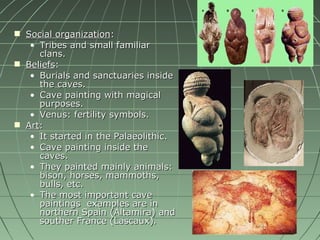
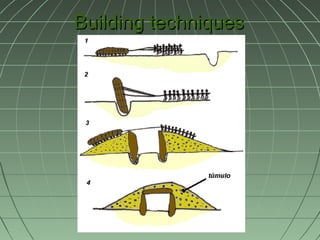
Human evolution began around 5 million years ago with early human ancestors like Australopithecus afarensis in Africa. Homo habilis who lived around 2 million years ago were the first to make complex tools. Homo sapiens emerged around 200,000 years ago in Africa and spread across the world. Prehistoric human development involved progressing through the Stone Ages including the Palaeolithic and Neolithic periods defined by their tool usage and subsistence strategies like hunting and gathering or agriculture. During the later Metal Ages of the Copper, Bronze and Iron Ages, humans transitioned to metal tools and the rise of early civilizations.