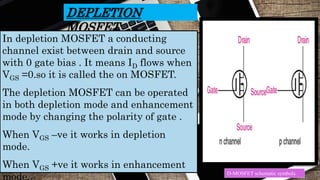
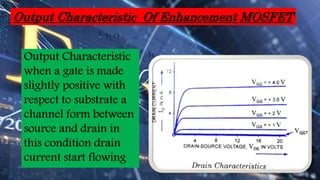
This document provides an overview of JFETs and MOSFETs. It discusses the history and invention of FETs, outlines the basic construction and working of JFETs and MOSFETs, and compares their drain and transfer characteristics. Key topics covered include n-channel and p-channel JFET/MOSFET operation, depletion and enhancement MOSFETs, and how drain current varies based on gate-source voltage and drain-source voltage for each device. Applications of FETs and MOSFETs are also briefly mentioned.