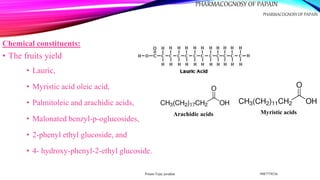
Papain, derived from the latex of Carica papaya, is a proteolytic enzyme with various uses, including as a protein digestant and in the meat industry for tenderizing. It is chemically composed of 212 amino acids and is resistant to heat but inactivated by metal ions and oxidants. The latex must be dried promptly to maintain its activity, with careful collection and storage methods required to ensure quality.