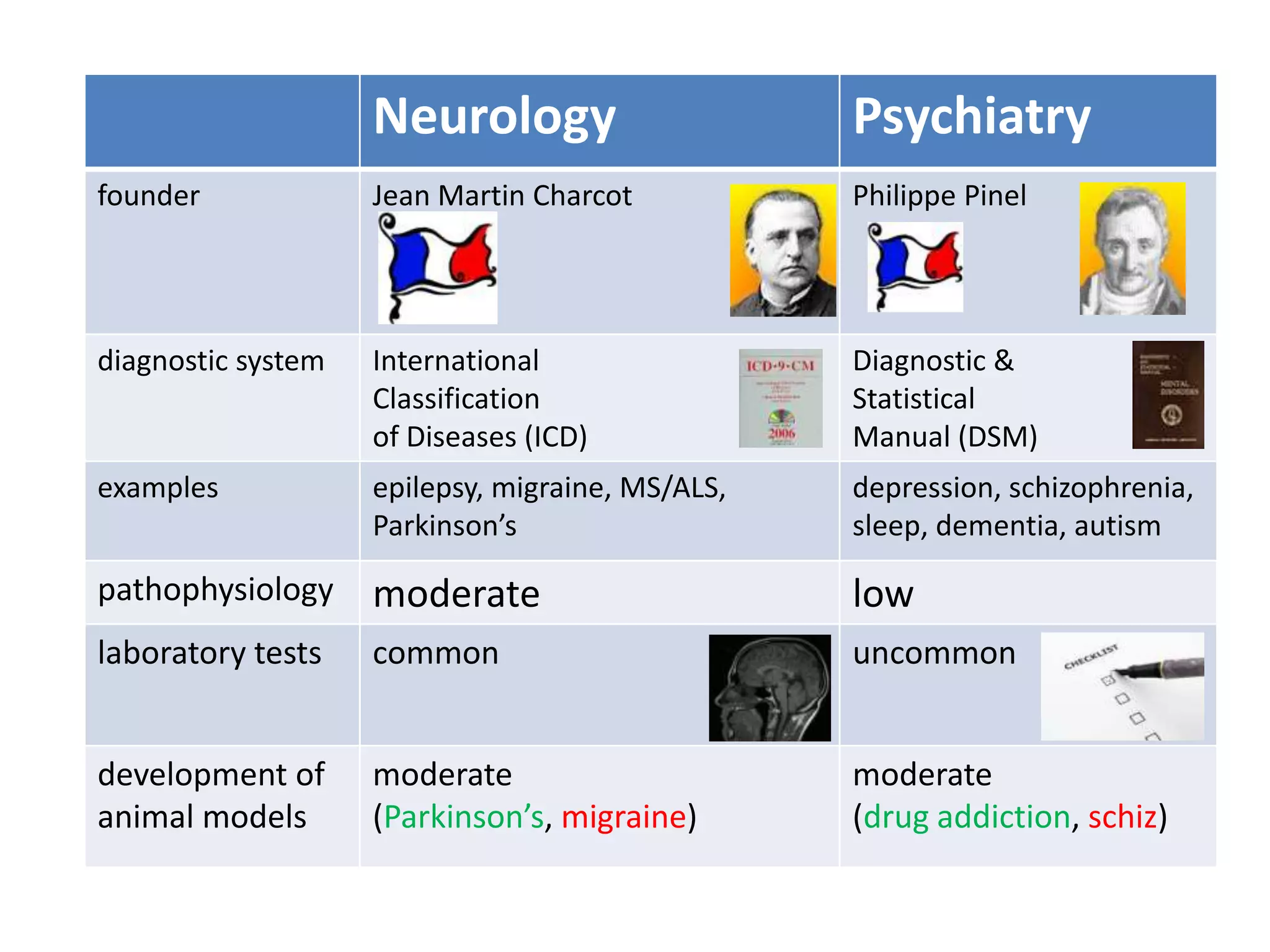
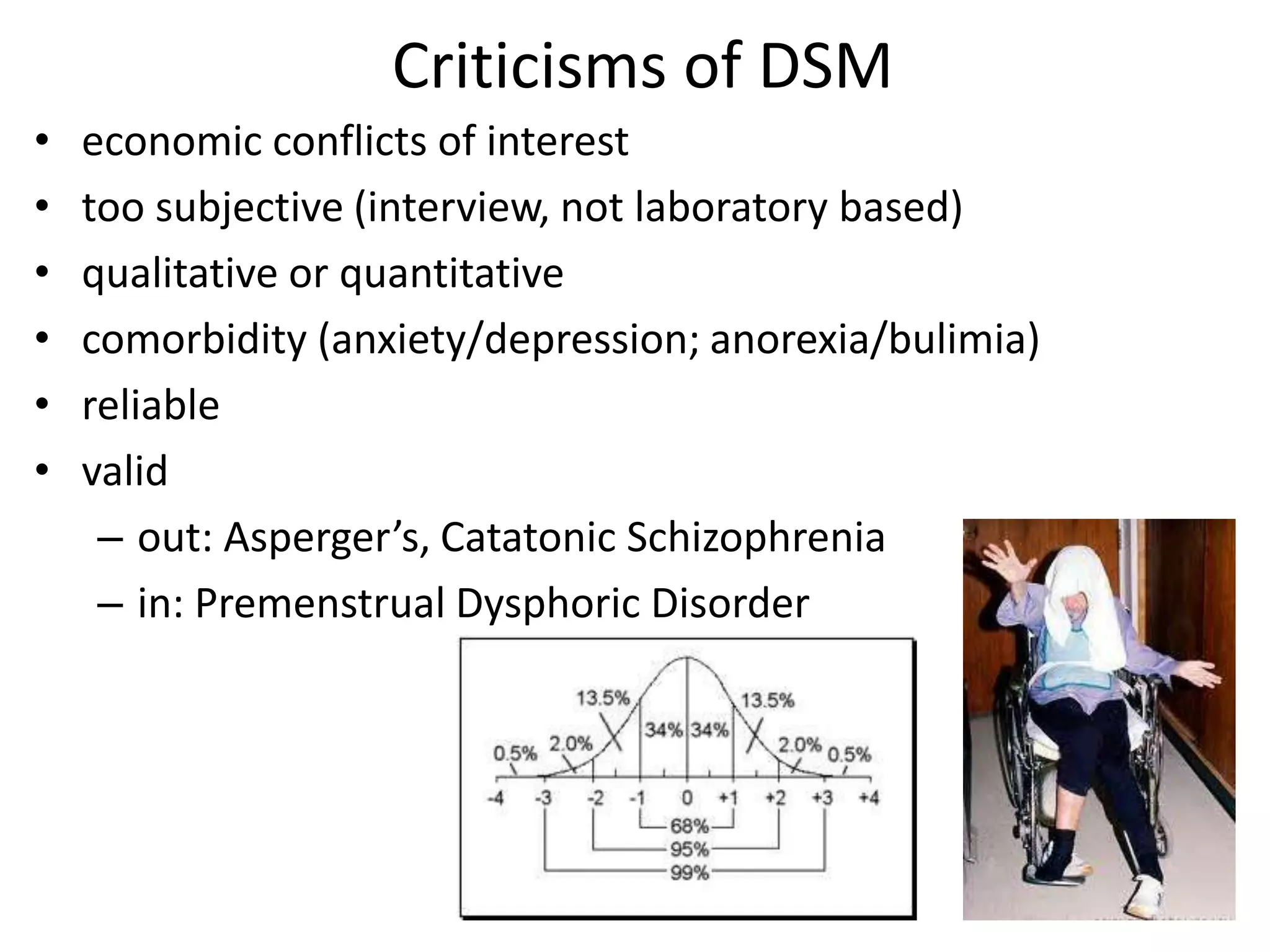
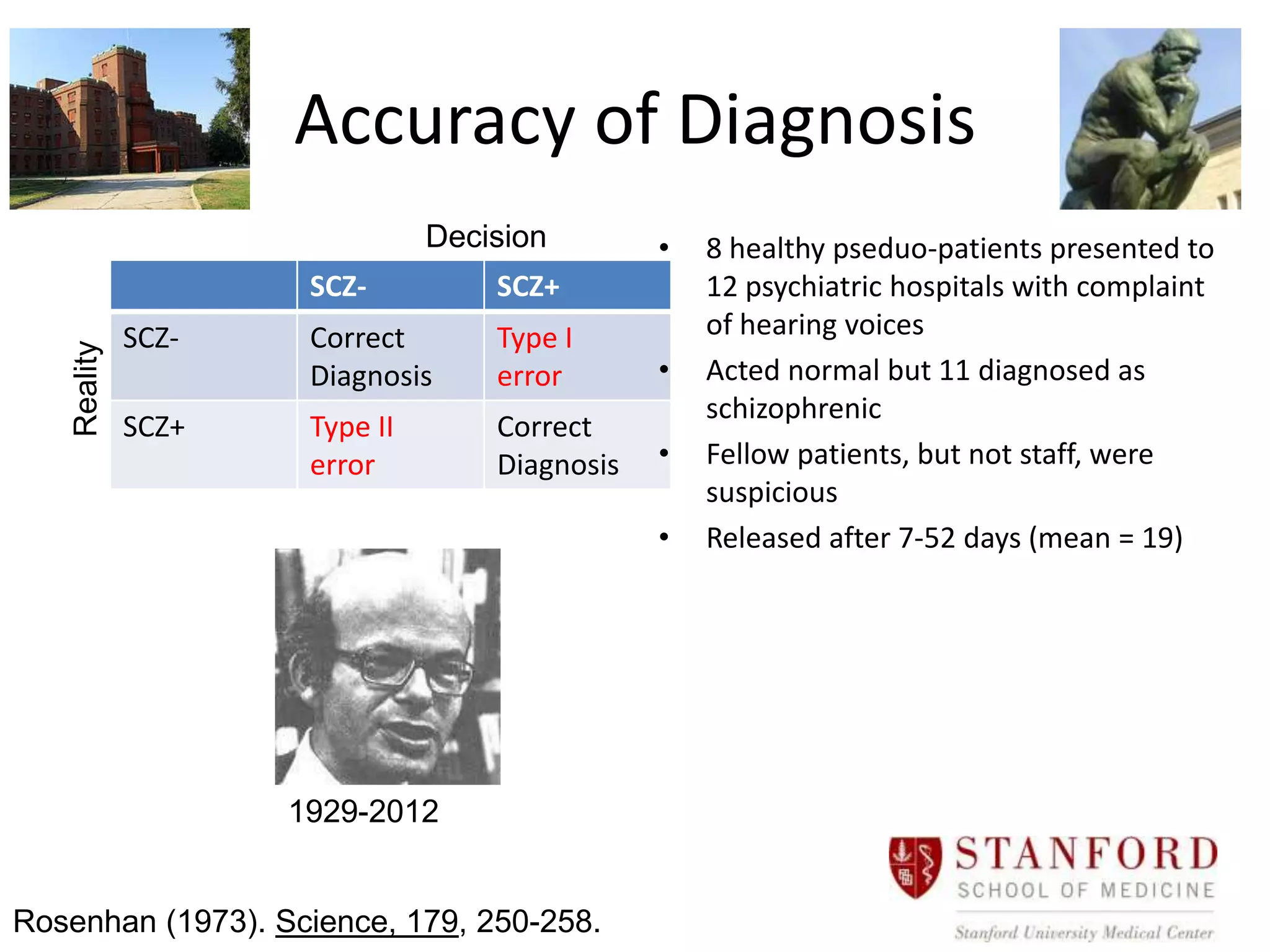
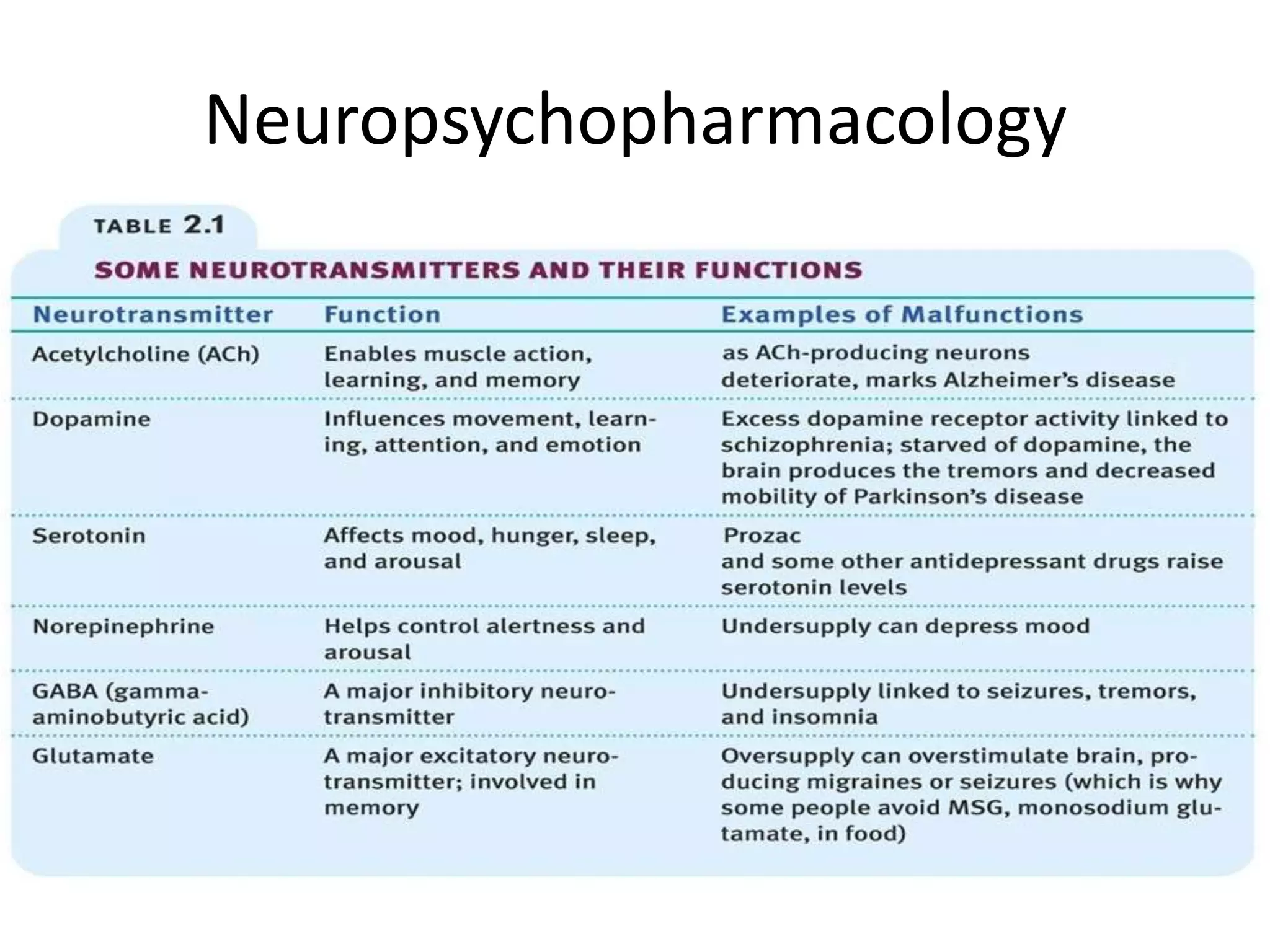
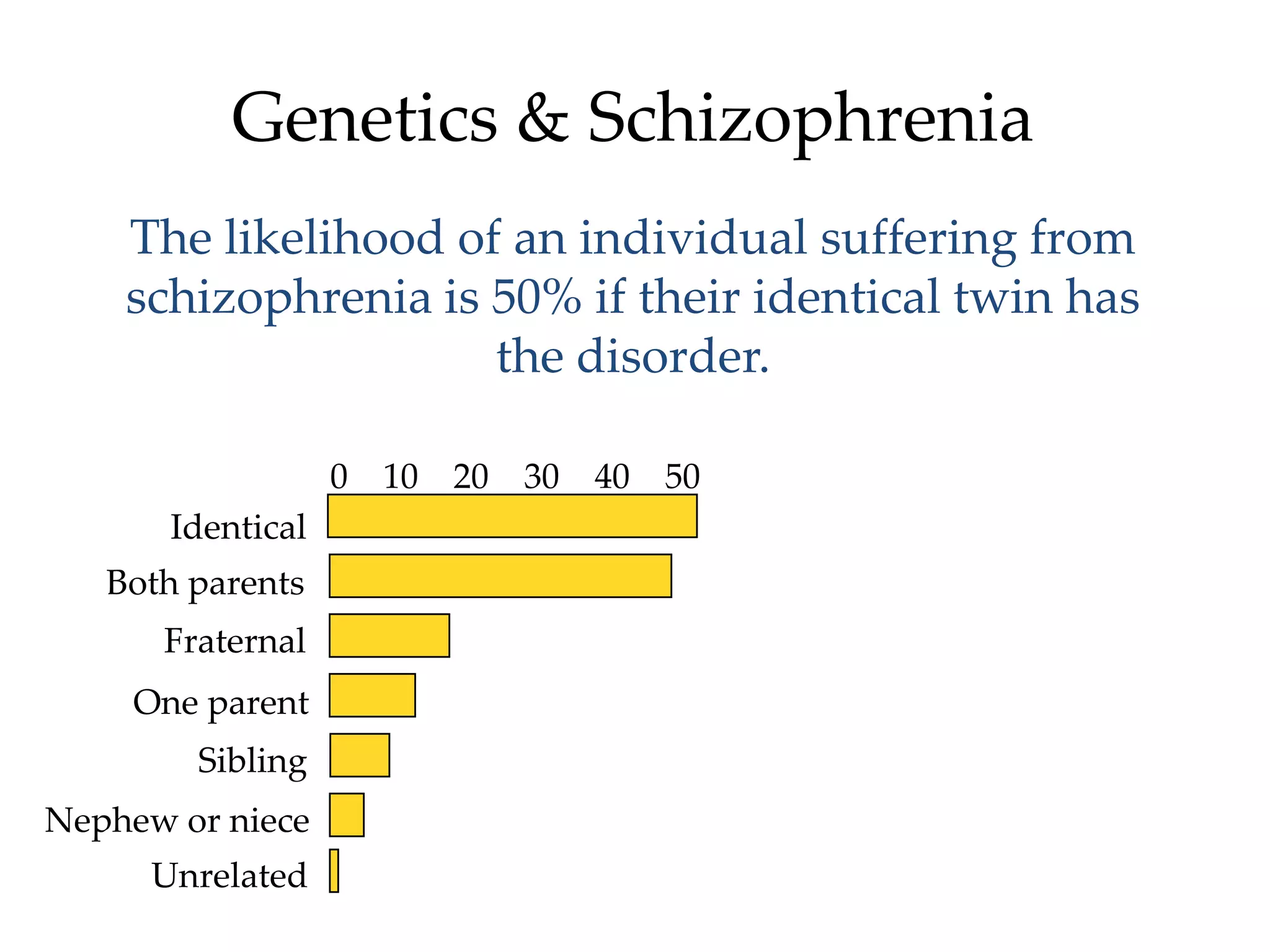
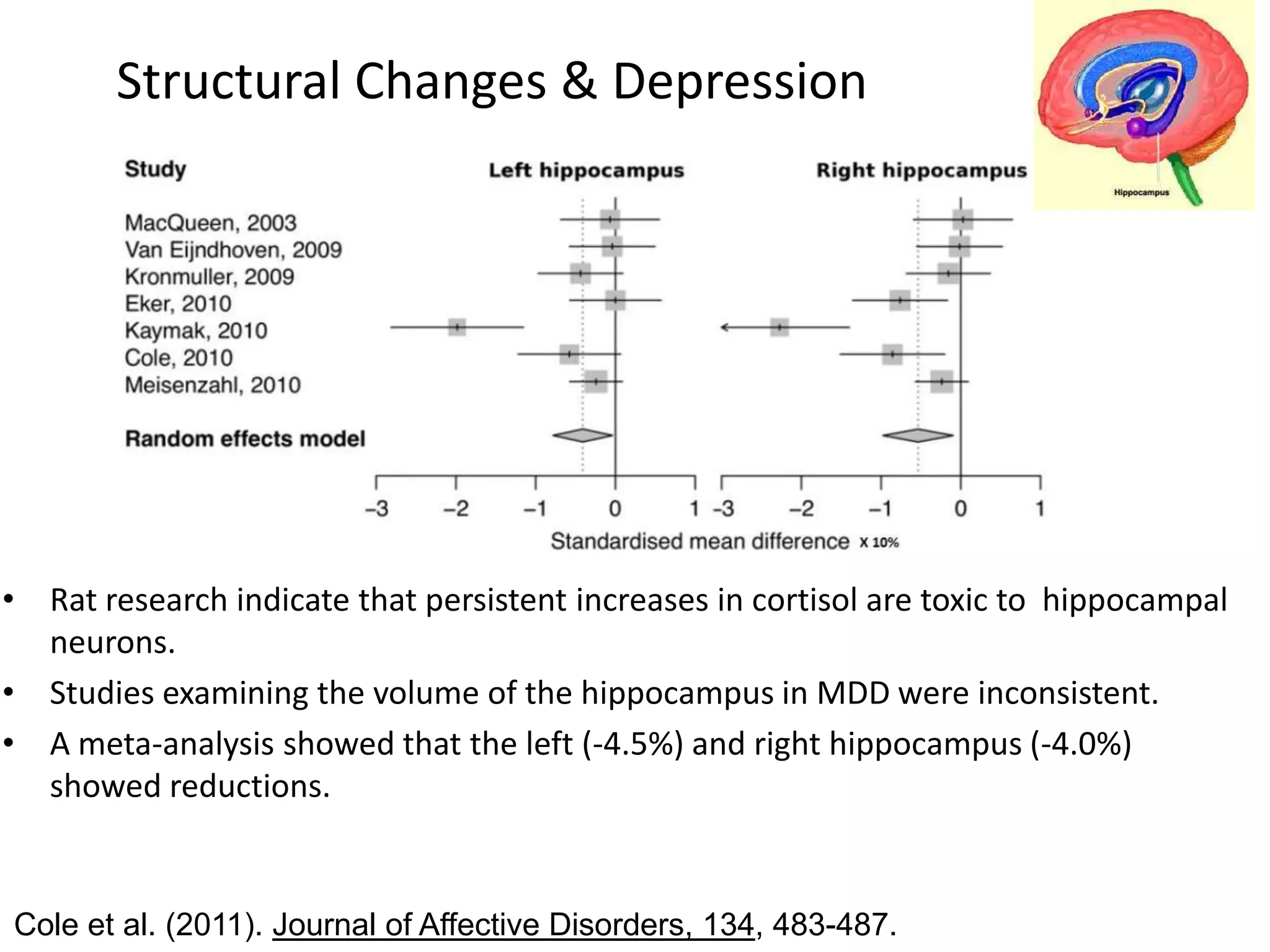
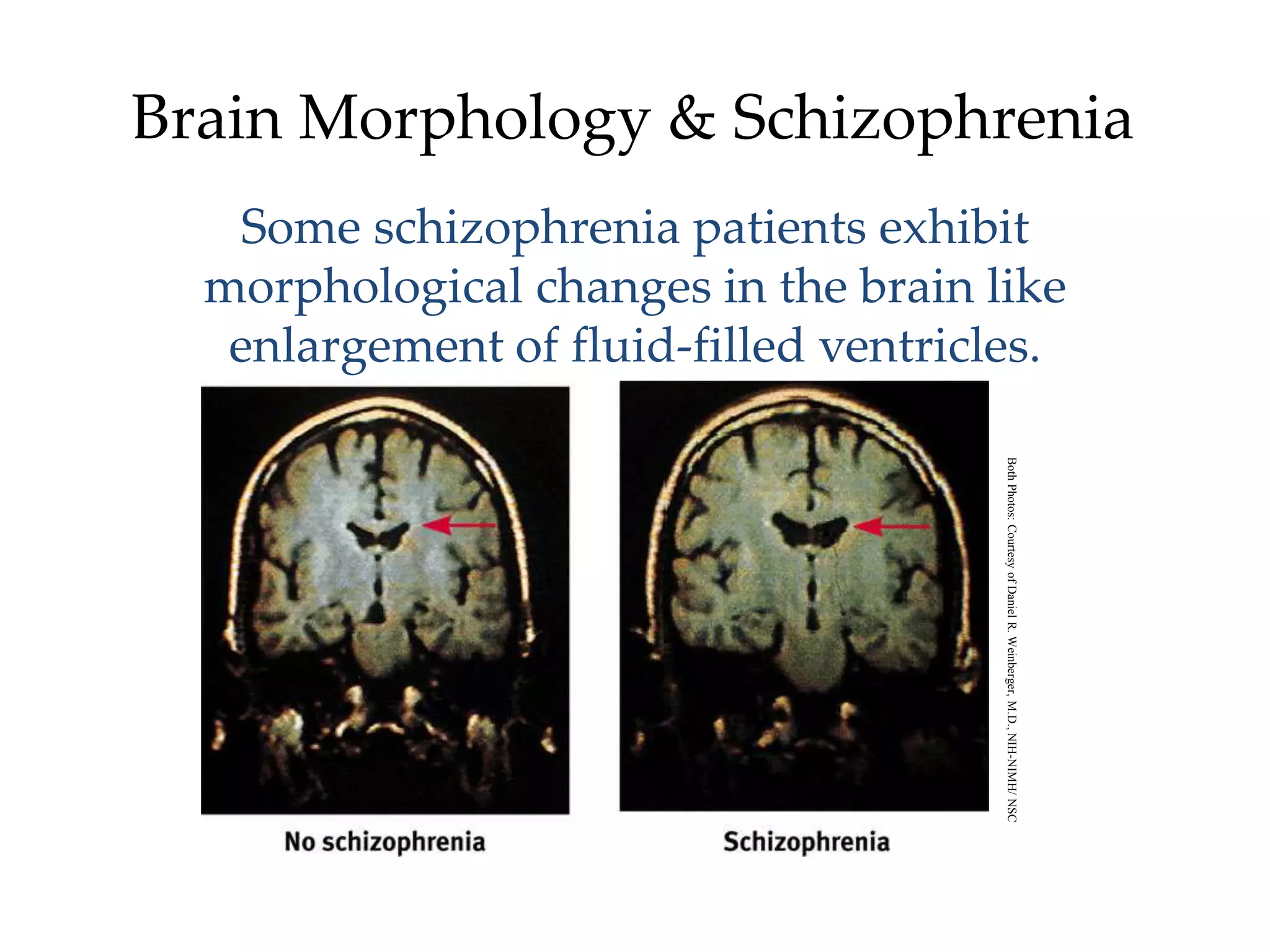
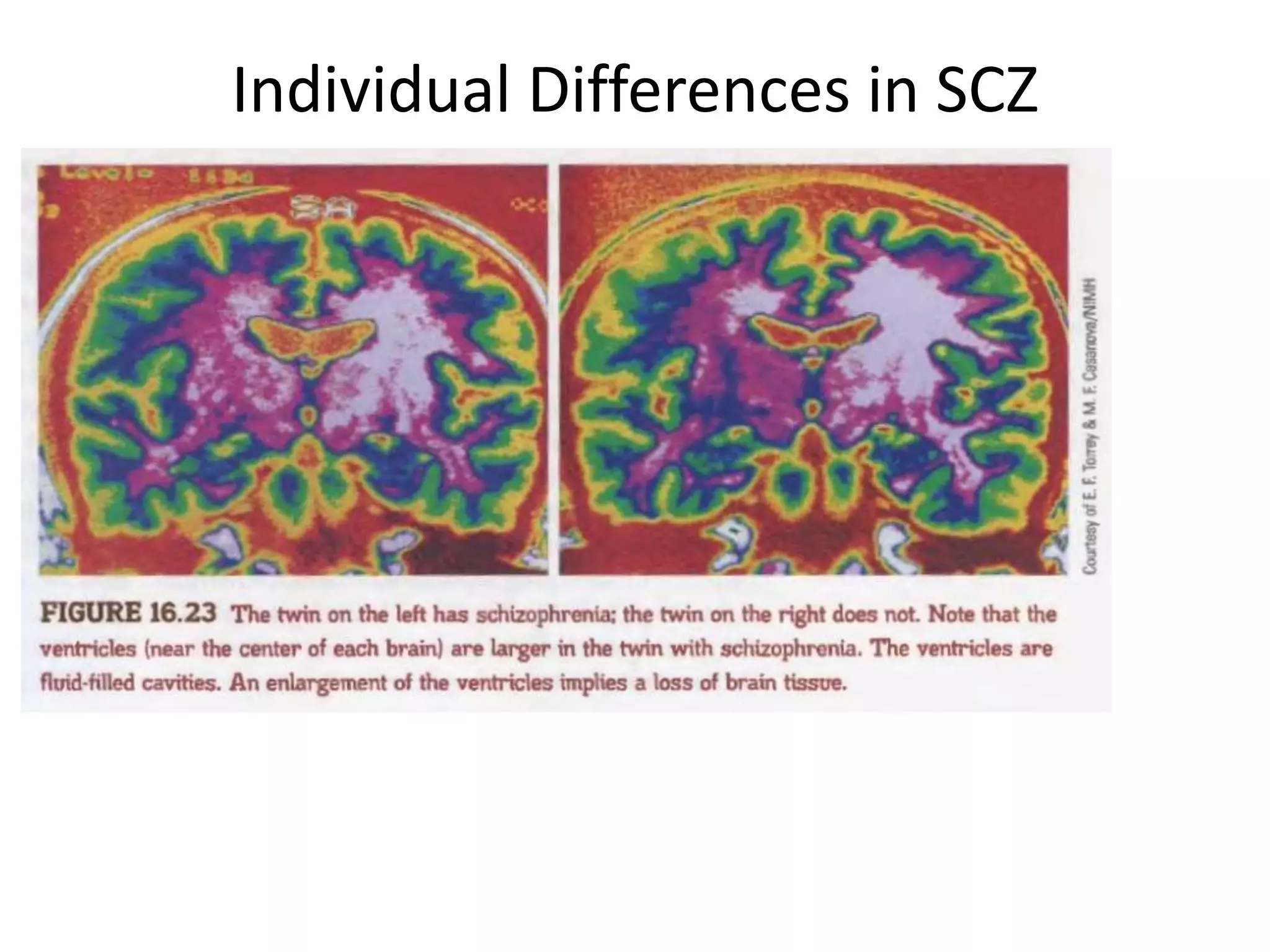
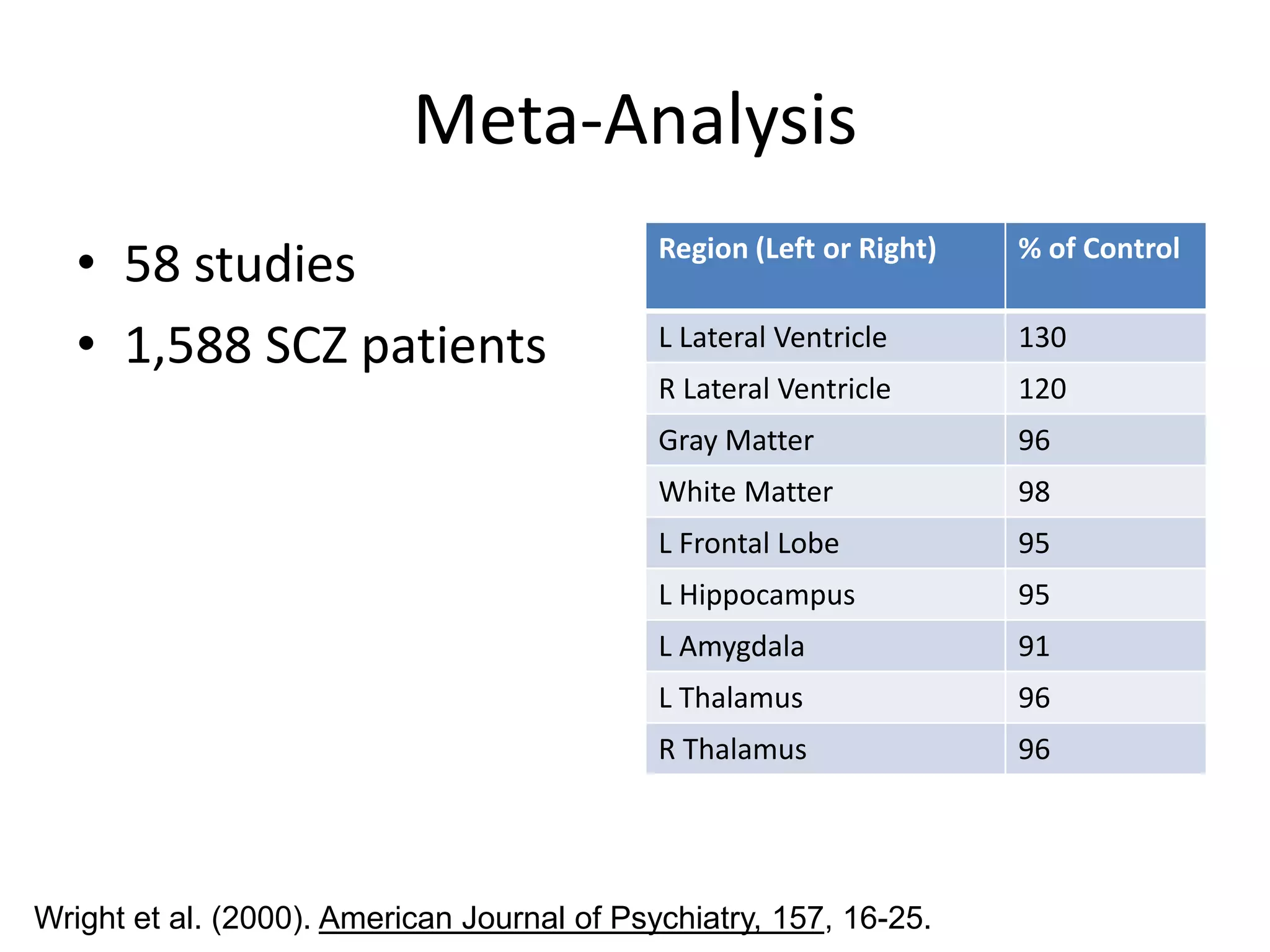
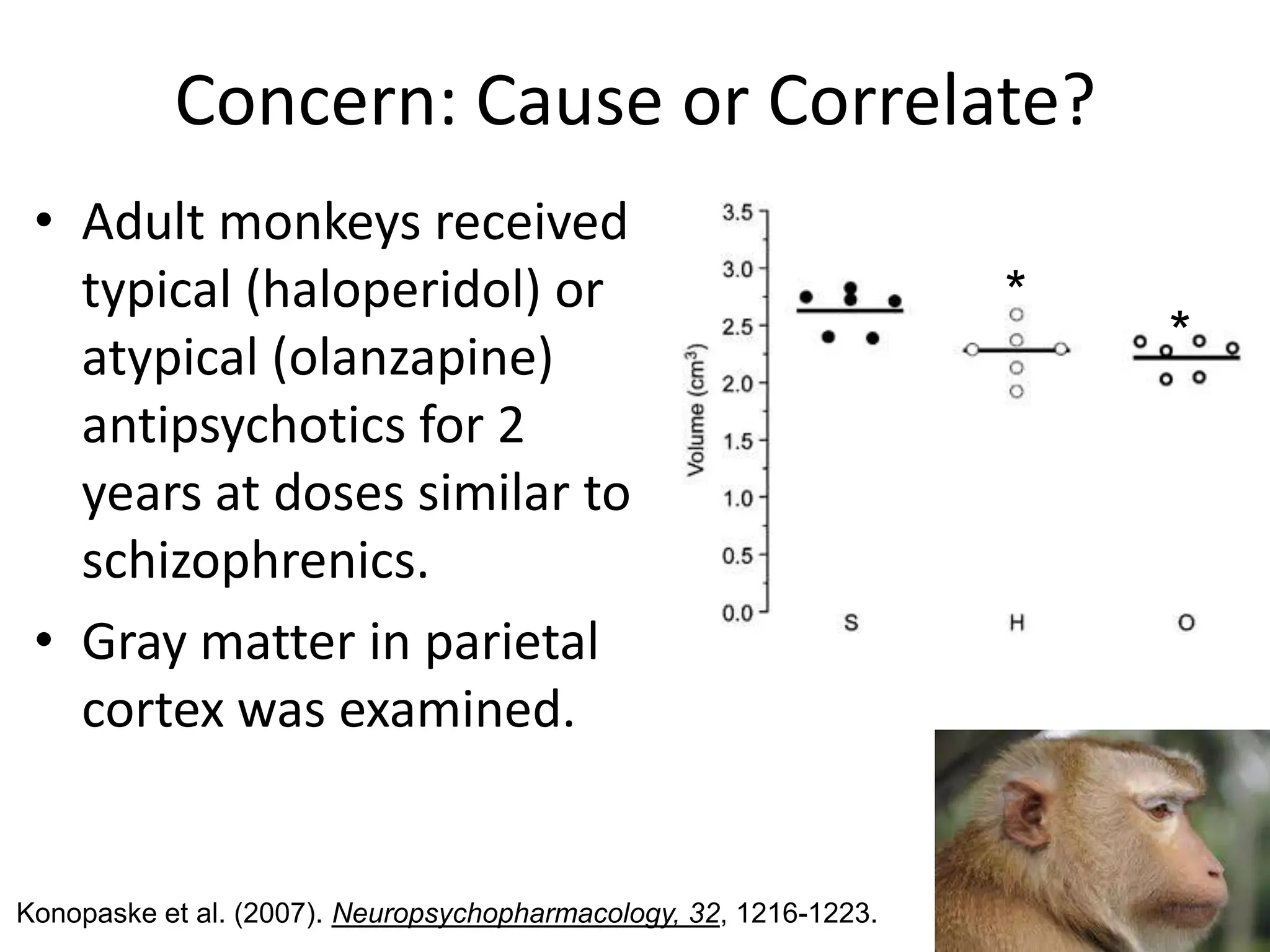
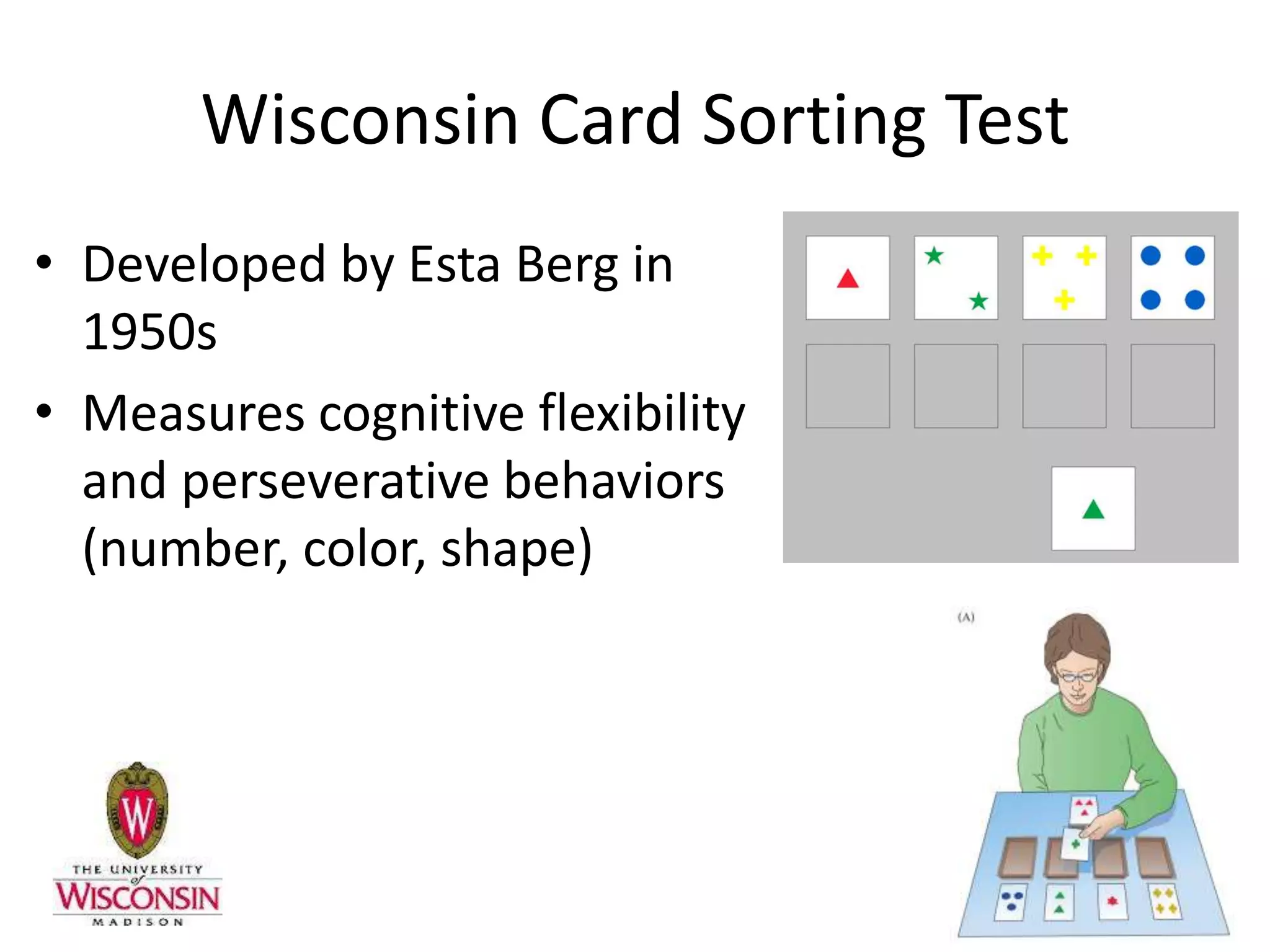
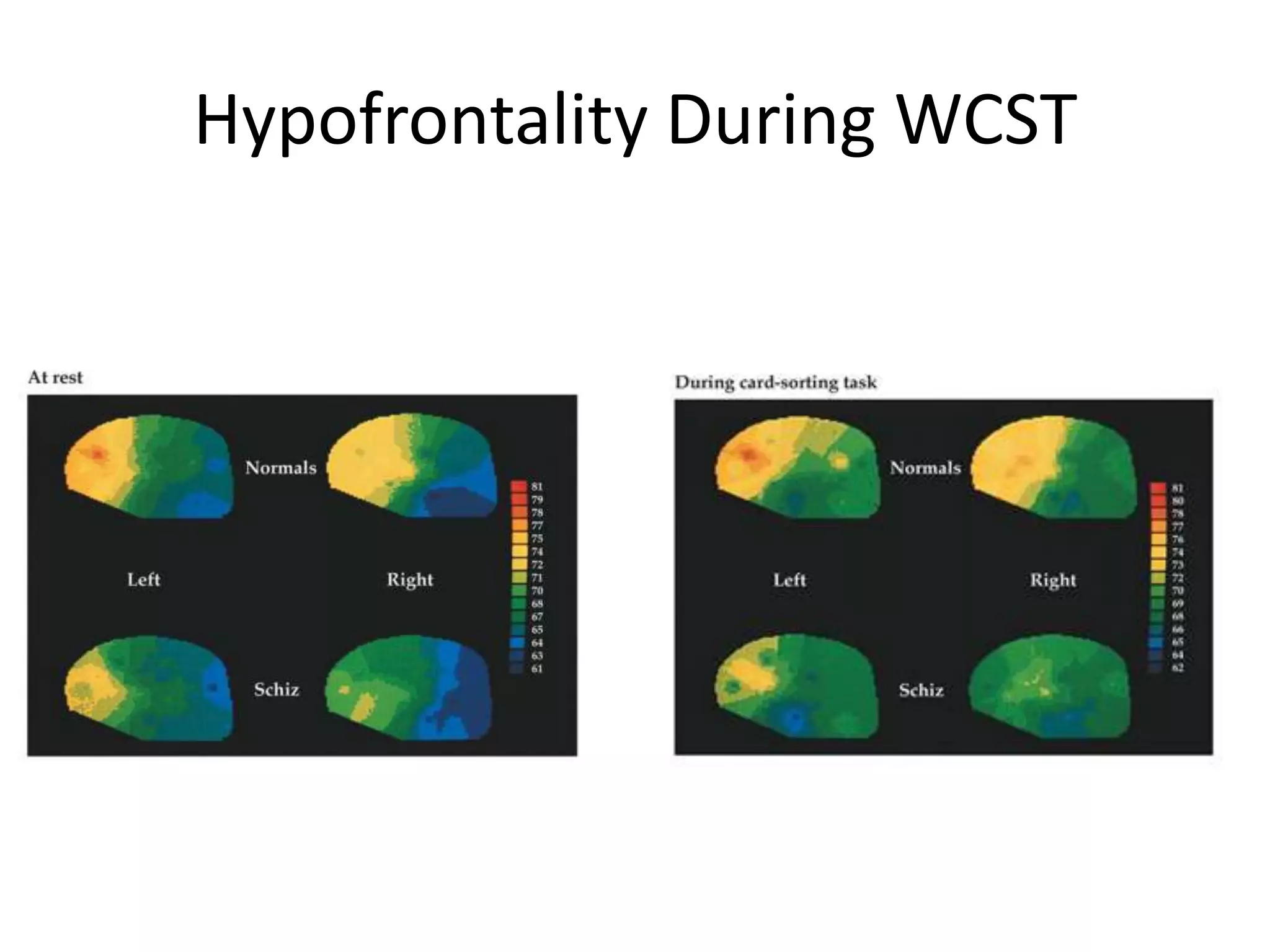
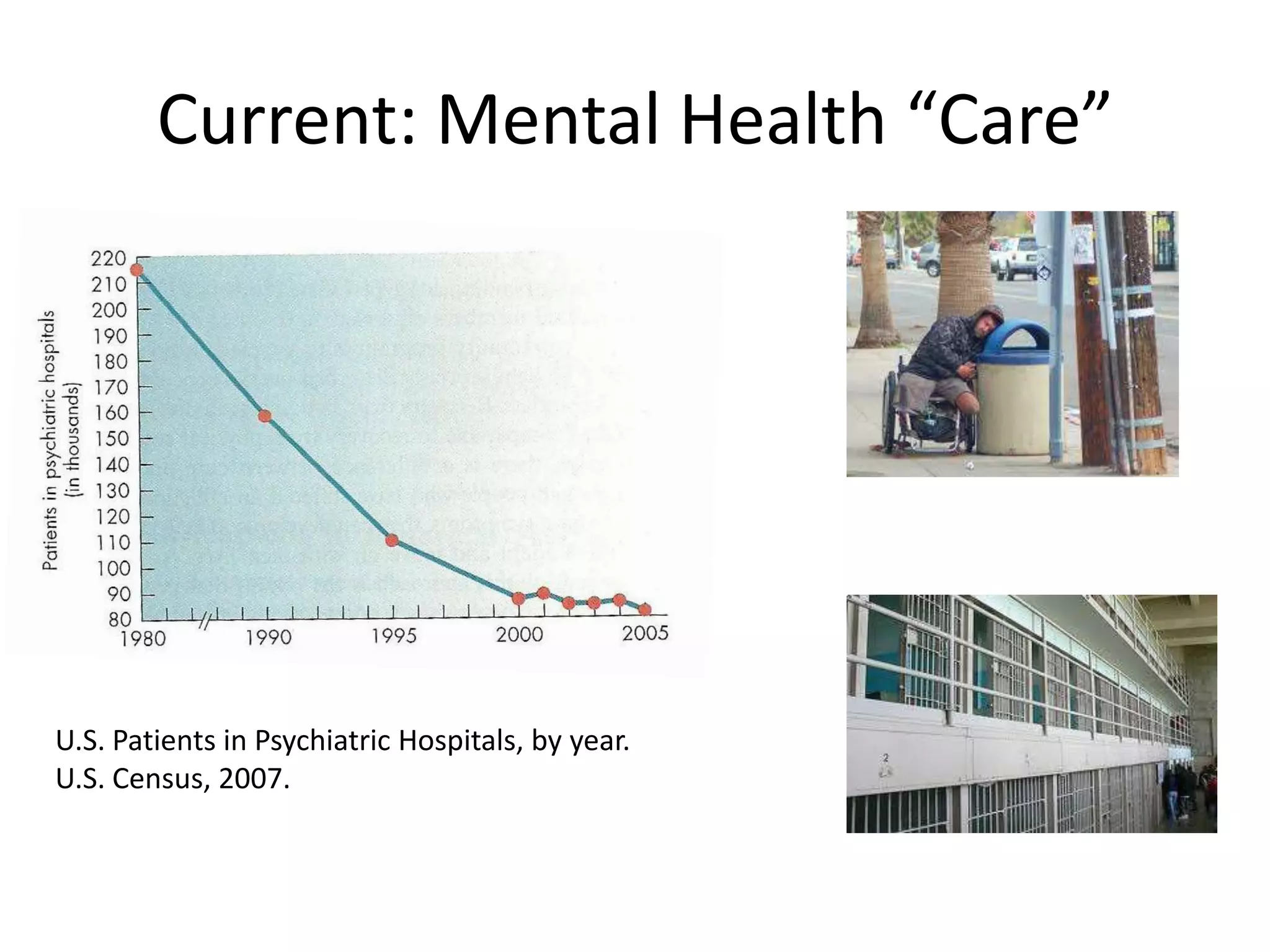
The document provides an overview of neurological and psychiatric disorders, contrasting the two fields through their historical foundations, diagnostic systems, and examples of various conditions. It discusses the evolution of classification systems like the ICD and DSM, highlights significant figures such as Philippe Pinel and Jean Martin Charcot, and addresses issues related to diagnosis and the genetic basis of disorders like schizophrenia. Additionally, it presents insights from neurobiology and animal models used in research to understand these conditions.