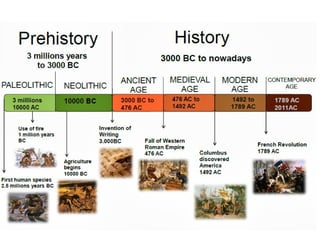
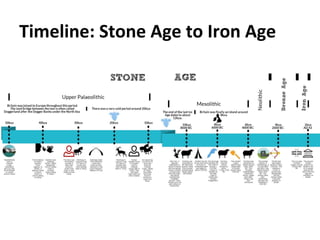
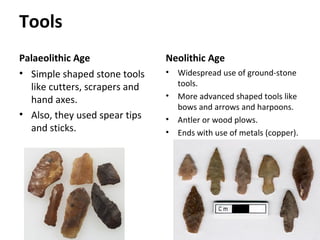
The document outlines the differences between the Paleolithic and Neolithic ages, highlighting changes in food sources, shelter, clothing, tools, culture, and society. During the Paleolithic era, people were nomadic hunters and gatherers, while the Neolithic era saw the advent of agriculture, permanent homes, and social stratification. Key advancements included the development of more sophisticated tools and the establishment of trade and population centers.