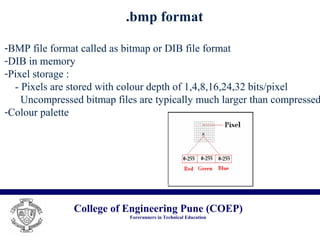
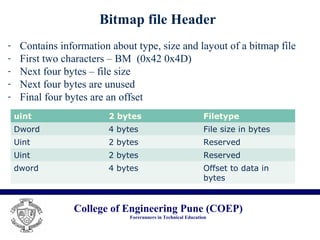
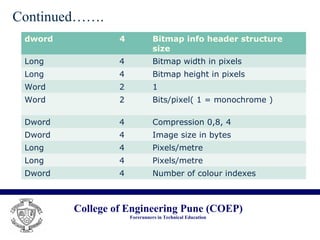
The document discusses the .bmp image file format. It describes the basic structure of a .bmp file, which includes a bitmap file header containing metadata like file type and size, a bitmap information header containing image width, height and color properties, an optional color table, and the pixel data stored from bottom to top in uncompressed form. It notes that while .bmp files have a large size, the format is simple, well-documented, and supports lossless compression. Common uses of the .bmp format include its simplicity and lack of patents.





![College of Engineering Pune (COEP)
Forerunners in Technical Education
References
[1] https://en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/Image_file_formats
[2] John Miano, "Compressed Image File Formats“, ISBN - 0-201-60443-4,1999
[3] R. Witrow, “ OpenGL Graphics through Applications”, Springer-verlag London
Limited, 2008](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminardvipmahesh121697010-170125102824/85/bmp-image-data-format-12-320.jpg)
