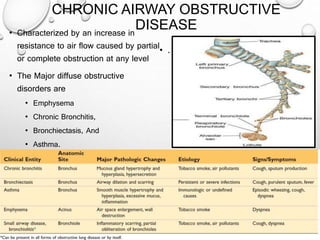
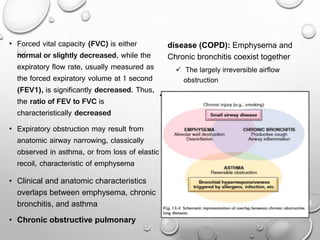
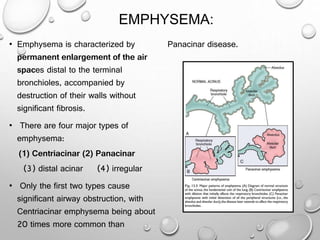
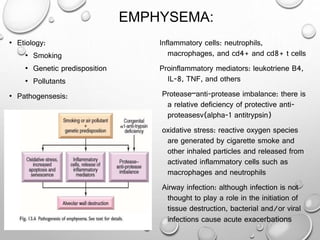
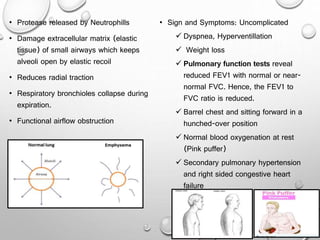
This document summarizes chronic obstructive airway diseases including emphysema, chronic bronchitis, bronchiectasis, and asthma. It describes the pathophysiology of each condition including causes, mechanisms of airflow obstruction, signs and symptoms. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is defined as emphysema and chronic bronchitis occurring together, resulting in largely irreversible airflow obstruction. In contrast, asthma involves reversible airflow obstruction. The document provides details on the types and features of emphysema and chronic bronchitis, and compares the pathophysiology of COPD versus asthma.