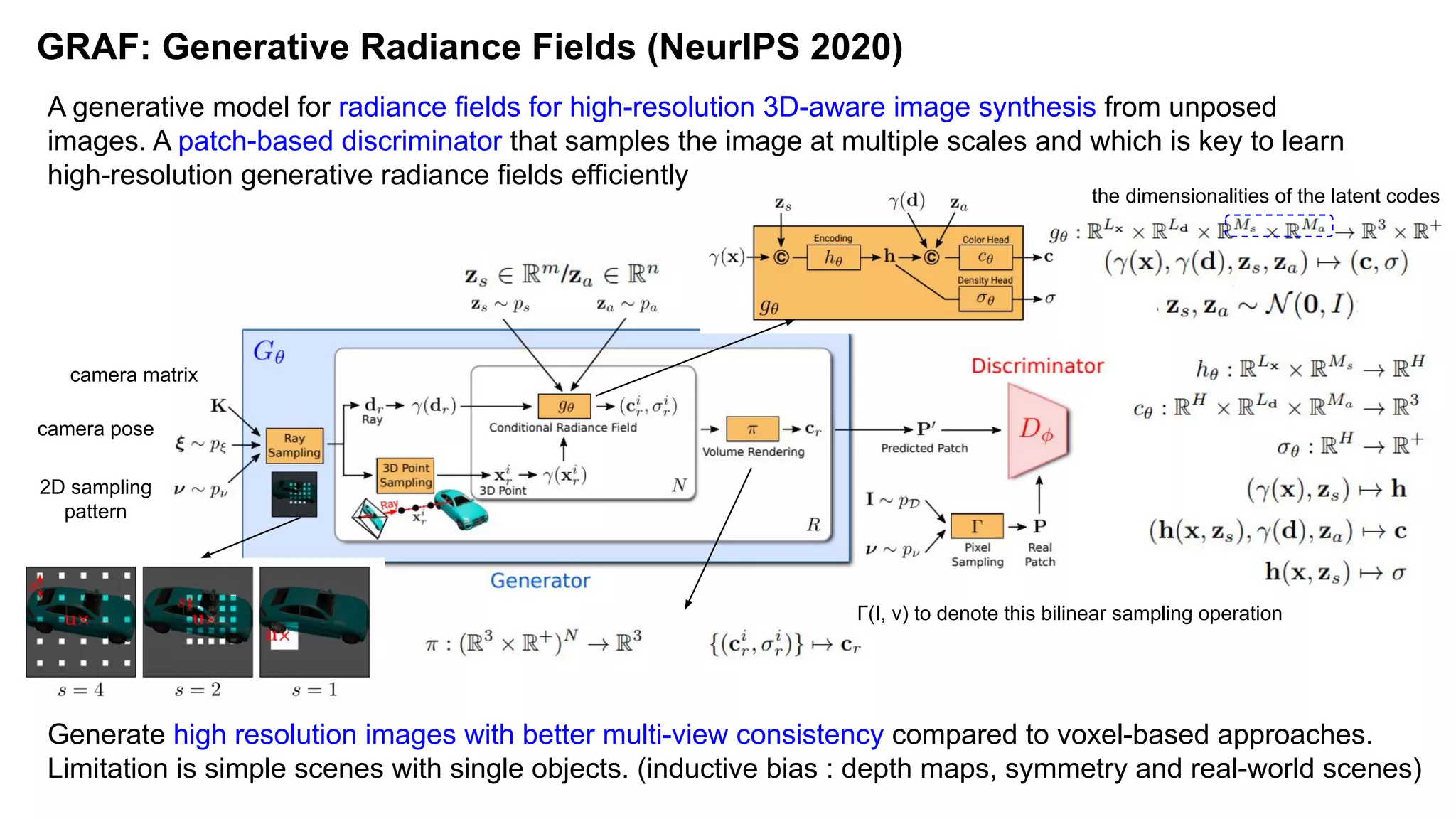
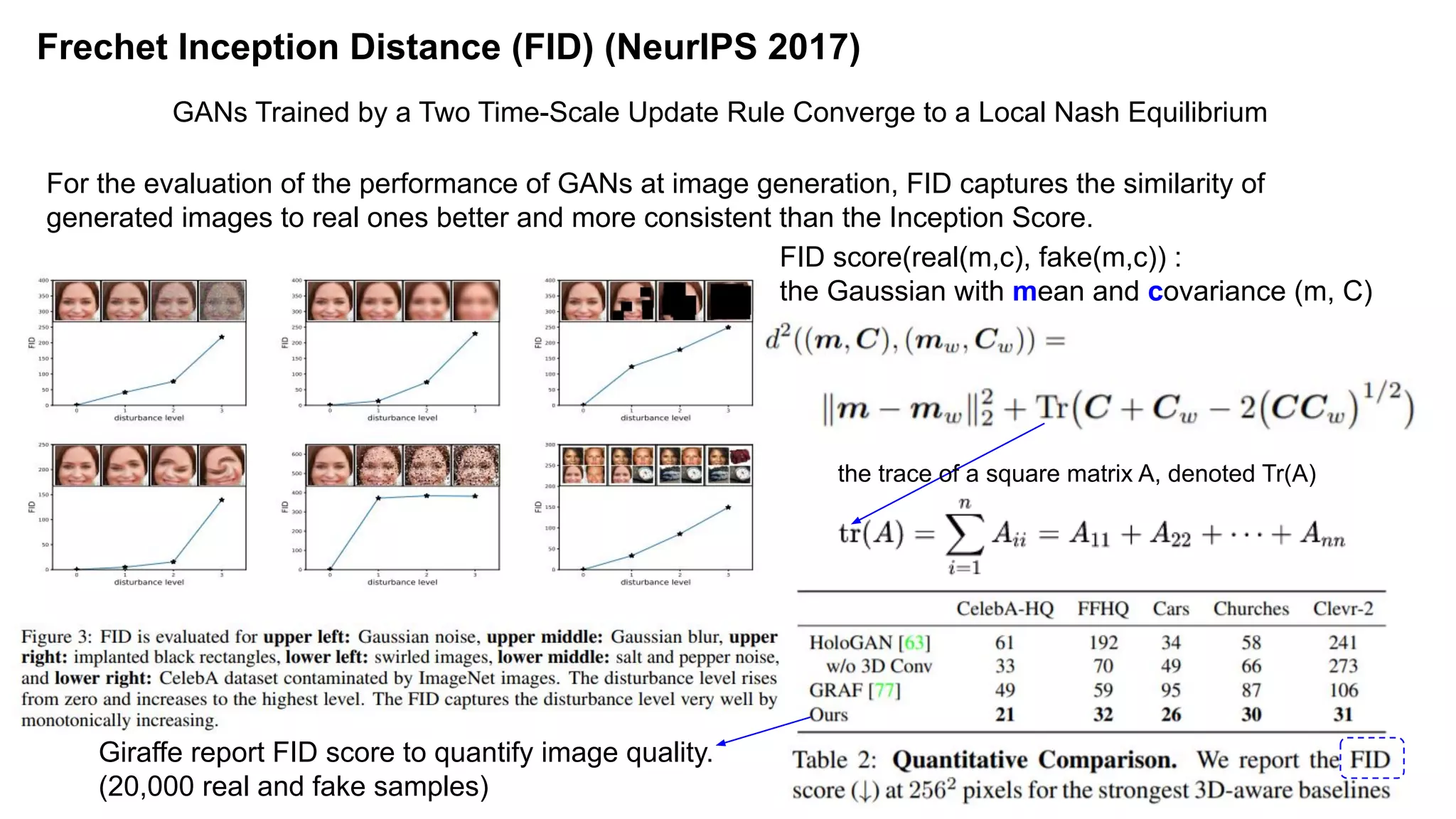
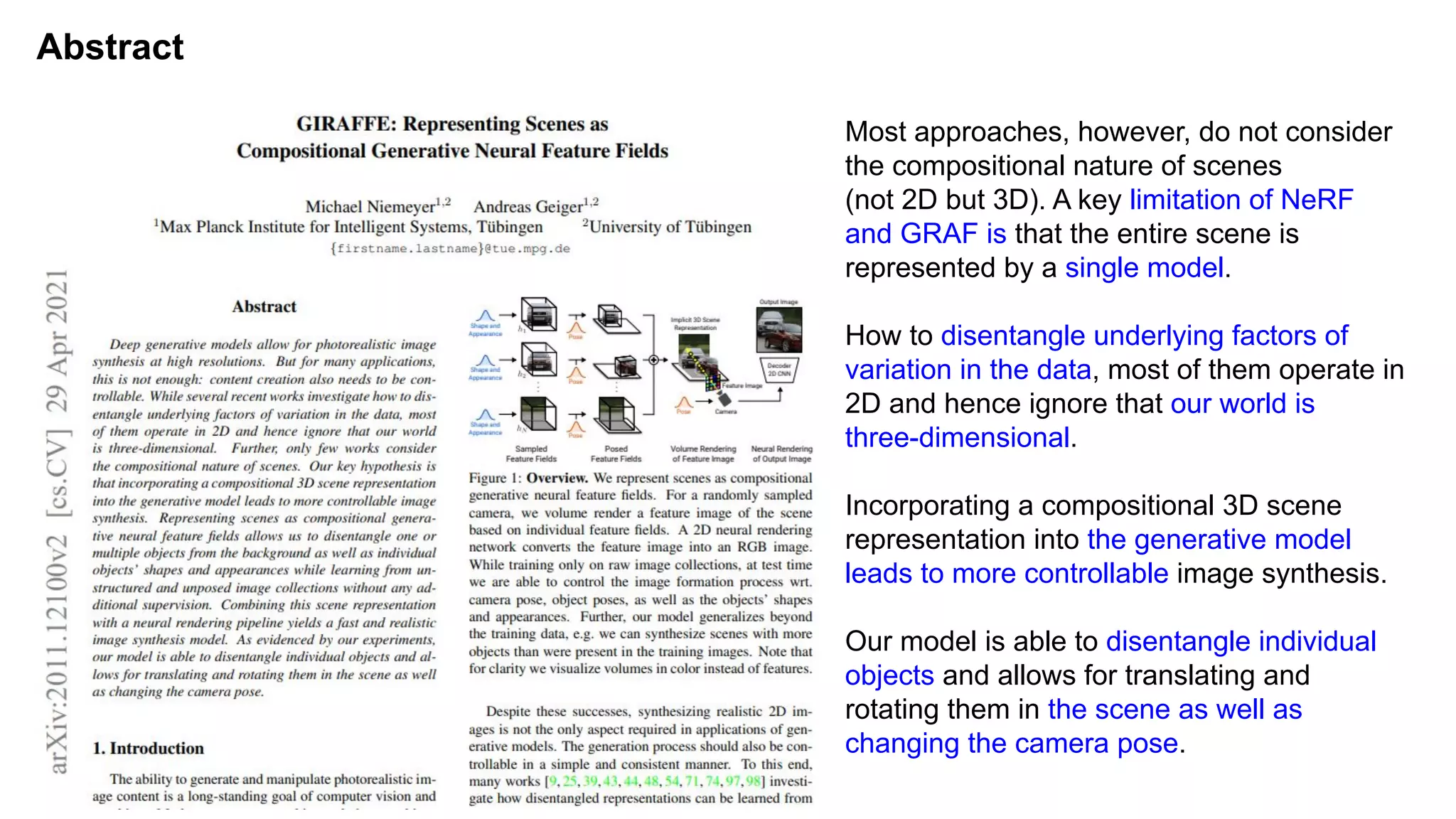
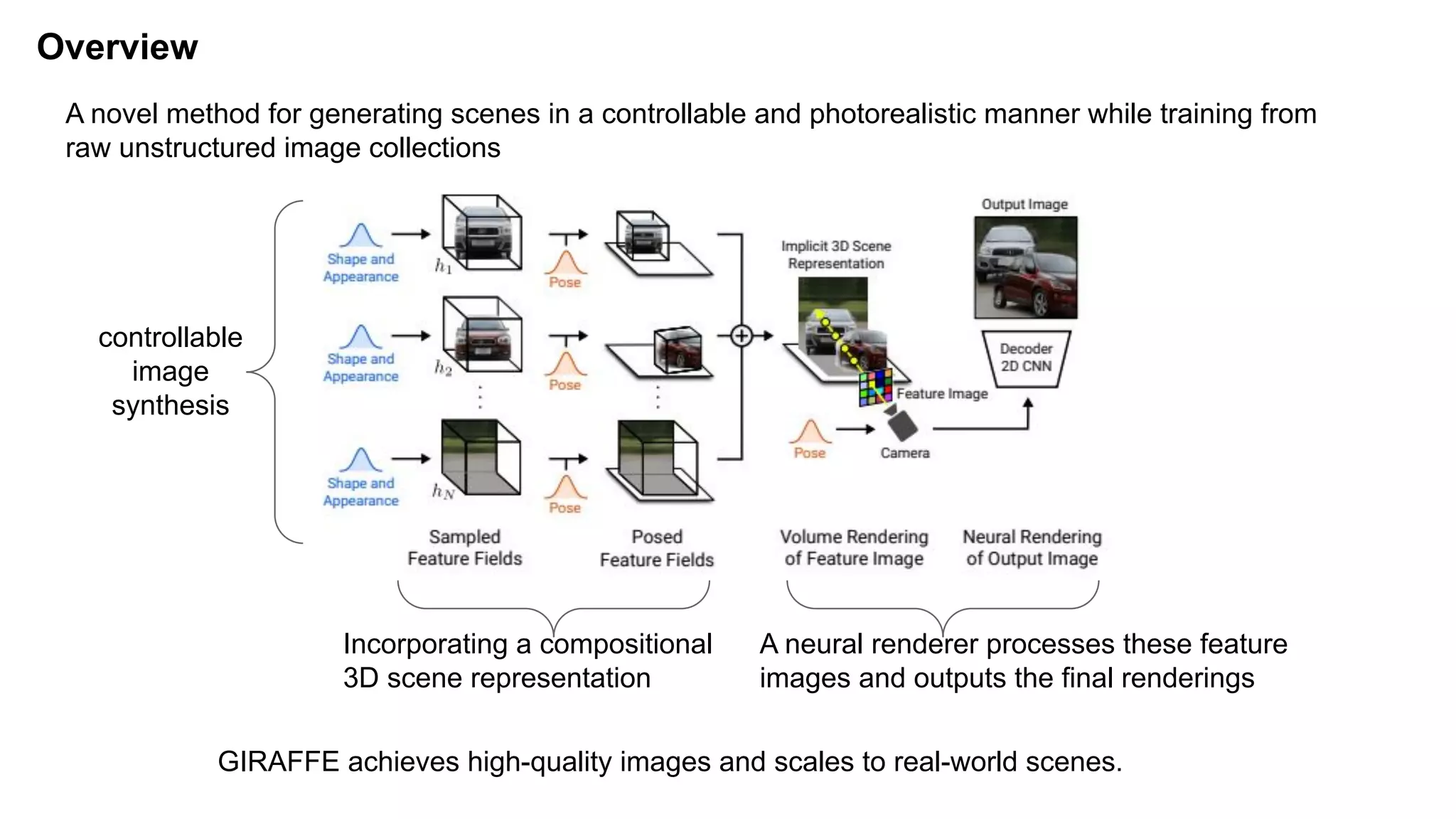
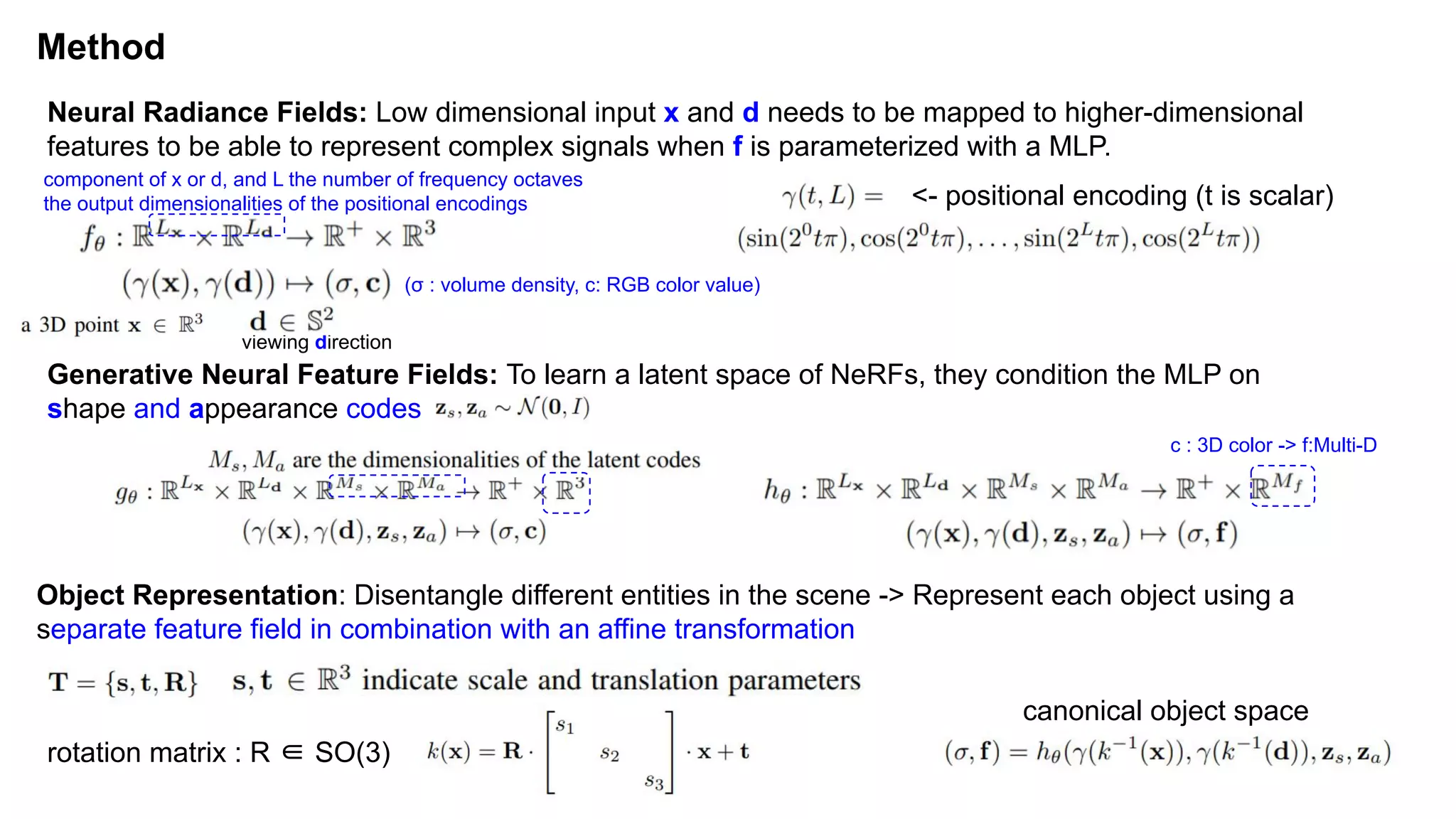
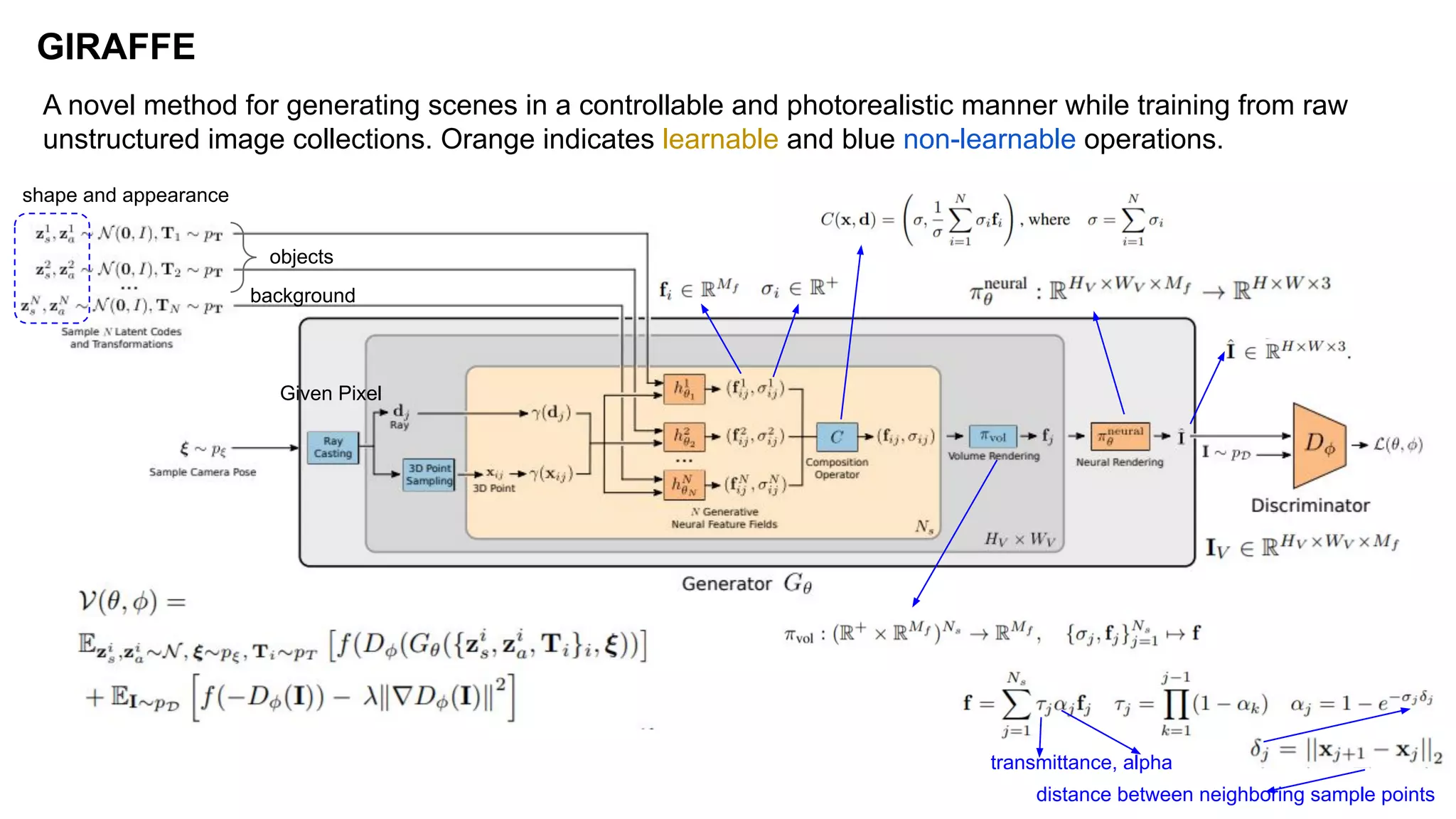
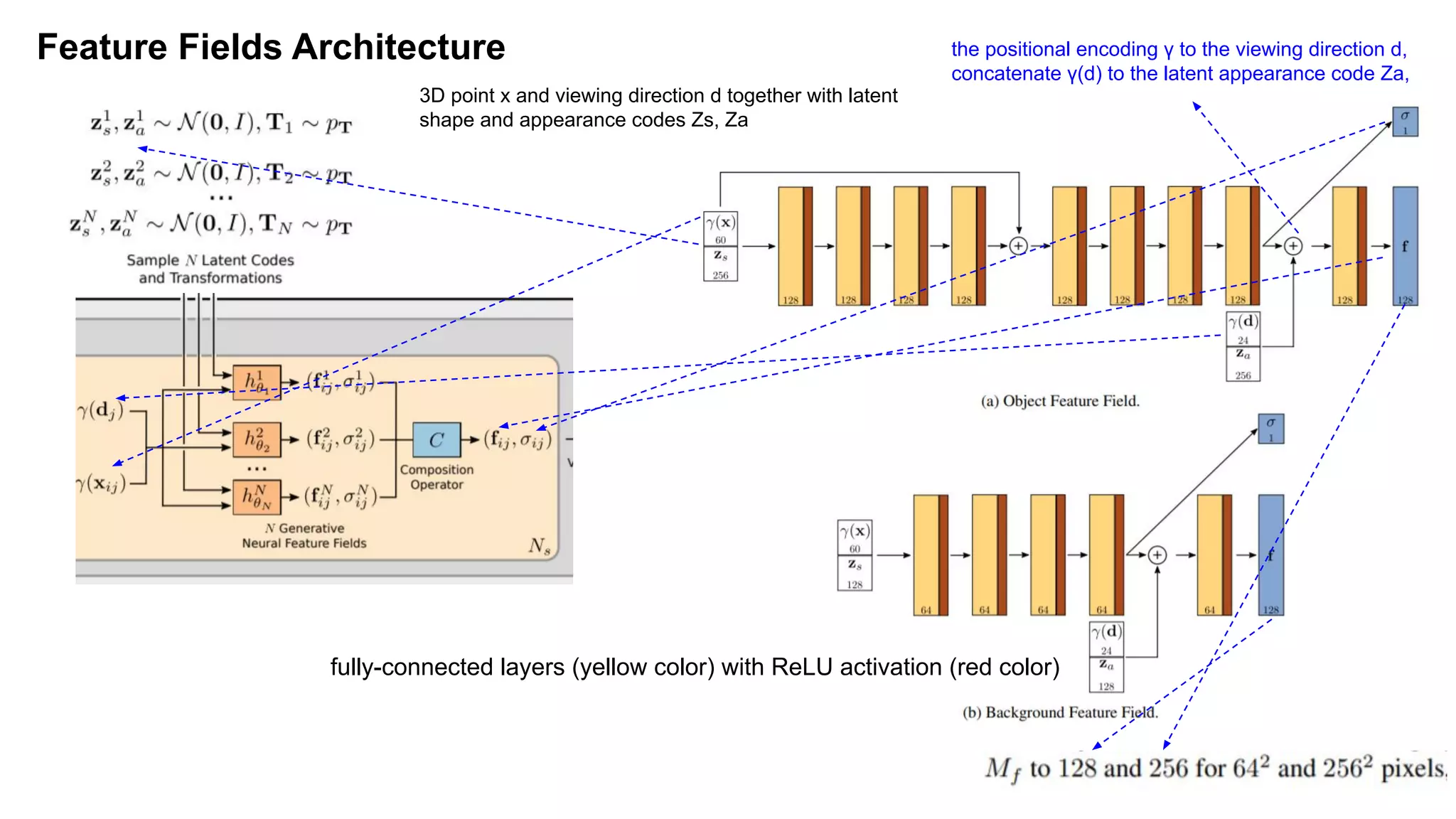
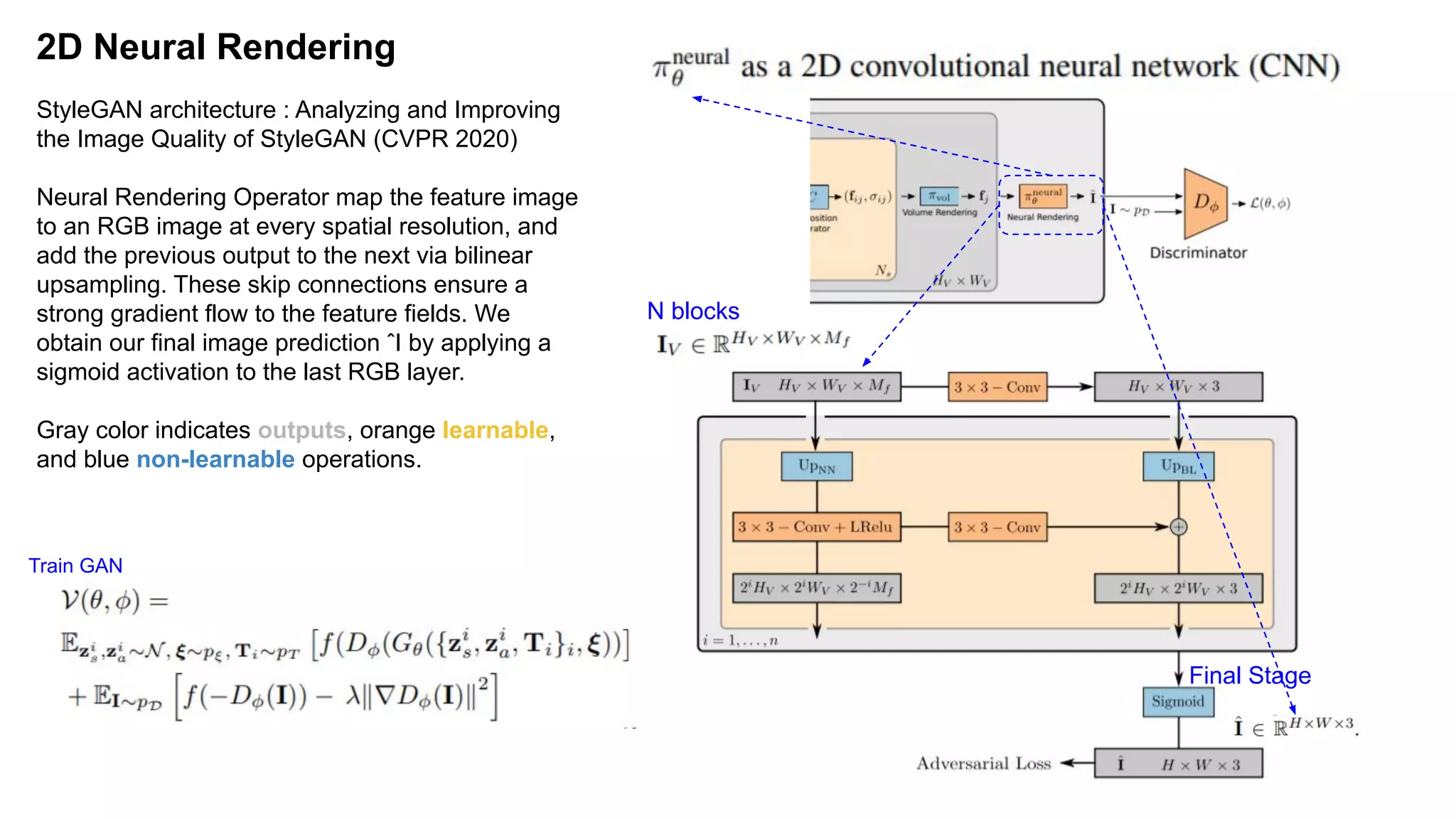
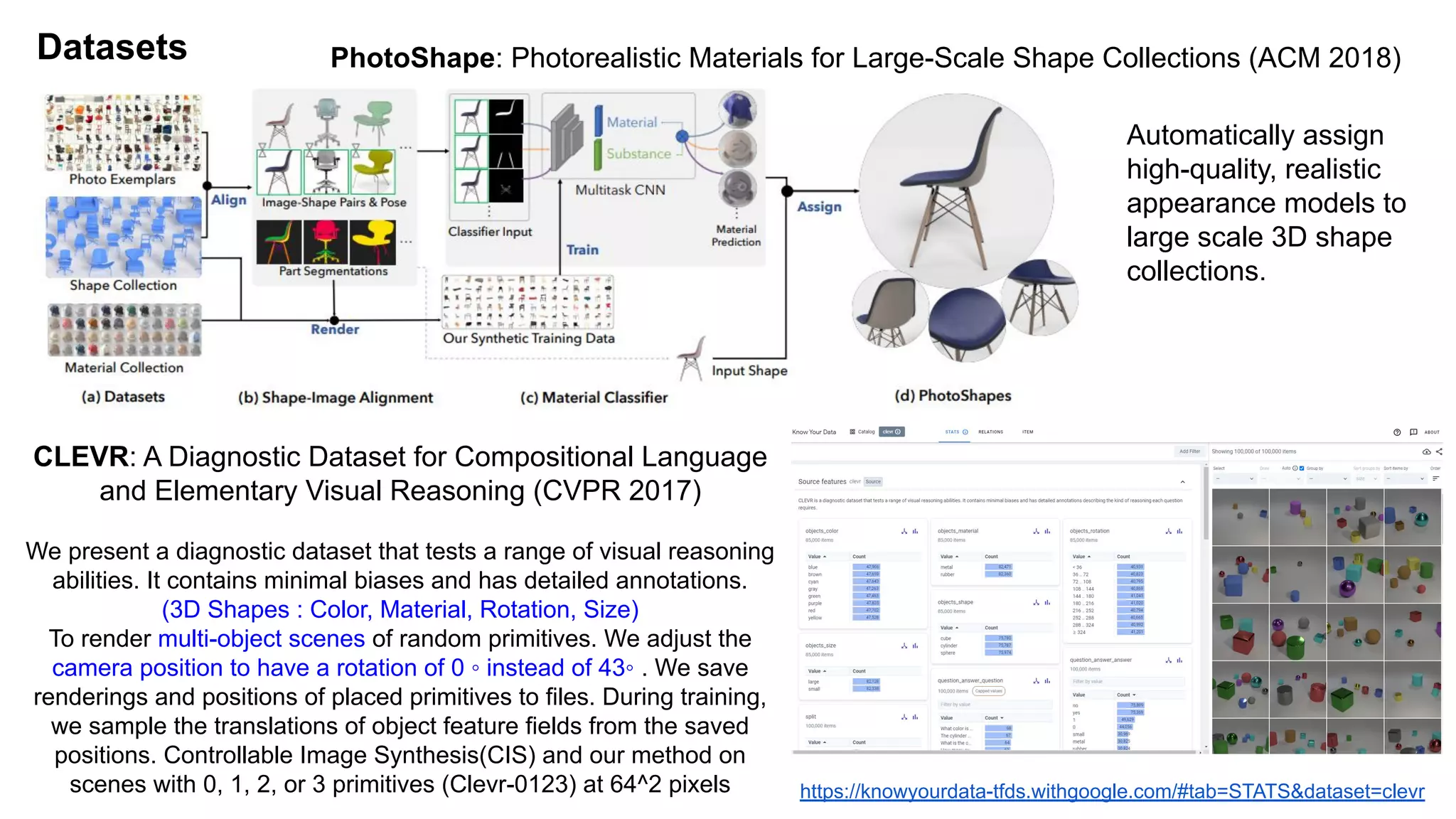
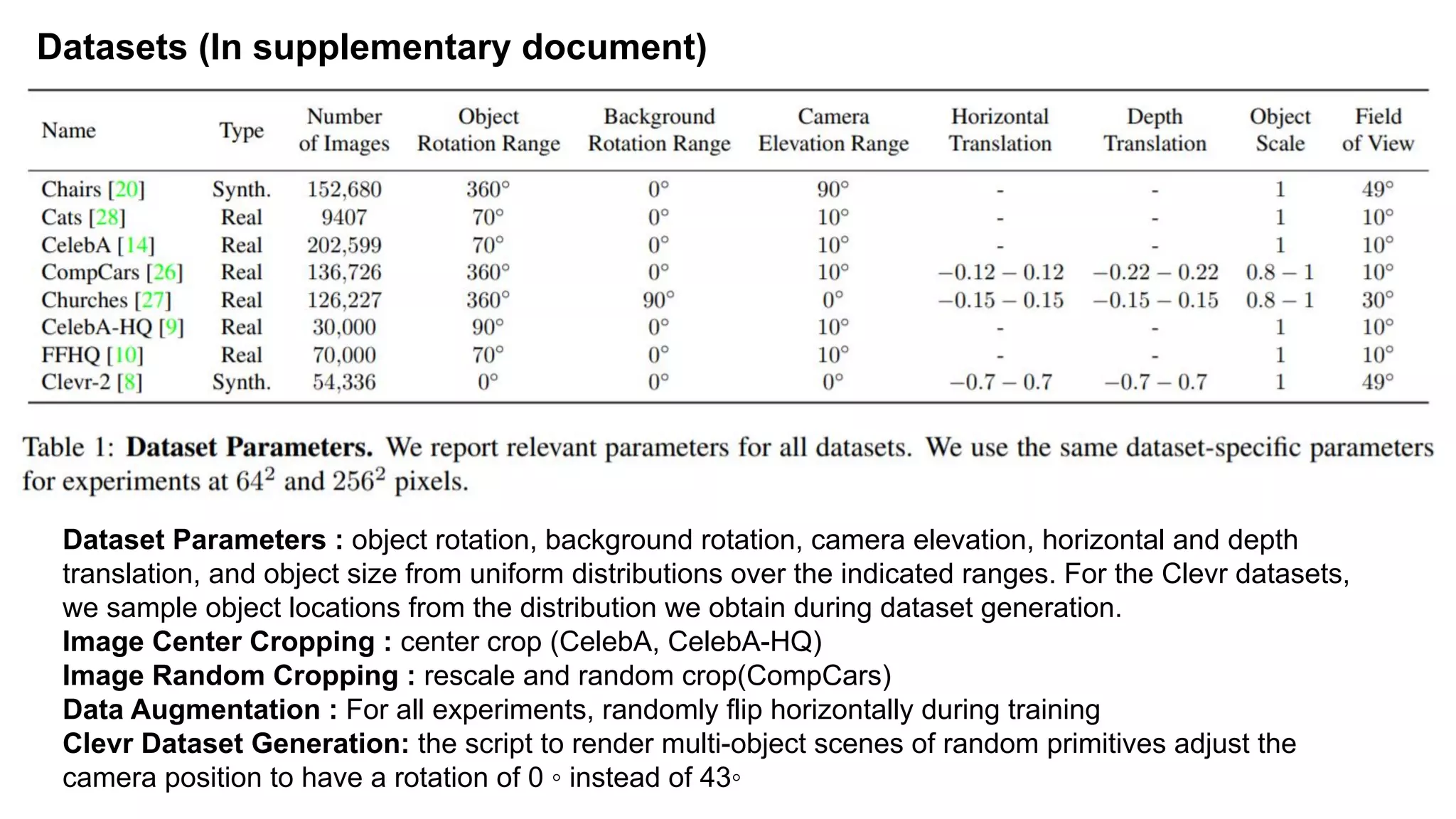
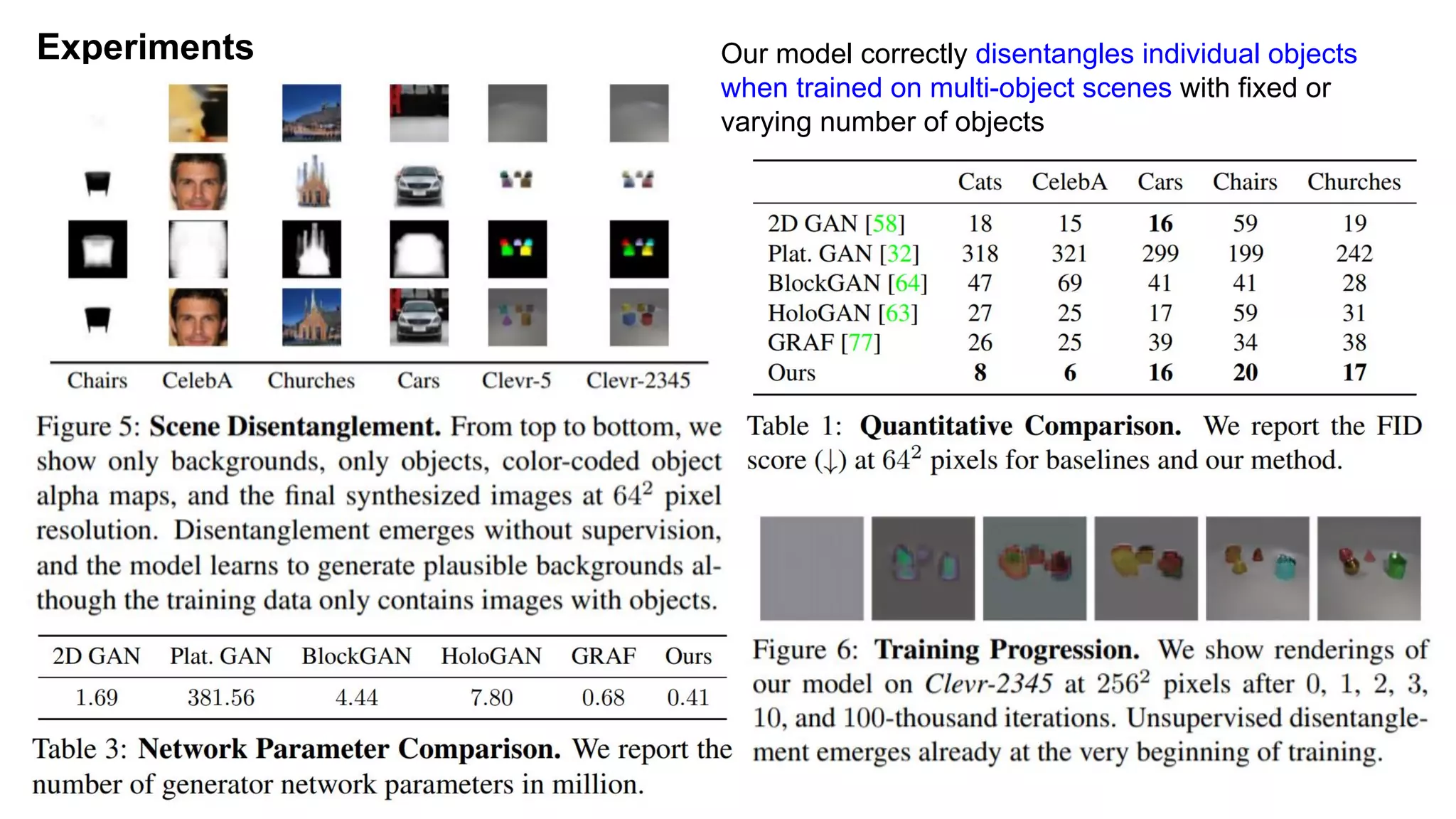
The document discusses 'Giraffe', a novel method for controllable image synthesis that represents 3D scenes using compositional generative neural feature fields, winning the CVPR 2021 Best Paper Award. It addresses limitations of existing models such as NeRF and GRAF by allowing for the disentanglement of individual objects and their attributes in 3D space, thereby enhancing image generation from unstructured data. The approach successfully combines various techniques, allowing for better multi-view consistency and high-quality renderings in complex scenes.

![NeRF : Neural Radiance Fields (ECCV 2020 - Best Paper Honorable Mention)
Input is a single continuous 5D coordinate (spatial
location (x, y, z) and viewing direction (θ, φ)) and
whose output is the volume density and
view-dependent emitted radiance at that spatial
location
FΘ : (x, d) → (c, σ) and optimize its
weights Θ to map from each input 5D
coordinate to its corresponding
volume density and directional emitted
color
Positional encoding : γ(·) is applied separately to each of the three coordinate values in x (which are
normalized to lie in [−1, 1]) and to the three components of the Cartesian viewing direction unit vector d
(which by construction lie in [−1, 1]). In our experiments, we set L = 10 for γ(x) and L = 4 for γ(d).
higher dimensional space to enable our MLP to more easily approximate a higher frequency function](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/papergirafferepresentingscenesascompositionalgenerativeneuralfeaturefields-210823043723/75/Paper-GIRAFFE-Representing-Scenes-as-Compositional-Generative-Neural-Feature-Fields-3-2048.jpg)