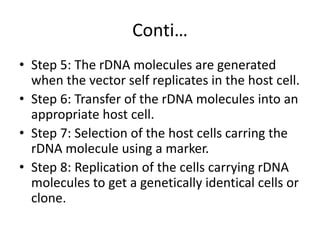
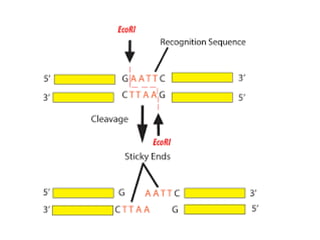
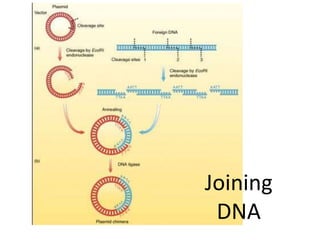
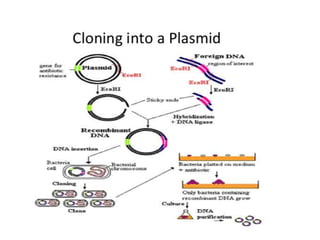
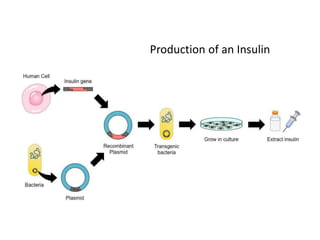
Recombinant DNA is DNA formed by combining DNA from multiple sources. It is created through molecular cloning techniques. The process involves isolating the desired DNA fragment, inserting it into a vector DNA, introducing the vector into a host cell, and allowing the host cell to replicate, generating multiple copies of the recombinant DNA. Examples of applications include producing insulin by introducing the human insulin gene into bacteria, gene mapping, disease research, and gene therapy.