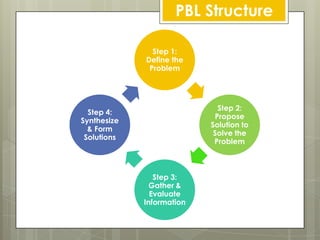
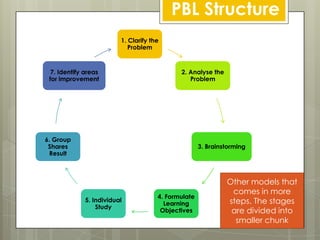
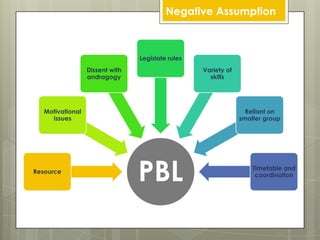
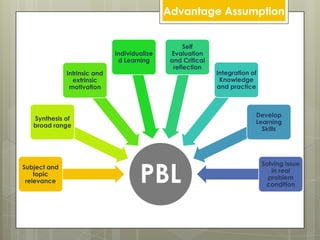
Problem-based learning (PBL) is a constructivist educational approach initiated in the 1970s that emphasizes learning through engagement with real-world problems. It focuses on student-centered learning where the teacher acts as a facilitator, guiding students through defining problems, proposing solutions, and synthesizing information. PBL aims to develop competencies such as clinical decision-making and teamwork in abnormal circumstances.