Divya Shree Nandini, a B.Sc. (Hons.) Mathematics student, presents an overview of oxygen, its properties, applications, and significance in various fields including medicine, industry, and biology. Oxygen, a highly reactive nonmetal, is essential for respiration, supports combustion, and plays a crucial role in forming organic compounds. The document also highlights its abundance in the universe and its importance in environmental and biological processes.







![BASIC PROPERTIES OF OXYGEN
Atomic Number: 8
Atomic Mass: 16
AtomicWeight: 15.9994
Melting Point: -219 degrees C
Boiling Point: -183 degrees C
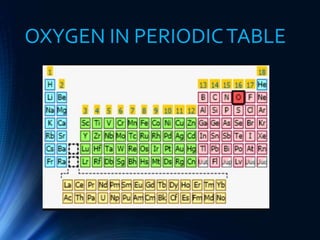
Group, Period: group 16 (chalcogens), period 2
Block: p-block
Electron Configuration: [He] 2s² 2p⁴
Phase: Gas
Electron per shell: 2,6
Heavier than air, three isotopes, Highly paramagnetic, electronegative,
highly oxidized, Releasing heat.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oxygen-180610180620/85/Oxygen-11-320.jpg)




