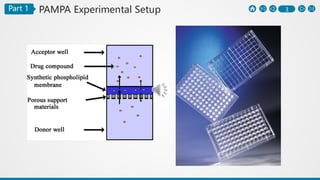
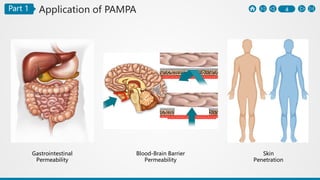
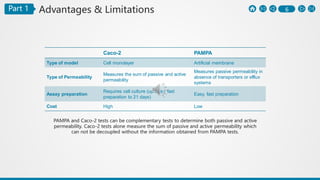
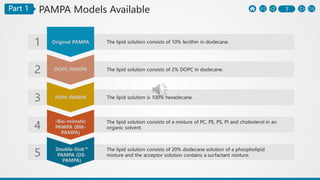
The PAMPA (Parallel Artificial Membrane Permeability Assay) is a method to assess permeability through an artificial membrane mimicking biological conditions, effective for studying gastrointestinal and blood-brain barrier permeability. Advantages include cost-effectiveness and automation, while limitations highlight differences from physiological membranes and lack of transport systems. The document outlines preparation methods, procedures, and comparisons with the Caco-2 assay for measuring different types of permeability.