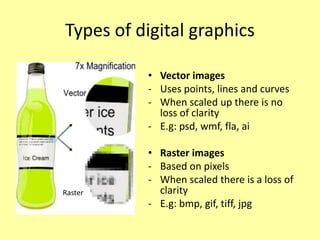
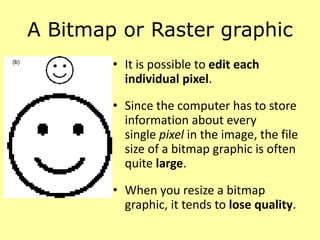
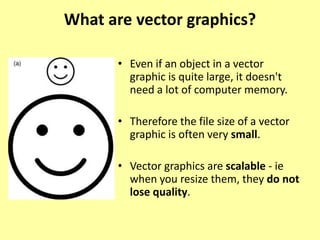
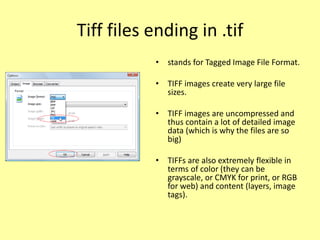
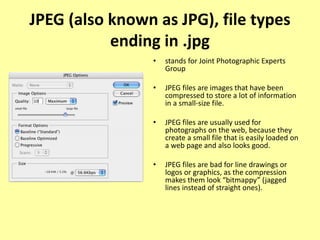
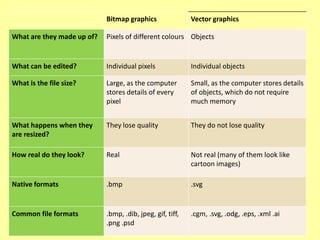
This document discusses different types of digital images including raster and vector images. Raster images are composed of pixels and lose clarity when scaled up, while vector images use points, lines and curves and maintain clarity when scaled. Common file formats for raster images include BMP, GIF, TIFF and JPG, which can be lossy and compress files by losing quality or lossless by maintaining quality. Vector files include AI, PSD and WMF and scale well without losing quality.