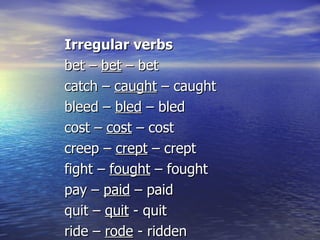
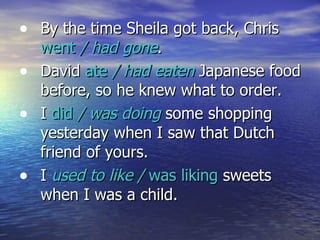
The document discusses various aspects of using tenses in the past, including:
- The past simple tense for completed actions
- The past continuous tense for ongoing actions in the past
- The past perfect tense for actions completed before another past action
- "Used to" for past habits or states
Examples are provided to illustrate the different uses of these tenses.