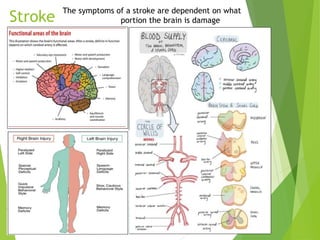
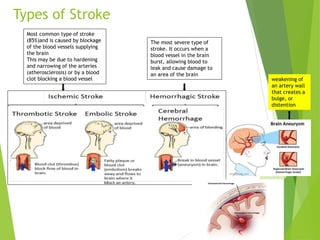
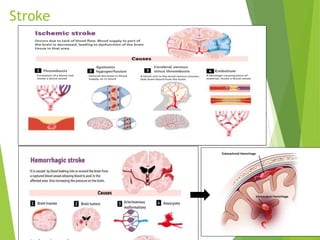
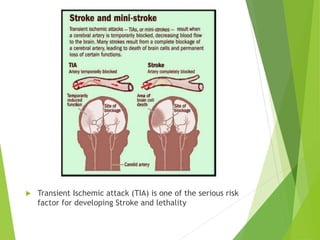
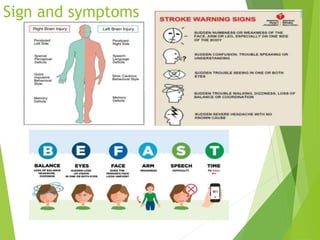
Stroke occurs when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted or reduced, leading to brain damage and neurological deficits. It is a medical emergency. According to the WHO, 15 million people suffer strokes worldwide each year, resulting in 5 million deaths and 5 million cases of permanent disability. The main types of stroke are ischemic, which accounts for 85% of cases and is caused by a blockage of blood vessels in the brain, and hemorrhagic, which results from a ruptured blood vessel in the brain. Risk factors include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, smoking, obesity, physical inactivity, previous TIAs, and older age. Symptoms depend on the affected area of the brain and may include weakness, numb