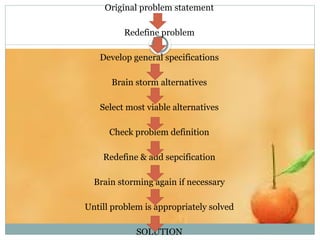
Problem-Based Learning (PBL) originated at McMaster University in the late 1960s to enhance students' motivation and critical thinking through collaborative, real-world problem solving. The PBL process involves selecting roles within groups, engaging in brainstorming, and utilizing structured sessions for understanding and synthesizing information, followed by evaluation of student performance. While PBL fosters skills such as self-directed learning and teamwork, it presents challenges like time constraints, difficulty in assessment, and a transition from traditional teaching methods.