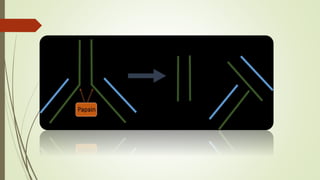
Papain, a cysteine protease enzyme from papaya, has a molecular weight of 23,406 daltons and consists of 212 amino acids. Its primary functions include breaking down tough meat fibers, aiding in cell dissociation for culture preparations, and it's used in dental applications. It is produced by extracting latex from unripe papaya fruits, which is further purified to obtain the active enzyme.