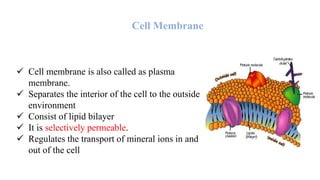
This document discusses passive transport mechanisms in cell membranes. It defines passive transport as the movement of molecules or ions across the cell membrane without requiring energy. There are three main types of passive transport: diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and osmosis. Diffusion is the random movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration. Facilitated diffusion uses carrier proteins to transport molecules across the membrane. Osmosis is the diffusion of water across the membrane, moving from an area of lower solute concentration to higher concentration.