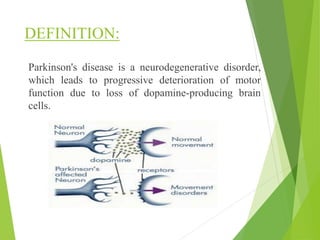
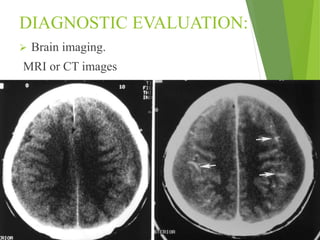
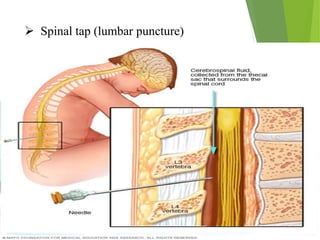
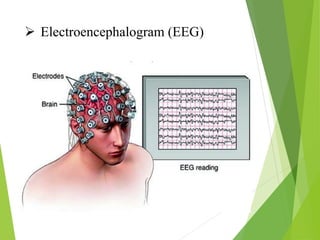
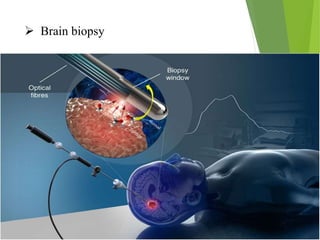
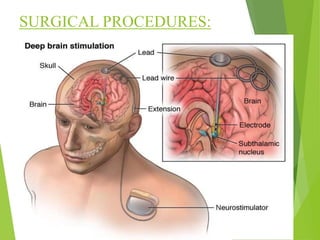
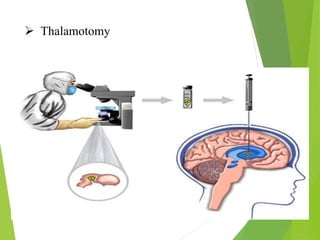
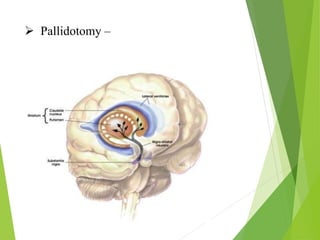
Parkinson's disease is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the progressive loss of dopamine-producing neurons, leading to motor function deterioration. Approximately 60,000 Americans are diagnosed each year, with symptoms including tremors, rigidity, and slowed movement. Diagnosis involves brain imaging, and while there is no known cause, certain risk factors exist, with management options ranging from medications to surgical procedures.