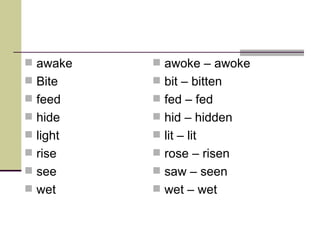
This document discusses various aspects of using past tense verbs in English, including:
- The past simple tense and how it is formed for regular and irregular verbs.
- The past continuous tense and how it is used to describe ongoing actions in the past.
- The past perfect simple tense and how it is used to refer to actions completed before other past actions.
- How the different past tenses are used together in narratives to clarify sequencing and timing of events.
It also covers using the past perfect continuous tense, expressions of habit in the past like "used to" and "would", and choosing the appropriate past tense in different contexts.