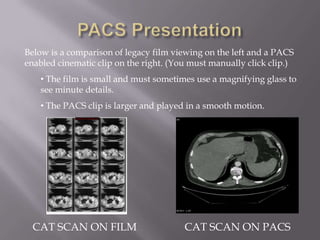
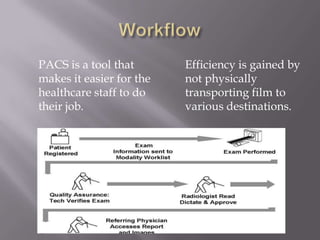
PACS (Picture Archive Communication System) is becoming a standard tool in radiology for storing and viewing digital medical images. It provides benefits like higher quality images, instant access to patient films from any location, and integration with digital medical records. PACS acquires images directly from medical equipment, stores them in a database, and allows viewing through workstations. It replaces physical film with a digital system for more efficient sharing of images between radiology staff and physicians.