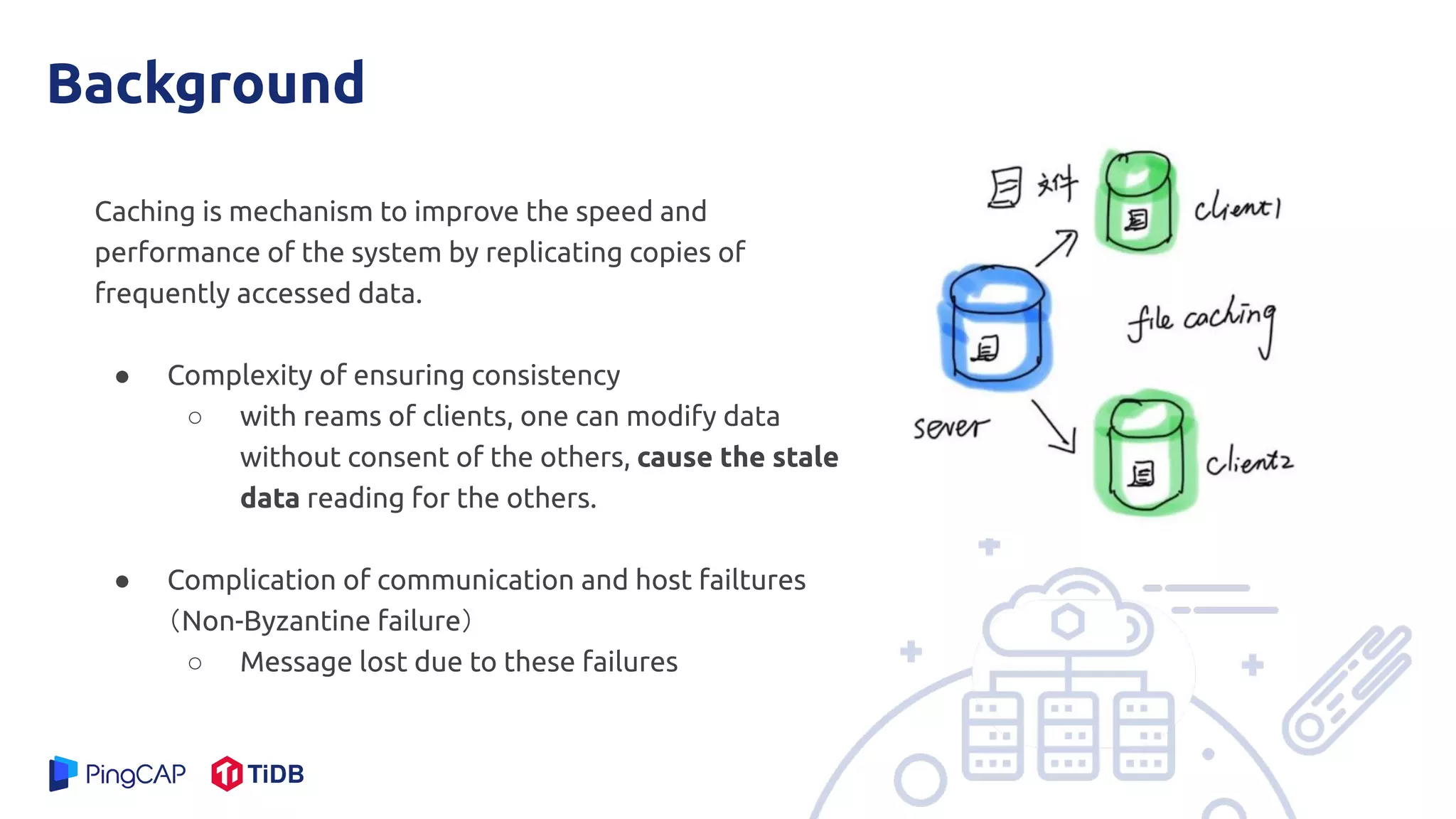
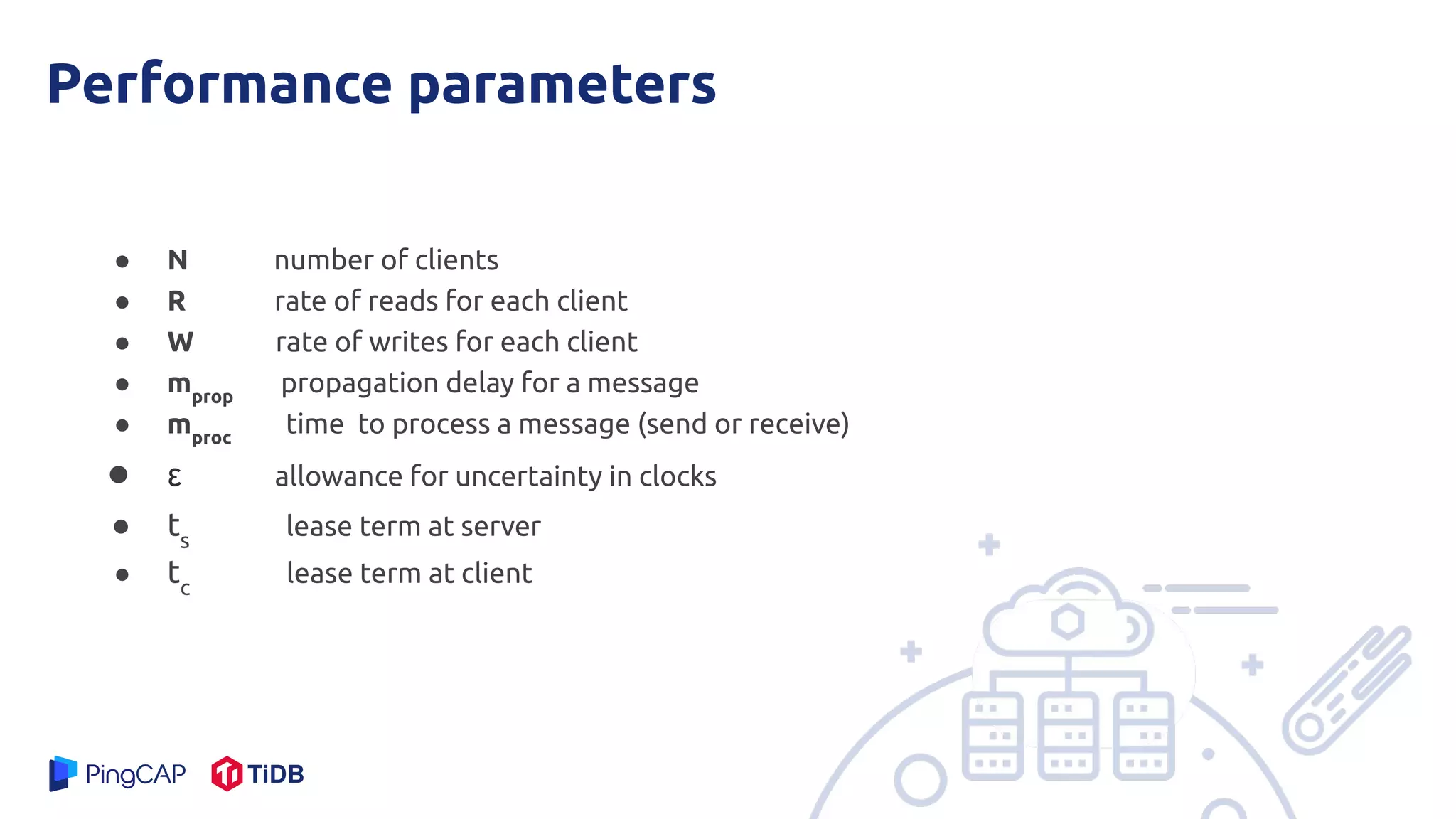
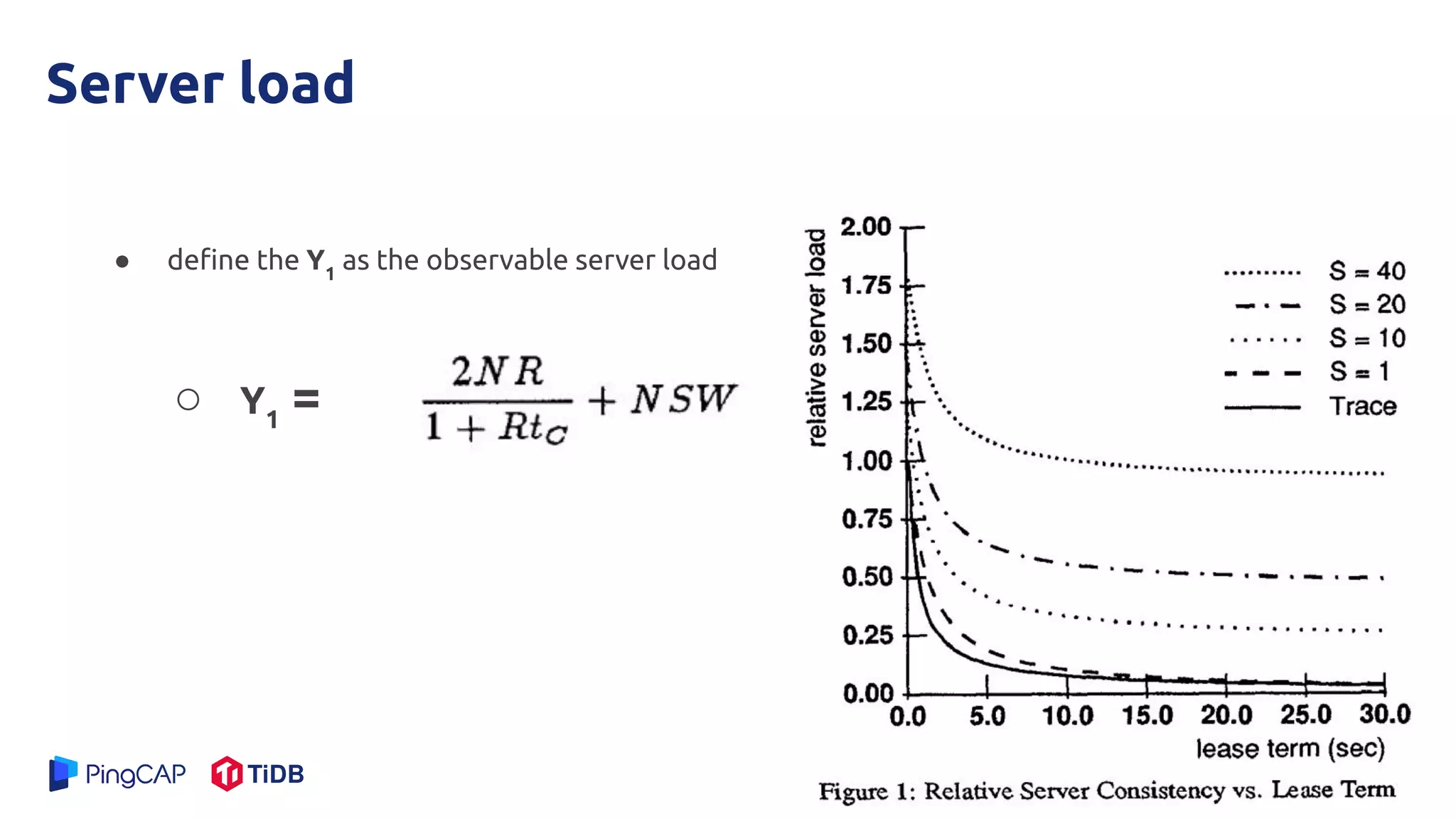
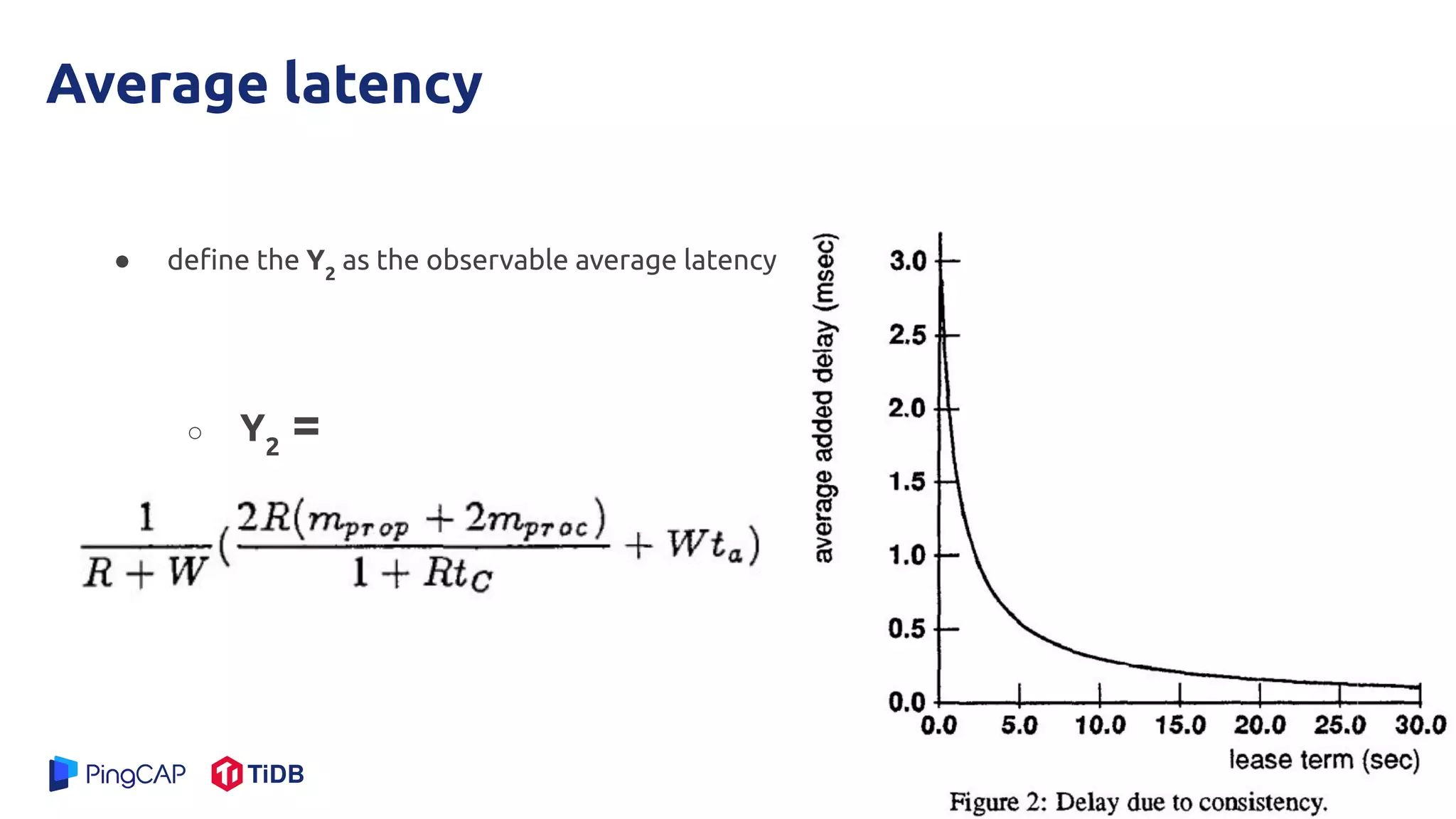
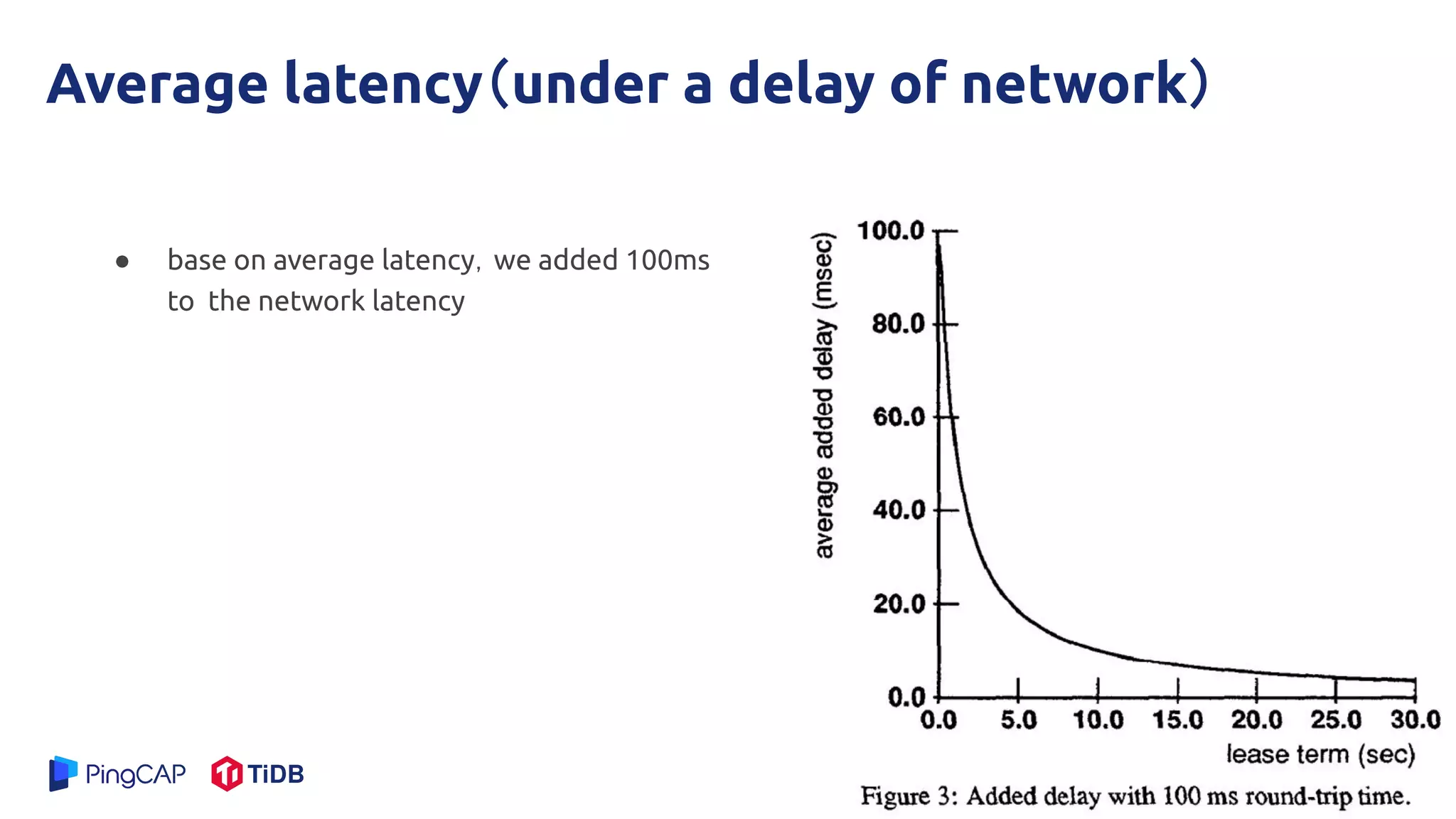
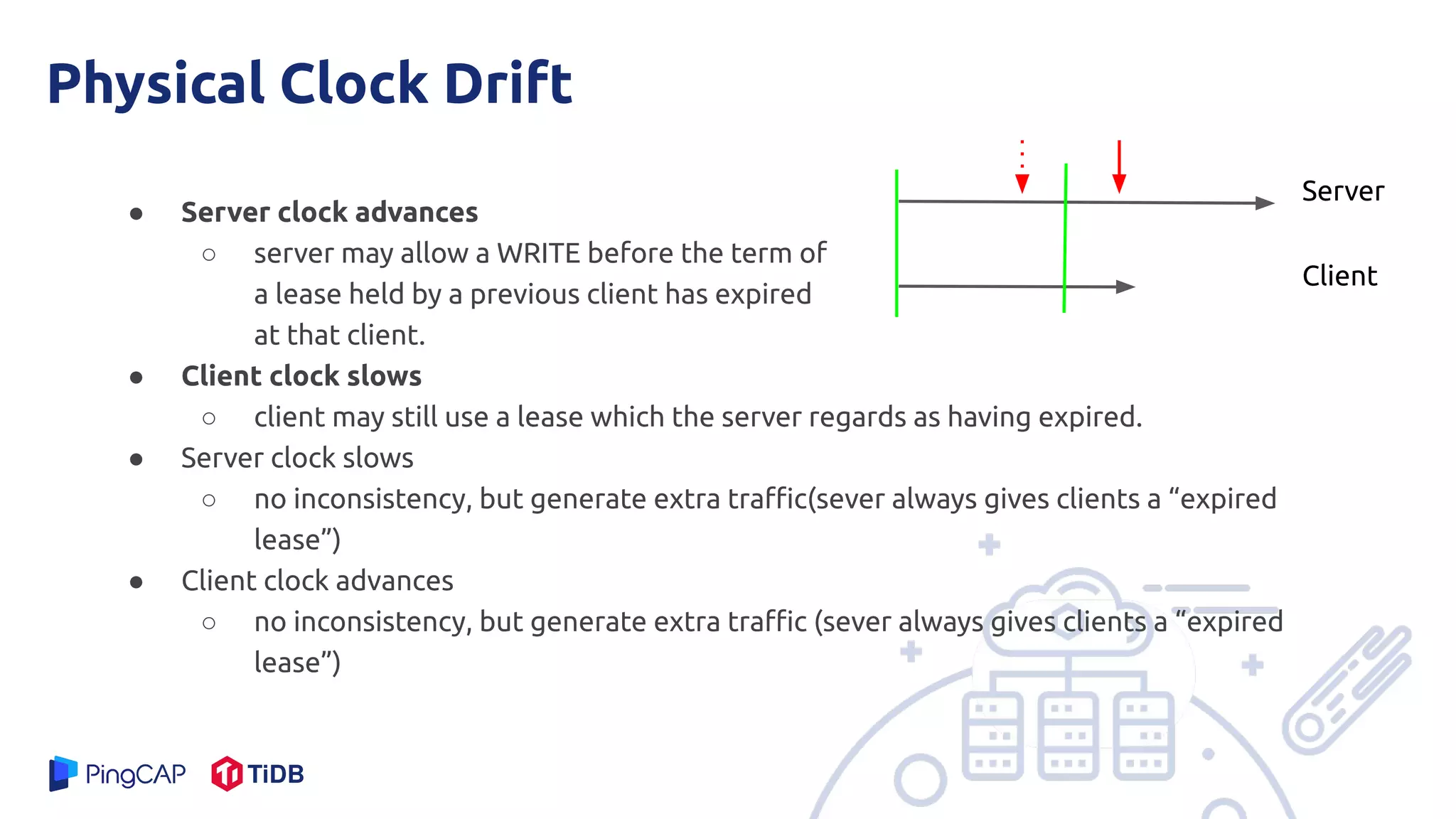
The document presents a mechanism called leases to improve fault tolerance and efficiency in distributed file systems by managing caching to reduce consistency overhead. It discusses the importance of lease terms, their impact on read and write operations, and strategies for optimizing lease management based on file characteristics. Ultimately, leases enhance the performance of large-scale systems by increasing the client-to-server ratio and minimizing server load.