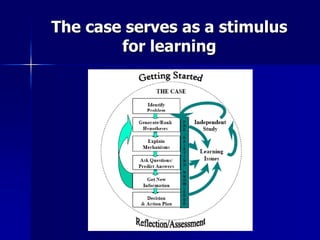
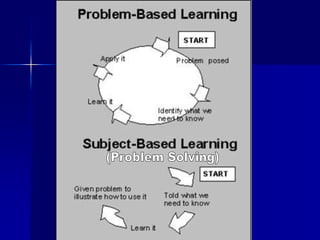
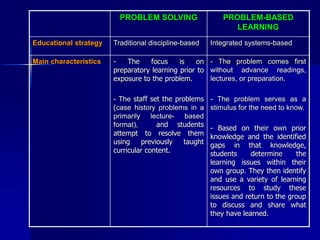
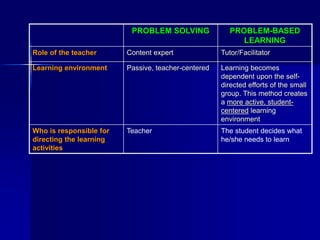
Problem-based learning (PBL) is a student-centered approach that uses clinical problems to stimulate learning. Students define their own learning needs, conduct self-directed research, integrate theory and practice, and develop solutions. In contrast to traditional curricula, PBL is integrated, systems-based, and focuses on applying knowledge to clinical problems rather than first acquiring basic sciences. Proponents argue that PBL better prepares students for medical practice by making learning more relevant and promoting long-term retention through self-directed, context-based study of real problems.