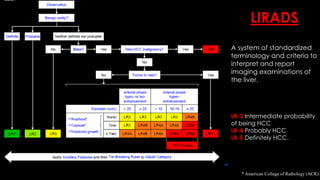
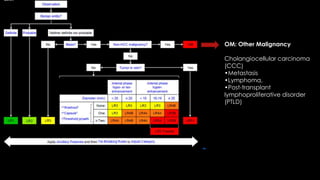
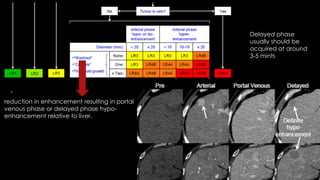
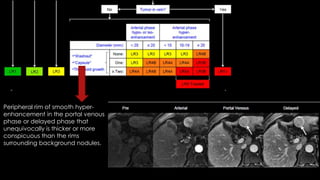
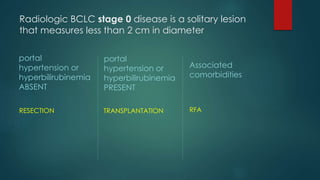
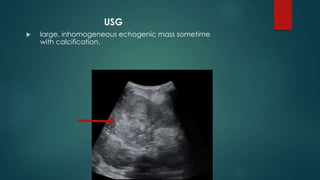
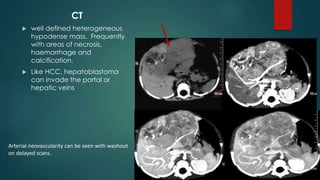
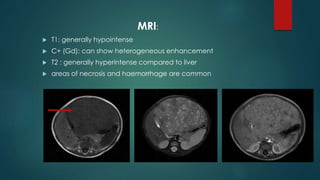
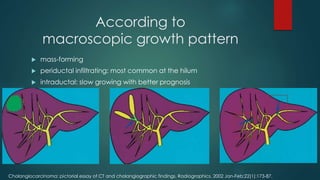
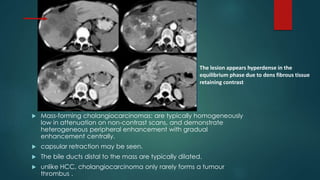
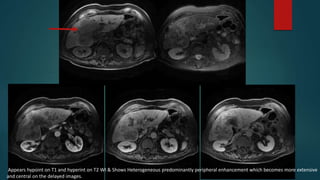
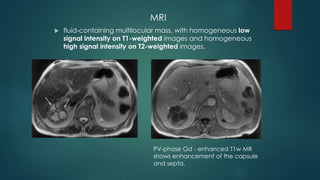
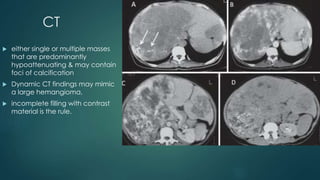
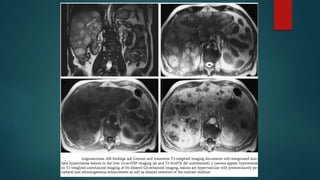
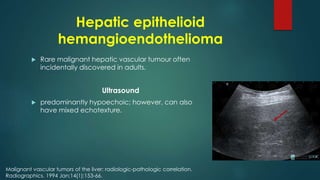
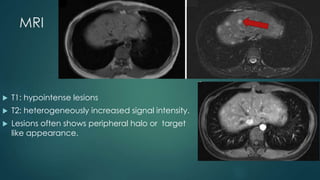
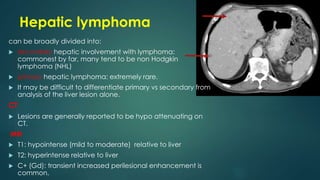
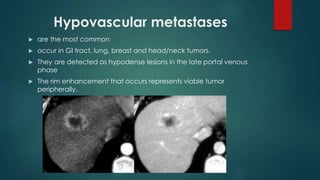
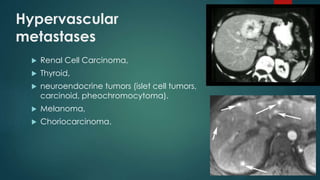
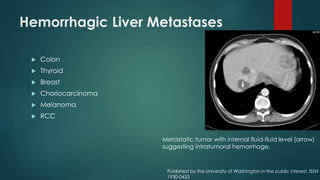
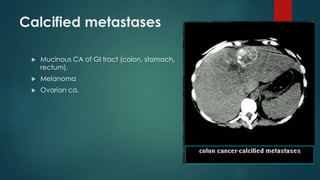
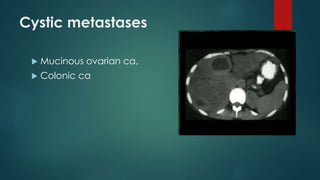
This document discusses various malignant liver lesions including primary and secondary tumors. For primary liver cancers, it describes hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) as the most common type, risk factors such as hepatitis, and imaging features. It also discusses cholangiocarcinoma, hepatoblastoma, and rare tumors such as fibrolamellar carcinoma. Secondary cancers and criteria for staging HCC are also summarized.