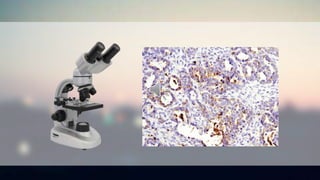
Immunohistochemistry uses antibodies to detect antigens in tissue samples in order to localize proteins and study biological processes. It has various applications including cancer prognosis, tumor identification, and research. The process involves deparaffinizing tissue, antigen retrieval, blocking, primary/secondary antibody incubation, signal development using enzymes, counterstaining, and mounting slides. Different methods like direct, indirect, PAP, ABC, and LSAB are used depending on the desired sensitivity and specificity. Careful antibody selection and protocol optimization are important for obtaining high quality results.