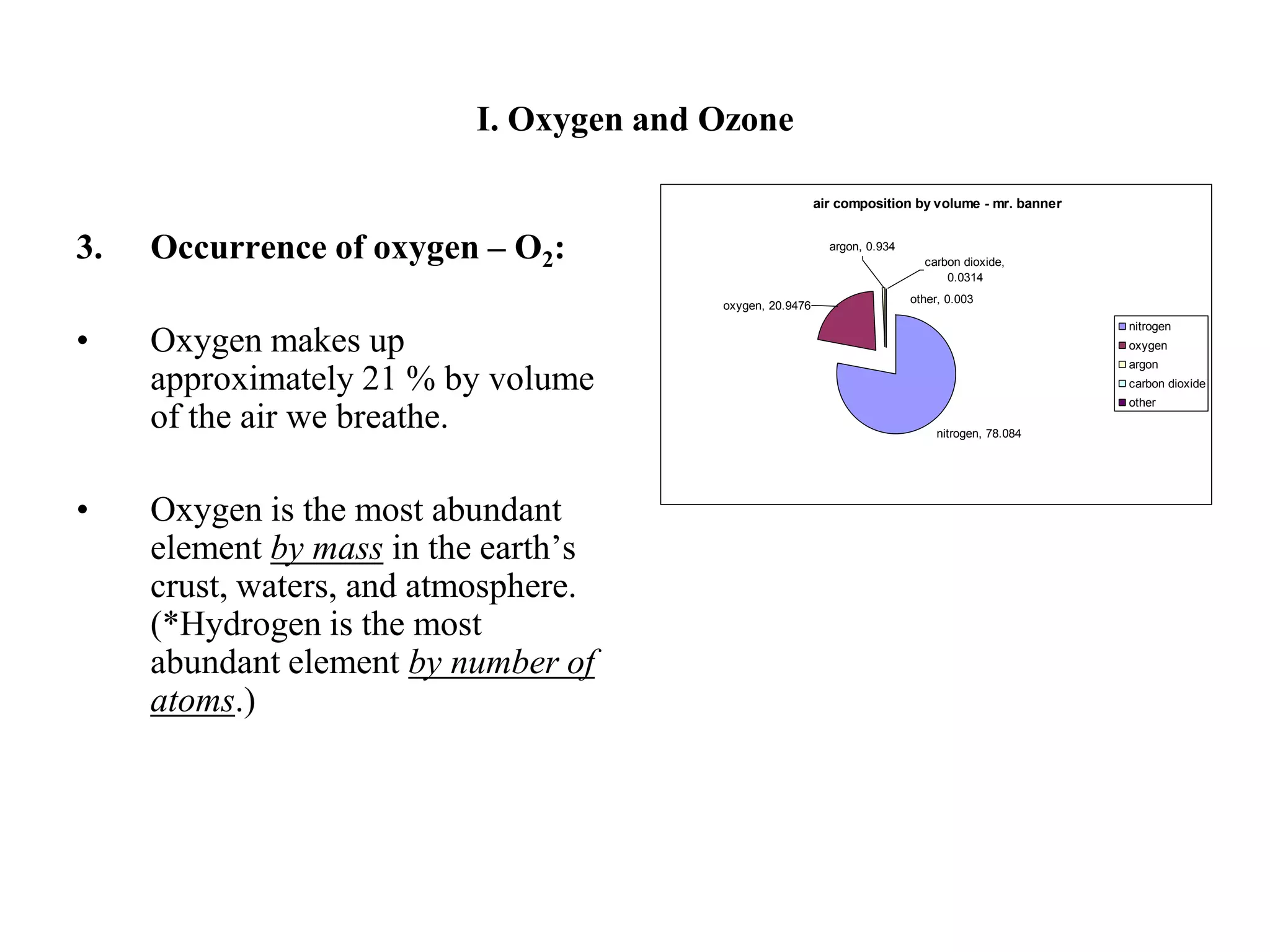
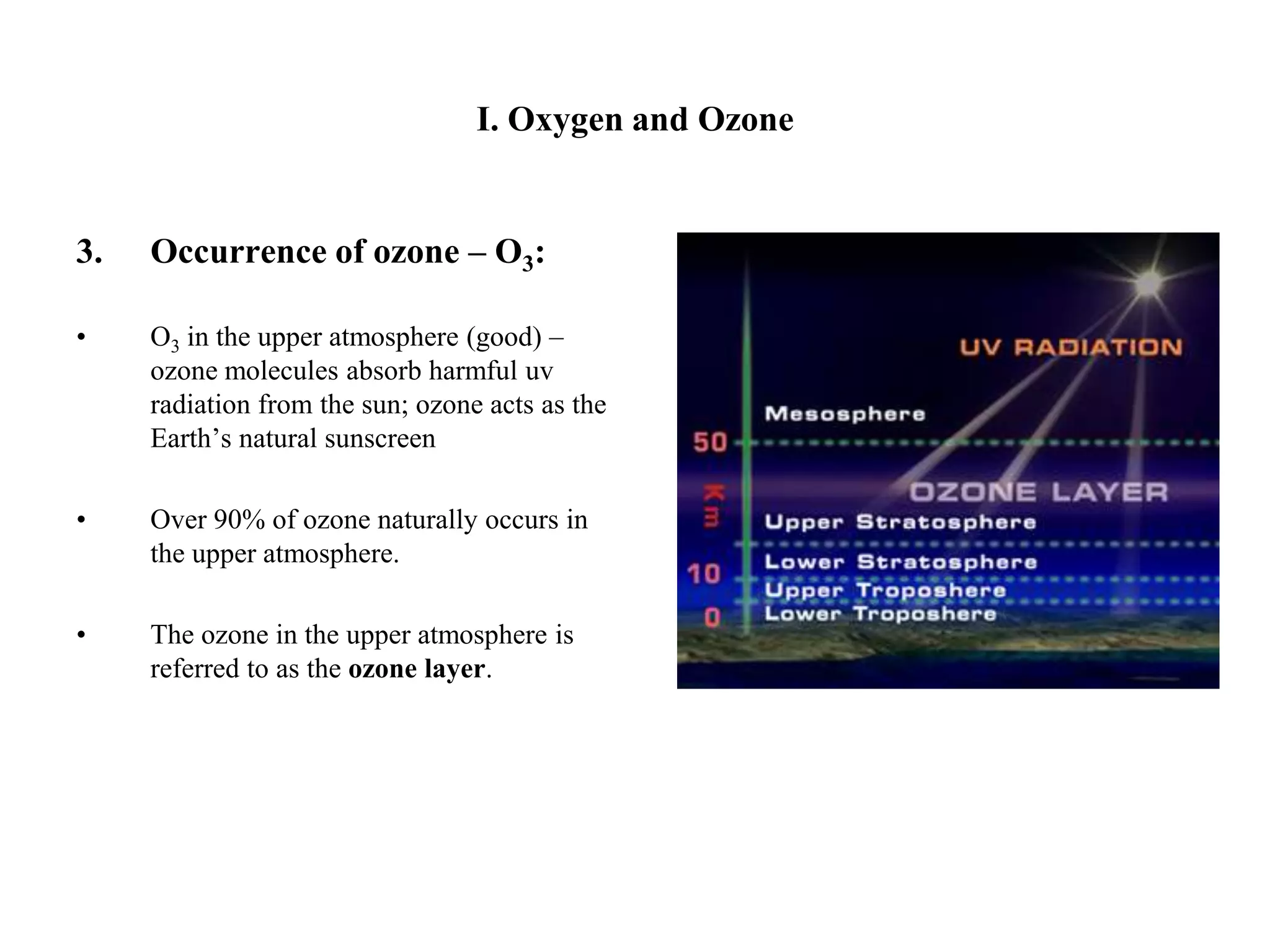
There are two allotropes of oxygen that exist in the atmosphere: oxygen (O2) and ozone (O3). Oxygen exists as colorless, odorless diatomic molecules and makes up 21% of the air. It is very reactive. Ozone exists as bent triatomic molecules and has different properties depending on its location - it is hazardous near the ground as part of smog but beneficial in the upper atmosphere as it absorbs harmful UV radiation and protects the Earth.